Drucker Diagnostics Paralens Advance User Manual
Page 42
6.3.1 Description
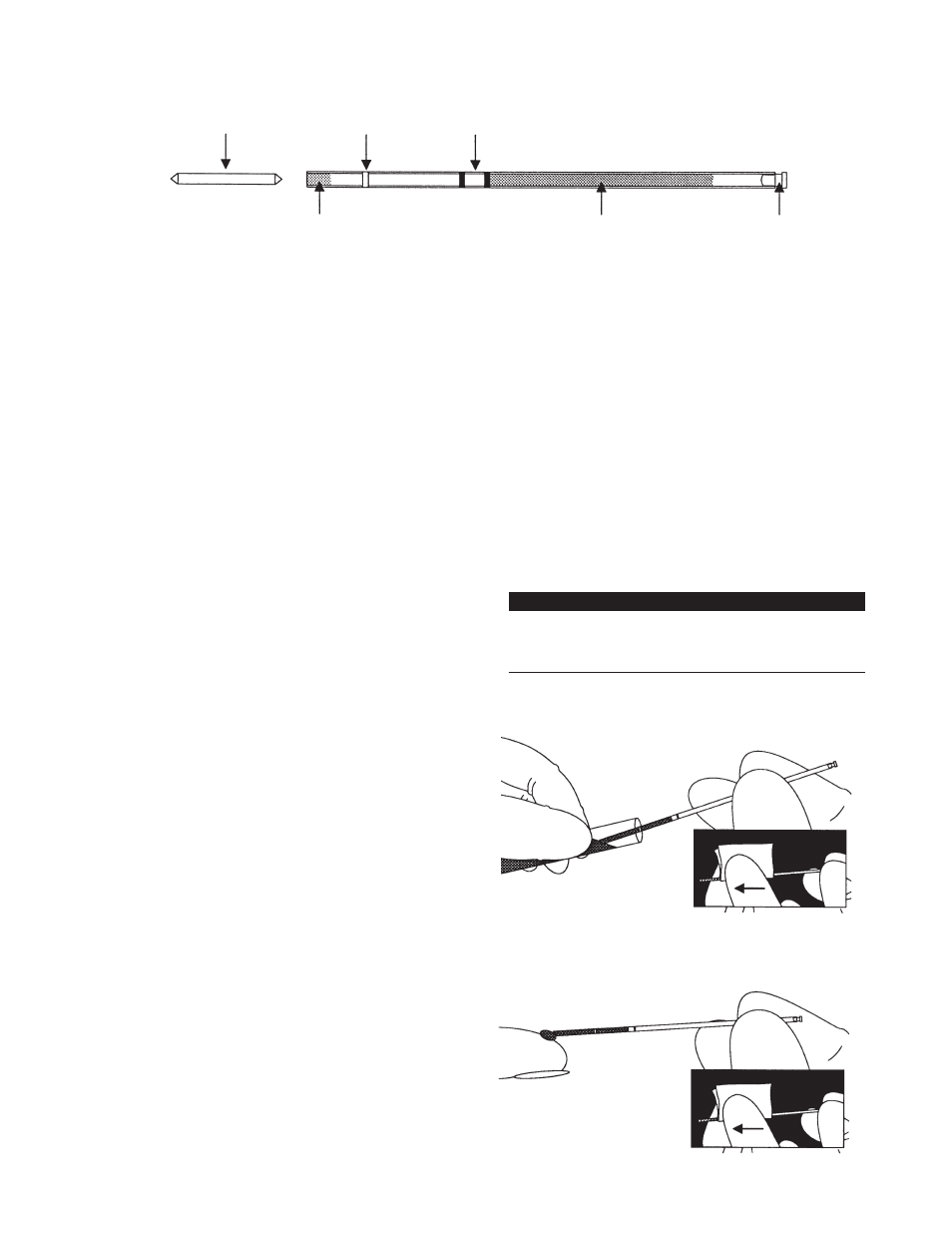
The AccuTube (Figure 6-1) can be filled with either
venous or capillary blood and incorporates an
identification line, graduated fill lines, precoated
reagents, and a partially seated stopper. It is filled
with capillary blood by capillary action or with
venous blood by capillary action or by means of
a QBC pipetter fitted with an AccuTube spacer.
Nominal fill of the AccuTube is 70 µL with either
blood specimen. After mixing the specimen and
seating the stopper, the plastic float is inserted,
and the tube is centrifuged for 5 minutes. The
centrifuged tube is placed in the Autoread Plus
analyzer for automatic scanning and reporting of
results.
6.3.2 Preparation and Handling of AccuTubes
Running a Patient Sample
Step 1: Fill the AccuTube
Note: Do not allow the blood to touch the
AccuTube rubber stopper while performing this
step.
Venous Blood – Gently mix the sample at least
6 times by inversion, or for 5 minutes on a
mechanical mixer immediately before filling the
AccuTube. Tilt the blood tube as shown, and
place the open end of the AccuTube in contact
with the blood. Fill the AccuTube to between
the two black fill lines. Wipe the outside of the
AccuTube with lint-free tissue.
Note: For instructions on use of the pipetter,
refer to Section 4.8.
Capillary Blood – Place the open end of the
AccuTube in contact with the finger puncture
blood. Hold the AccuTube close to horizontal
to avoid air bubbles. Fill the AccuTube until
the blood level is between the two black lines.
Wipe the outside of the AccuTube with lint-free
tissue.
Avoid air bubbles when filling.
Mix blood well with coating
Step 1
Fill Tube (venous)
Step 1
Fill Tube (capillary)
Figure 6-1.
AccuTube with Partially Seated Stopper and Separate Float
6-2
WIPE
ACCUTUBE
70 µL
FLOAT
I.D. LINE
NOMINAL FILL
ANTICOAGULANT
REAGENT
STOPPER
COATING
WIPE
