Red Lion PAXR User Manual
Page 18
18
18
RATE INPUT VALUE FOR SCALING POINT 2
Enter the corresponding Rate Input Value for the second Scaling Point by
using the arrow keys. Rate Input values for scaling points can be entered by
using the Key-in or the Applied method described below.
Key-in Method:
Enter the Rate Input value (
) that corresponds to the entered Rate
Display value (
) by pressing the
F1 or F2 keys. This value is always in
pulses per second (Hz).
Applied Method:
Apply an external rate signal to the appropriate input terminals. At the Rate
Input Value (
) press and hold the
F1 and F2 keys at the same time. The
applied input frequency (in Hz) will appear on the display. (To verify correct
reading wait for at least the length of the Low Update Time. Then press and
hold the
F1 and F2 keys at the same time again. The new value should be ±
0.1% of the previous entered value.) Press
PAR to enter the displayed
frequency as the Rate Input value. To prevent the displayed value from being
entered, press
DSP. This will take the meter out of Programming Mode and the
previous Rate Input value will remain.
Rounding values other than one round the Rate display to the nearest
increment selected (e.g. rounding of ‘5’ causes 122 to round to 120 and 123 to
round to 125). Rounding starts at the least significant digit of the Rate display.
RATE DISPLAY ROUND
The Low Cut Out value forces the Rate display to zero when the Rate display
falls below the value entered.
LOW CUT OUT
to
to
When the Rate value is above the present Maximum rate value for the
entered amount of time, the meter will capture that Rate value as the new
Maximum value. A delay time helps to avoid false captures of sudden short
spikes. Maximum detection will only function if Rate is assigned to Input A or
B. The Maximum rate value is shown with an annunciator of ‘
’ in the display
and will continue to function independent of being displayed.
MAXIMUM CAPTURE DELAY TIME
to
seconds
When the Rate value is below the present Minimum rate value for the entered
amount of time, the meter will capture that Rate value as the new Minimum
value. A delay time helps to avoid false captures of sudden short spikes.
Minimum detection will only function if Rate is assigned to Input A or B. The
Minimum rate value is shown with an annunciator of ‘
’ in the display and will
continue to function independent of being displayed.
MINIMUM CAPTURE DELAY TIME
to
seconds
RATE SCALING
To scale the Rate, enter a Scaling Display value with a corresponding Scaling
Input value. (The Display and Input values can be entered by Key-in or Applied
Methods.) These values are internally plotted to a Display value of 0 and Input
value of 0 Hz. A linear relationship is formed between these points to yield a
rate display value that corresponds to the incoming input signal rate. The PAXI
and PAXR are capable of showing a rate display value for any linear process.
KEY-IN SCALING METHOD CALCULATION
If a display value versus input signal (in pulses per second) is known, then
those values can be entered into Scaling Display (
x
) and Scaling Input
(
x
). No further calculations are needed.
If only the number of pulses per ‘single’ unit (i.e. # of pulses per foot) is
known, then it can be entered as the Scaling Input value and the Scaling Display
value will be entered as the following:
NOTES:
1. If # of pulse per unit is less than 10, then multiply both Input and Display
values by 10.
2. If # of pulse per unit is less than 1, then multiply both Input and Display
values by 100.
3. If the Display value is raised or lowered, then Input value must be raised
or lowered by the same proportion (i.e. Display value for per hour is
entered by a third less (1200) then Input value is a third less of # of pulses
per unit). The same is true if the Input value is raised or lowered, then
Display value must be raised or lowered by the same proportion.
4. Both values must be greater than 0.0.
EXAMPLE:
1. With 15.1 pulses per foot, show feet per minute in tenths. Scaling Display
= 60.0 Scaling Input = 15.1.
2. With 0.25 pulses per gallon, show whole gallons per hour. (To have greater
accuracy, multiply both Input and Display values by 10.) Scaling Display
= 36000 Scaling Input = 2.5.
