Virtual disk information—disabled operations tab, Creating virtual disks, Virtual disk disabled operations tab fields – HP SAN Virtualization Services Platform User Manual
Page 104
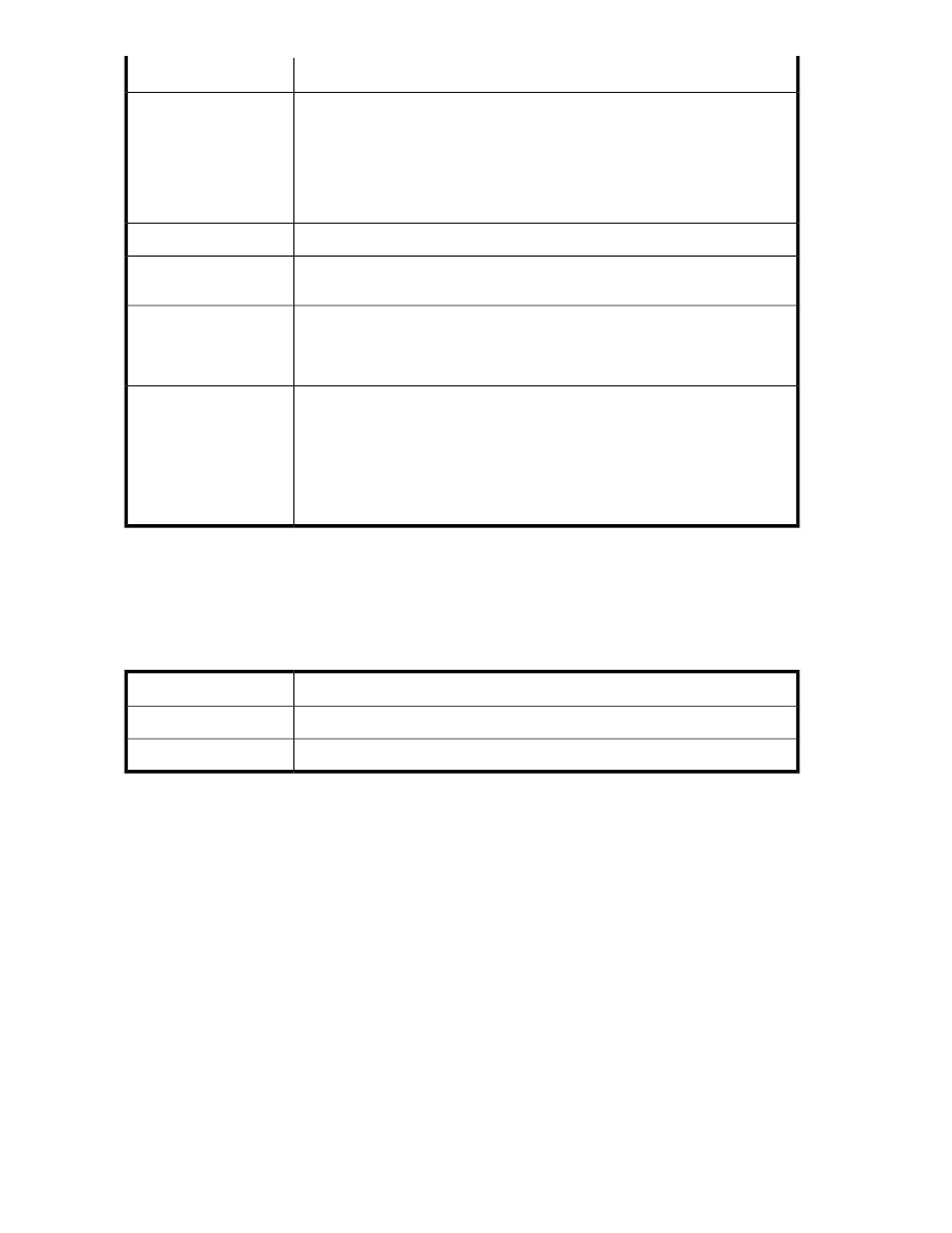
Description
Property
The ID (WWPN) of the holder of the persistent reservation.
•
For most reservation types, this is the initiator port for which the reservation
was established.
•
For the reservation types Write Exclusive—All Registrants and Exclusive Ac-
cess—All Registrants, the holder of the persistent reservation can be any re-
gistered initiator port.
Initiator ID
The name of the host that owns the persistent reservation.
Host Name
The ID (WWPN) of the DPM target port that received the reservation from the
holder of the persistent reservation.
Target ID
Active Persist Through Power Loss. Possible values:
•
true—The persistent reservation is preserved indefinitely, even after reboots.
•
false—VSM clears the persistent reservation following a reboot of both DPMs.
APTPL
Information about all initiators registered with the virtual disk for persistent
reservations:
•
Initiator ID
•
Host Name
•
Target ID
•
Key
Registrants
Virtual disk information—Disabled Operations tab
The Disabled Operations tab shows which operations you cannot currently perform on the selected
virtual disk and the reason for each. See the release notes for a current list of disabled operations.
Table 49 Virtual disk Disabled Operations tab fields
Description
Display field
The name of an operation that is disabled.
Operation name
The reason why the operation is disabled.
Reason
Creating virtual disks
Before creating a new virtual disk, decide from which storage pools you want to allocate capacity to
the virtual disk. You can allocate all the capacity for the virtual disk for one storage pool, or you can
allocate capacity from a combination of storage pools. To create a virtual disk, you need at least one
storage pool with available free capacity. For information about creating storage pools, see
“
Aside from the initial allocation of capacity to the virtual disk, the virtual disk creation wizard enables
you to set various other virtual disk attributes. In most cases, these settings are optional and can be
modified later, as described in the following procedure.
To create a virtual disk:
1.
In the navigation tree, expand the Entities node.
2.
Right-click the Virtual Disk node.
Working with virtual disks
104
