Raid 5, Figure 2-9. diagram of a raid 5 write – HP StorageWorks 3000 RAID Array User Manual
Page 58
2-16 RAID Array 3000 Controller Shelf Hardware User’s Guide
Compaq Confidential – Need to Know Required
Writer: Bob Young Project: RAID Array 3000 Controller Shelf Hardware User’s Guide Comments:
Part Number: EK-SMCPQ-UG. D01 File Name: c-ch2 RAID Array 3000 Controller.doc Last Saved On: 12/4/00 1:08 PM
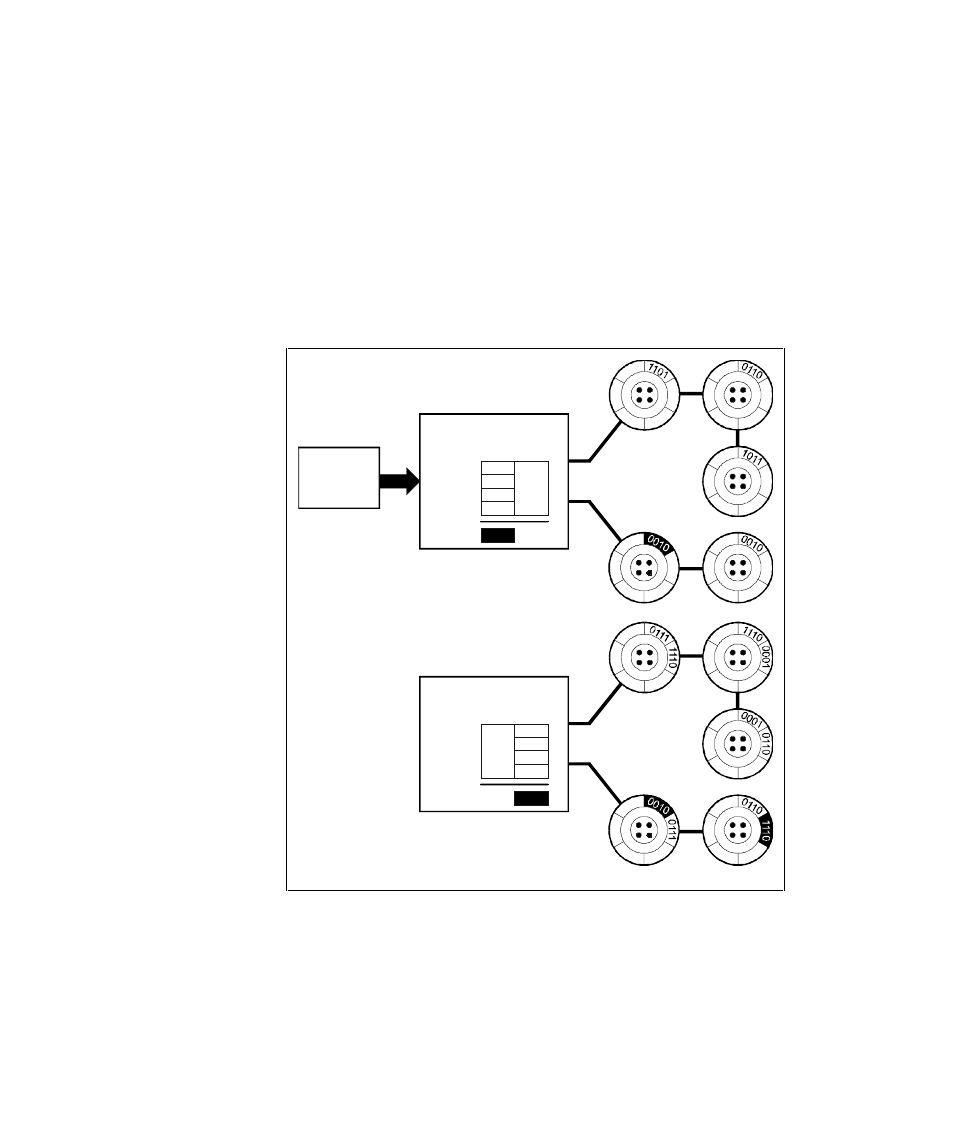
RAID 5
RAID 5 addresses the bottleneck issue for barrages of widely scattered, small
I/O operations (Figure 2– 9). Like RAID 4, RAID 5 breaks up data into chunks,
calculates parity, and then writes the chunks in stripes to the disk drives,
saving one drive one each stripe for the parity data. Unlike RAID 4, however,
RAID 5 changes the parity drive on each stripe. This means, for instance, that
a write operation involving drive 2 on stripe 1 can conceivably take place at
the same time as a write involving drive 3 on stripe 2, since they would be
addressing different parity drives.
1101
0110
1011
0010
0111
1110
0001
0110
Host Data
Controller divides the
data into chunksized units
and calculates parity
There is still data left
so the Controller
repeats the Process
1101
1011
0111
0111
0110
0110
1110
1110
1011
1011
0001
0001
0010
0010
0110
0110
Striped data and parity
written to the array
Striped data
written to the array
SHR-1058
0010
1110
XOr
XOr
Parity =
Parity =
and parity
Figure 2-9. Diagram of a RAID 5 write
RAID 5 handles drive failures in the same manner as RAID 4, except the
parity is different for each stripe. The controller either uses the parity
information on a stripe to reconstruct its data or simply reads the data as
normal, depending on the location of the stripe’s parity drive.
