tekmar 362 Mixing Control Installation User Manual
Page 7
7 of 36
Copyright © D 362 -
12/08
HRF 1
HRF 2
COIL
CONV
RAD
BASE
ROOM OCC & UNOCC (ROOM)
(
CHARACTERIZED
HEATING
CURVE
)
The ROOM is the desired room temperature for the mixing zones and it provides a parallel shift of the
Characterized Heating Curve.
The room temperature desired by the occupants is often different from the design indoor temperature (MIX INDR). If the room
temperature is not correct, adjusting the ROOM
setting increases or decreases the amount of heat available to the building. If the
Setback / None DIP switch is set to Setback, a ROOM setting must be made for both the Occupied and UnOccupied modes.
MIXING TARGET TEMPERATURE (MIX TRG)
(
RESET
RATIO
&
CHARACTERIZED
HEATING
CURVE
)
The MIX TRG temperature is determined from either the
Characterized Heating Curve or the Reset Ratio settings and the outdoor air
temperature. The control displays the temperature that it is currently trying to maintain as the mixing supply temperature. If the control
does not presently have a requirement for heat, it displays “- - -” in the LCD.
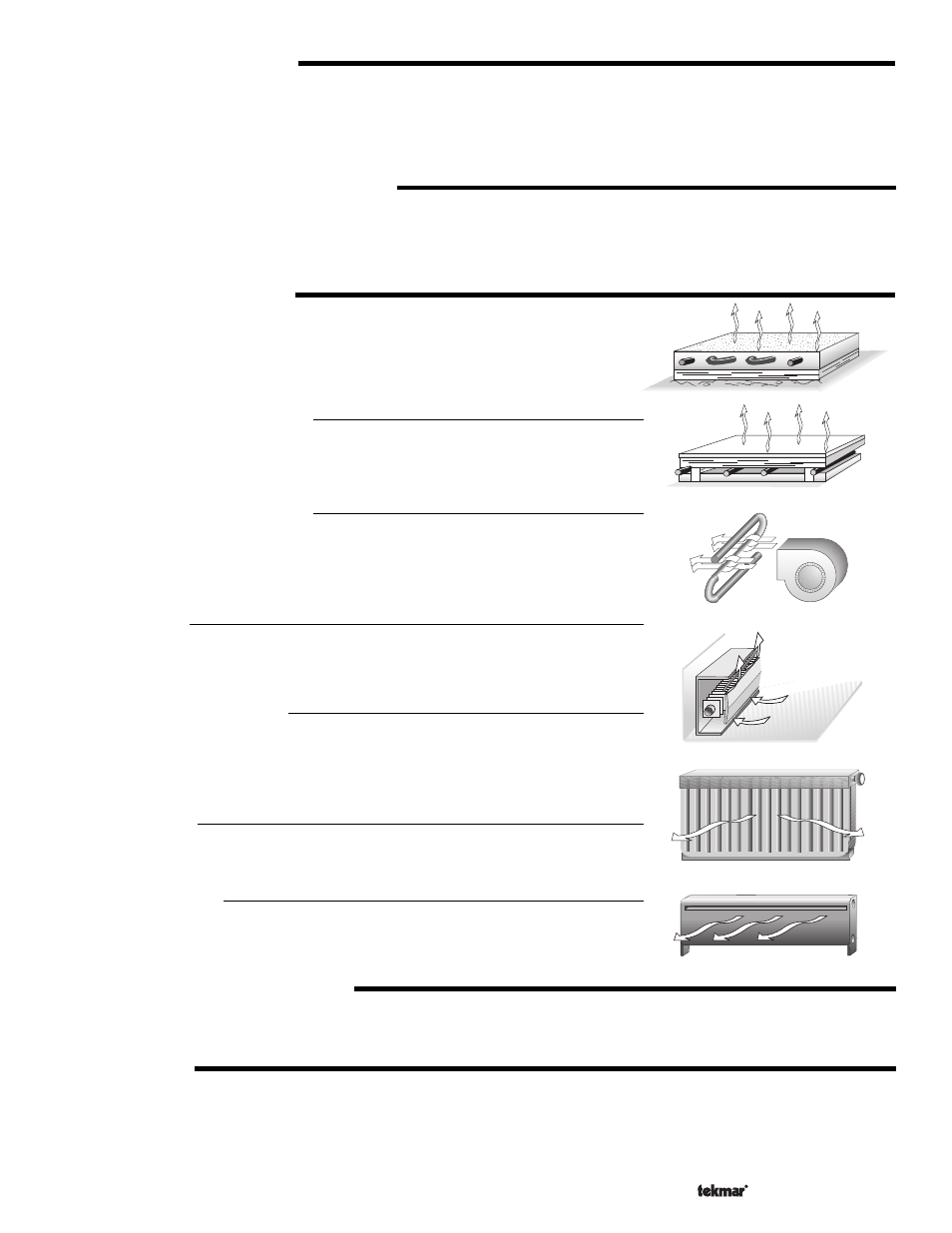
TERMINAL UNITS (TERMINAL)
When using a
Characterized Heating Curve, the control requires the selection of a terminal
unit. The terminal unit determines the shape of the
Characterized Heating Curve according
to how the terminal unit delivers heat into the building space. The 362 provides for selection
between six different terminal unit types: two types of radiant floor heat, fancoil, fin-tube
convector, radiator and baseboard.
Hydronic Radiant Floor (HRF 1)
HRF1 is a heavy, or high mass, hydronic radiant floor system. This type of a hydronic radiant
floor is embedded in either a thick concrete or gypsum pour. This heating system has a large
thermal mass and is slow acting.
Hydronic Radiant Floor (HRF 2)
HRF2 is a light, or low mass, hydronic radiant floor system. Most commonly, this type of
radiant heating system is either attached to the bottom of a wood sub floor, suspended in
the joist space, or sandwiched between the subfloor and the surface. This type of radiant
system has a relatively low thermal mass and responds faster than a high mass system.
Fancoil (COIL)
A fancoil terminal unit or air handling unit (AHU) consists of an hydronic heating coil and
either a fan or blower. Air is forced across the coil at a constant velocity by the fan or blower
and is then delivered into the building space.
Fin–tube Convector (CONV)
A convector terminal unit is made up of a heating element with fins on it. This type of terminal
unit relies on the natural convection of air across the heating element to deliver heated air
into the space. The amount of natural convection to the space is dependant on the supply
water temperature to the heating element and the room air temperature.
Radiator (RAD)
A radiator terminal unit has a large heated surface that is exposed to the room. A radiator
provides heat to the room through radiant heat transfer and natural convection.
Baseboard (BASE)
A baseboard terminal unit is similar to a radiator, but has a low profile and is installed at the
base of the wall. The proportion of heat transferred by radiation from a baseboard is greater
than that from a fin-tube convector.
MIXING PUMP OPERATION (Mix Pmp)
The Mixing Pump contact (
Mix Pmp, terminal 5) closes whenever there is a Mixing Demand and the 362 is not in WWSD. During WWSD,
the mixing pump is operated based on the EXERCISE setting in the
Adjust Menu.
PURGE (PURGE)
After the
Mixing Demand has been satisfied, the 362 can continue to operate the Mixing Pump for a period of time. The length of time
that the Mixing Pump continues to run is an adjustable time setting. This setting allows any excess heat to be purged out to the heating
system. The Mixing Pump continues to run until the Purging time has elapsed or the mixing supply temperature drops below the MIX
MIN setting. This setting should not be used if the mixing system is zoned using either zone pumps or fast acting zone valves.
Sequence, Section B
