Controller configuration, 5 scanning methods – Banner A-GAGE MINI-ARRAY Series User Manual
Page 31
P/N 43298 rev. E
31
Banner Engineering Corp.
•
Minneapolis, MN U.S.A.
www.bannerengineering.com • Tel: 763.544.3164
MINI-ARRAY
®
Instruction Manual
Figure 5-17. Interlaced Scan
Emitter
Interlaced Scan improves optical
resolution in the middle one-third
of the scanning range.
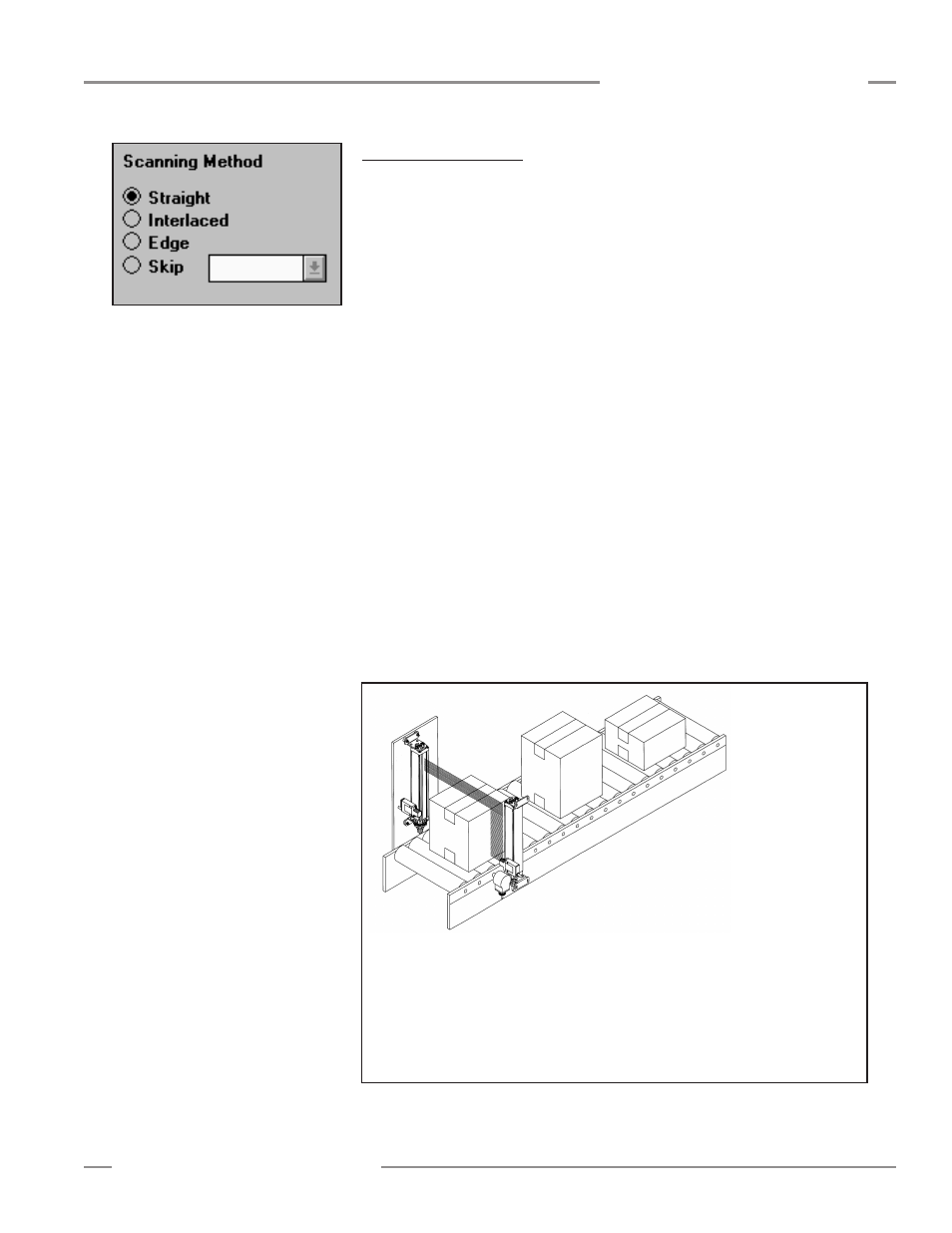
5.5.5 Scanning Methods
The control module may be configured for one of four available scanning methods
(see Figure 5-16):
Straight Scan
is the default mode in which all beams are scanned in sequence from
the bottom end (cable end) to the top end of the sensors.
Interlaced Scan
alternates a straight scan with a slanted-beam scan. A slanted-beam
scan begins with a beam established between the emitter's second channel and the
receiver’s first channel, and between the emitter’s third channel and receiver’s second
channel, continuing up the array to the last emitter channel and next-to-last receiver
channel. The last emitter channel is then reactivated to establish a beam to the last
receiver channel to complete the scan. Alternating this slanted-beam scan with a
straight scan improves optical resolution within the middle one-third of the scanning
range. See Figure 5-17.
Edge Scan
activates only the beams located near the top edge of an object in the light
screen. “Top edge” refers to the edge of the object passing nearest the top end of the
sensors (i.e., the top of the light screen, farthest from the sensor’s cabled end). Each
scan begins six beams prior to the last beam blocked during the previous scan. The
scan continues from this point and moves upward to the first unblocked beam, where
the scan is completed. When the array is clear, the system will execute straight scans.
Edge Scan begins again when a blocked channel is detected. This scanning mode is
designed to reduce sensing response time when measuring or locating only one edge
of an object. Use of the Edge Scan mode limits the scan analysis mode selection to
Last Beam Blocked (LBB).
Skip Scan
reduces response time at the expense of decreased sensing resolution.
Skip Scan mode allows from one to seven beams to be skipped during each scan.
For example, with one beam skipped, only beams #1, 3, 5, 7, etc. will be interrogated.
With two beams skipped, only #1, 4, 7, 10, etc. will be interrogated, and so on.
Receiver
Figure 5-16. MINI-ARRAY software:
scanning method selection
Controller Configuration