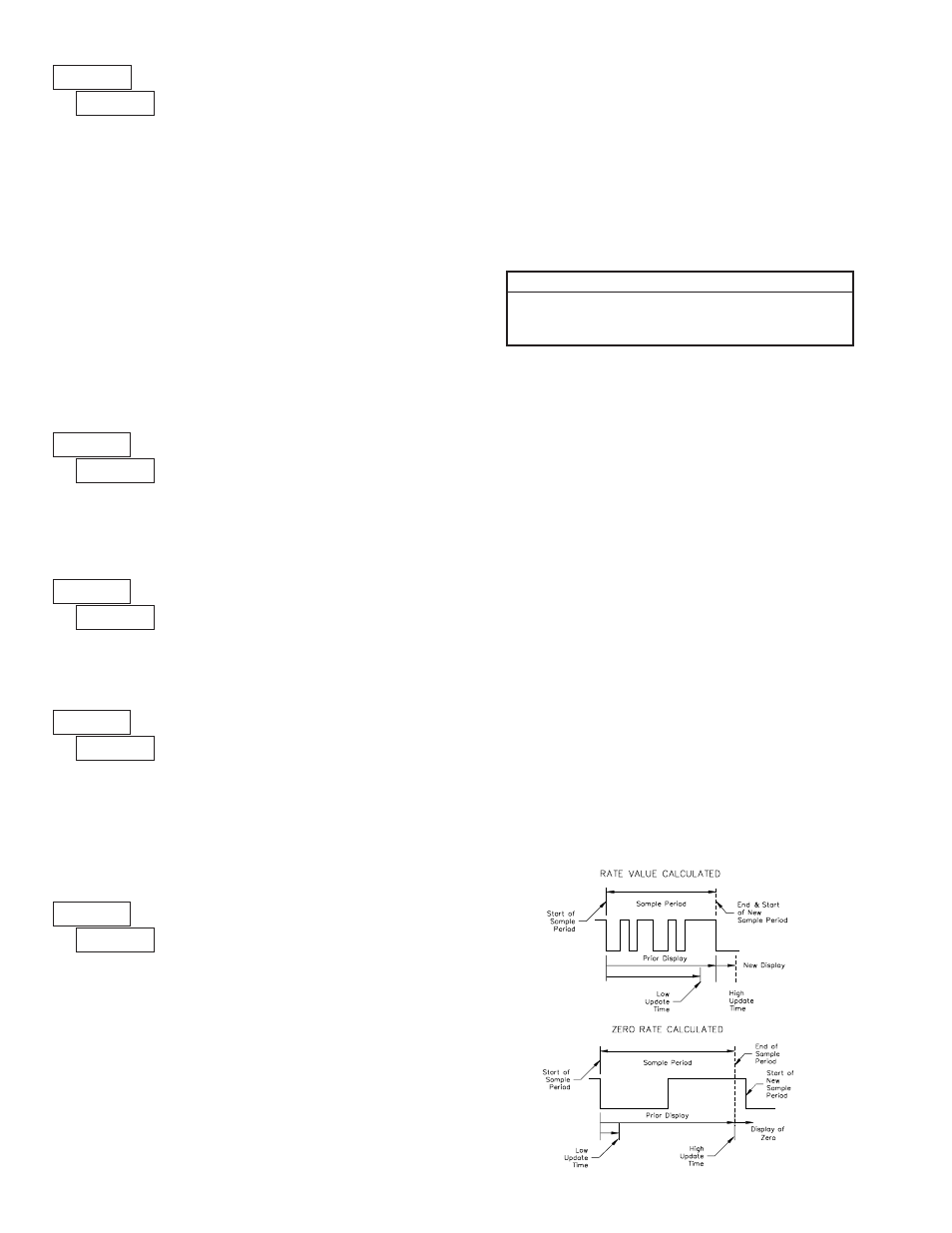
INPUT FREQUENCY CALCULATION
The meter determines the input frequency by summing the number of falling
edges received during a sample period of time. The sample period begins on the
first falling edge. At this falling edge, the meter starts accumulating time
towards Low Update and High Update values. Also, the meter starts
accumulating the number of falling edges. When the time reaches the Low
Update Time value, the meter looks for one more falling edge to end the sample
period. If a falling edge occurs (before the High Update Time value is reached),
the Rate display will update to the new value and the next sample period will
start on the same edge. If the High Update Time value is reached (without
receiving a falling edge after reaching Low Update Time), then the sample
period will end but the Rate display will be forced to zero. The High Update
Time value must be greater than the Low Update Time value. Both values must
be greater than 0.0. The input frequency calculated during the sample period, is
then shown as a Rate value determined by either scaling method.
RATE DISPLAY EXCEEDED
If the rate of the input signal causes a display that exceeds the capacity of the
Rate display (5 digits, 99999), then the display will indicate an overflow
condition by showing “
”. During this overflow condition, the Minimum
and Maximum rate values will stay at their values even during resets.
# of pulses per unit
3600
Hour
# of pulses per unit
60
Minute
# of pulses per unit
1
Second
INPUT (
x
)
DISPLAY (
x
)
RATE PER
