Kipp&Zonen LOGBOX SD Data Logger User Manual
Page 48
48
Example 3.
Calculation of battery capacity
Let’s assume we measure temperature, relative humidity and global radiation. Measuring
interval is one minute. Requested autonomy for battery is 7 days.
Now we will calculate power consumption of each component of the system.
For temperature measurement we will use PT100, where excitation current is 1mA
maximum. We need to add delay of 5 second to settle the output.
For relative humidity measurement we can use HumiAir8 sensor. It has power consumption
6mA max. Again, delay to stabilize output is 5 seconds.
For global radiation measurement we can use a pyranometer. Power consumption is zero.
Power consumption of LOGBOX SD during measuring period is 5mA, in sleep mode it is
20uA.
Power consumption during measurement:
1mA + 6mA + 5mA = 12mA
Power consumption during sleep mode:
0+0+0+20uA=20uA
Mean power consumption from the battery:
(12mA x 5s + 0.020mA x 55s)/60s=1.018mA
Number of hours:
24hours x 7days = 168 hours
Required minimum battery capacity:
168hours x 1,018mA= 0,1711Ah
4 AA alkaline batteries are recommended for maximal logging time.
Recommendations: The LOGBOX SD data logger is a high precision instrument. For
maximum accuracy apply standard guidelines for low noise operation. Avoid strong
electromagnetic field disturbance (do not install near HF antennas, electrical motors or
generators). Use short cables. Use shielded cables and connect shield to ground connection.
Proper grounding with maximum shielding is necessary. With extreme HF disturbance a
degraded accuracy can be expected.
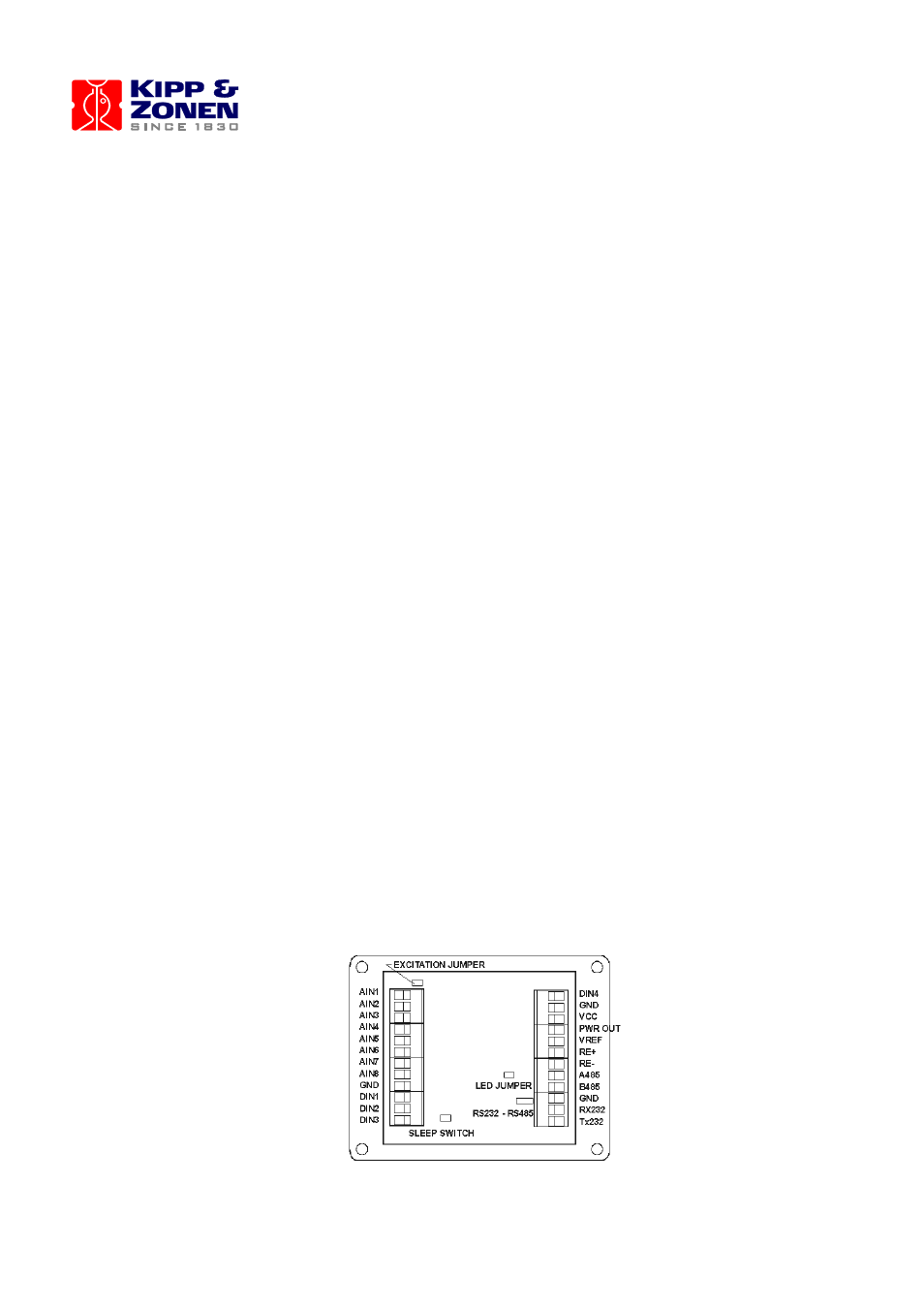
Connectors Layout
