9 liquid sampling considerations, Liquid sampling considerations – Metrohm NIRS XDS RapidLiquid Analyzer User Manual
Page 30
28
▪▪▪▪▪▪▪
•
If scanning at an elevated temperature using the controller, be sure samples are not already
above that temperature from prior processing, water baths, or for any other reason.
If in doubt about temperature consistency, check samples using a calibrated temperature device to
determine that sample temperature is well-controlled.
5.8
Instructions for closing the sample drawer using Vision
When the XDS Rapid Liquid Analyzer will not be
used for some time, the operator may wish to close
the sample drawer. This prevents damage, and
keeps airborne dust out of the sample drawer area.
The user must be connected to the instrument in
Vision
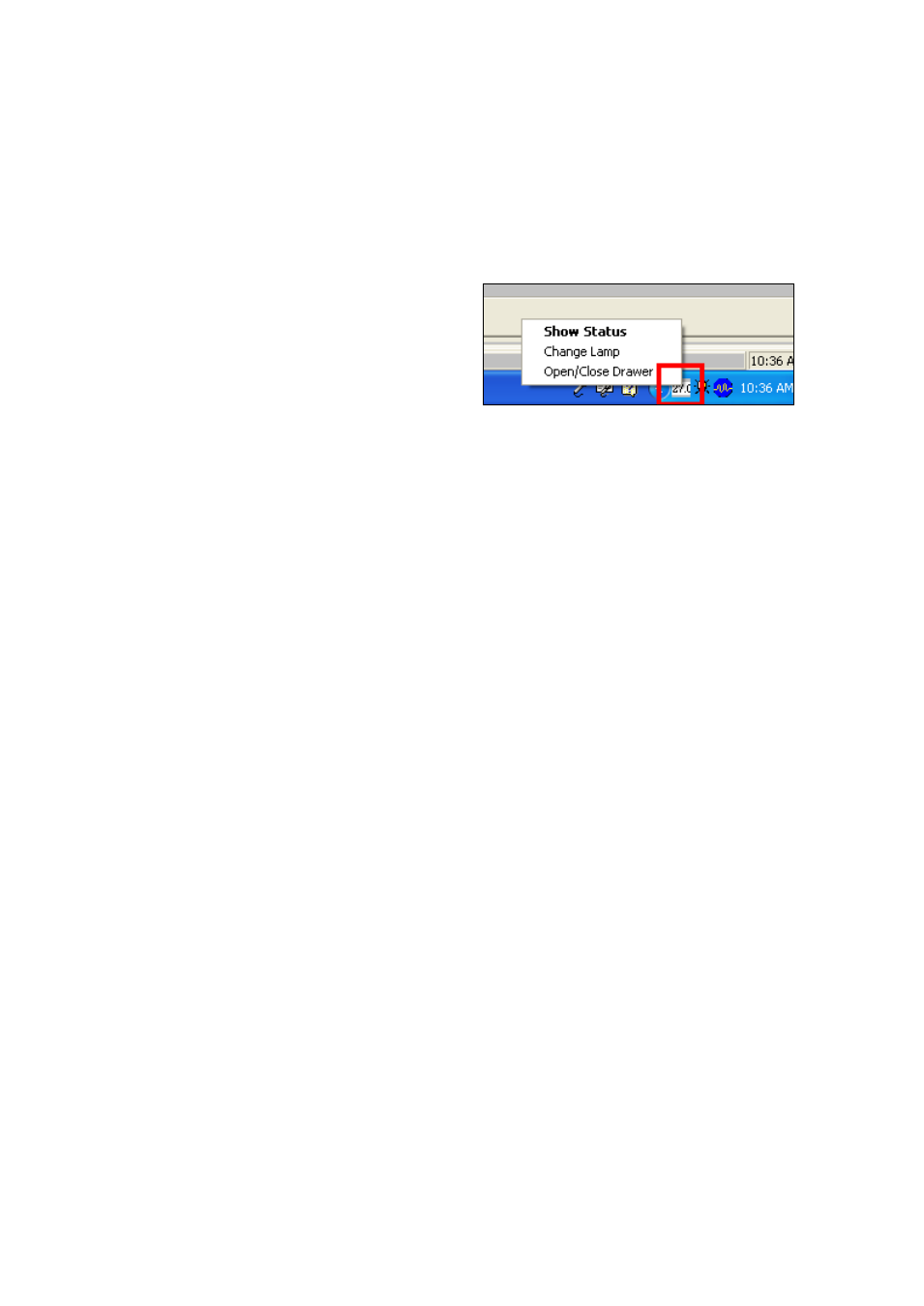
Look at the bottom right corner of the screen. Note the temperature readout (27.0 in this example).
Right-click on this icon. The menu shown will appear. Click on “Open/Close Drawer” to set the
sample drawer in the correct position. Click once, and the drawer will move to the “other” position.
When the sample drawer is in the desired position, disconnect from Vision.
5.9
Liquid Sampling Considerations
The XDS Rapid Liquid Analyzer is capable of detecting low levels of analytes in liquids. A brief
overview of absorbance and pathlength considerations on a simple type of sample may be helpful.
A suitable pathlength must be selected for the sample, in expected concentration levels. This
pathlength must be long enough that the analyte absorbs energy, and also must be short enough
that the absorption is not masked by other factors.
First, determine the wavelength areas for analysis. Take spectra of the pure materials to see where
the absorptions occur, without confusion from other components of the sample matrix.
Once the possible wavelength areas are determined, the sample should be run in cuvettes of different
pathlengths to determine what pathlength gives the optimum analytical results. The example below
illustrates some of the initial steps in this process.
In this example, we wish to measure 2-propanol in water, at concentrations up to 25% of 2-
propanol. We take spectra of each material, to see where the absorbances occur.
