Using the msg instruction – Rockwell Automation 1785-ENET USER MANUAL PLC-5 ETHERNET INTERFACE User Manual
Page 35
1785-6.5.19 November 1998
Communicating via the Interface Module
4-5
Using the MSG Instruction
The message (MSG) instruction transfers up to 1000 elements of
data; the size of each element depends on the data table section that
you specify and the type of message command that you use. One
binary element contains one 16-bit word, for example, and one
floating-point element contains two 16-bit words.
The MSG instruction transfers data in packets. Each packet can
contain up to 709 words for Ethernet processors and interface
modules. If your message transfer contains more words than fit in one
packet, the transfer requires more than one packet of transfer data.
The more packets of data to transfer, the longer the total
transfer takes.
Entering Parameters
The control block is where all of the information relating to the
message is stored. Ethernet message instructions use two consecutive
control blocks:
Important: Because Ethernet messages need two consecutive control
blocks, the message control block that you specify must start on an
even number.
Use your programming software package to enter the control block
address. After entering the control block, the programming terminal
automatically displays a data entry screen, from which you enter
instruction parameters that are stored at the control block address.
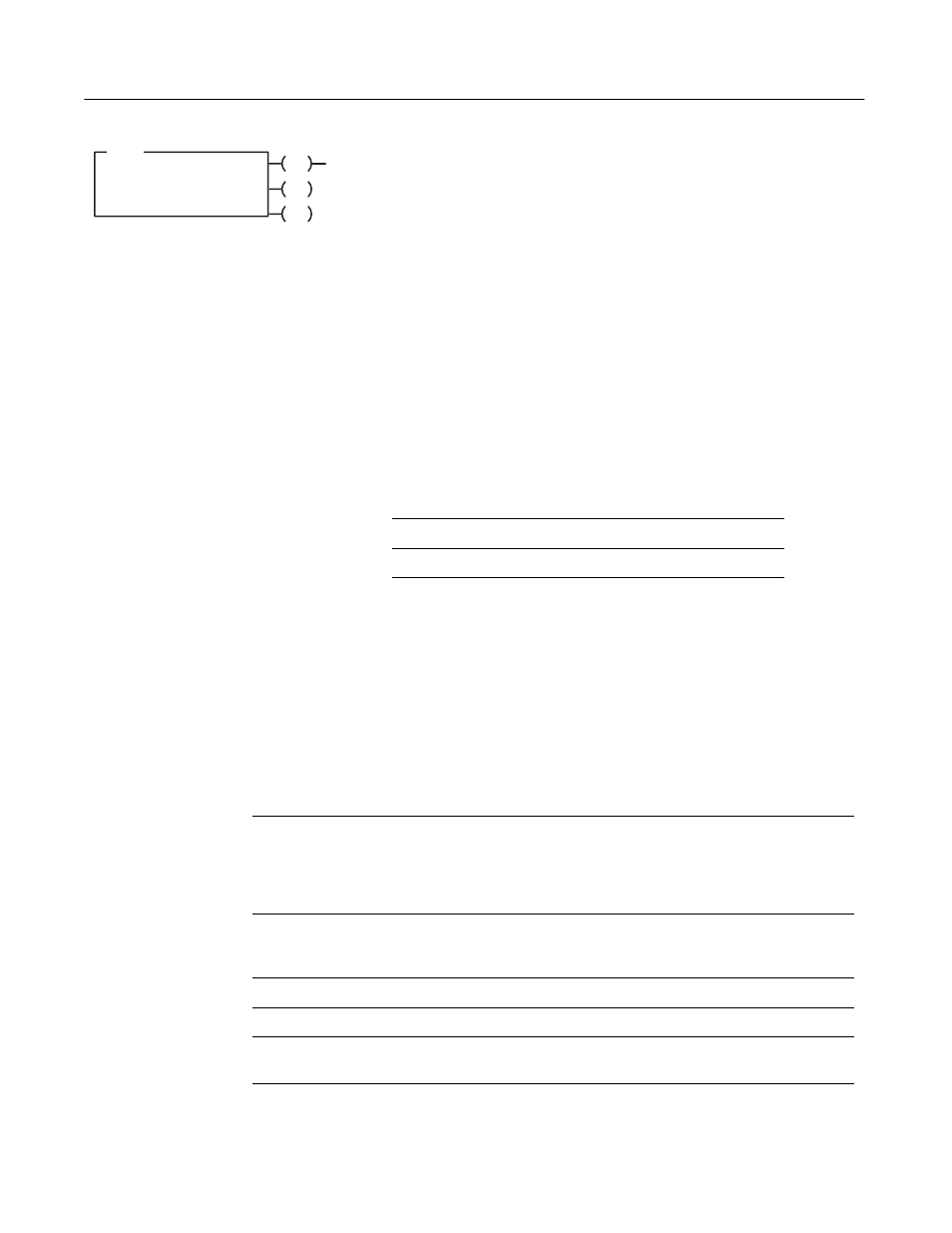
SEND/RECEIVE MESSAGE
EN
Control Block
DN
ER
MSG
This block
Contains
first
message information
second
destination address
This Parameter:
Specifies:
Command Type
Whether the MSG instruction performs a read or write operation. The software
toggles between: PLC-5 Typed Read, PLC-5 Typed Write, PLC-5 Typed Write to
SLC, PLC-5 Typed Read from SLC, SLC Typed Logical Read, SLC Typed Logical
Write, PLC-2 Unprotected Read, PLC-2 Unprotected Write, PLC-3 Word Range
Read, and PLC-3 Word Range Write.
PLC-5 Data Table Address
The data file address of the processor containing the message instruction. If the
MSG operation is write, this address is the starting word of the source file. If the
MSG operation is read, this address is the starting word of the destination file.
Size in Elements
The number of elements (1 – 1000) to be transferred.
Destination Address
The starting address of the source or destination file in the target processor.
Port Number
The channel for message communications. Communications through the Ethernet
interface module use channel 3A.
