Raid 0, Figure 2-5. raid 0 write – HP StorageWorks 3000 RAID Array User Manual
Page 52
2-10 RAID Array 3000 Controller Shelf Hardware User’s Guide
Compaq Confidential – Need to Know Required
Writer: Bob Young Project: RAID Array 3000 Controller Shelf Hardware User’s Guide Comments:
Part Number: EK-SMCPQ-UG. D01 File Name: c-ch2 RAID Array 3000 Controller.doc Last Saved On: 12/4/00 1:08 PM
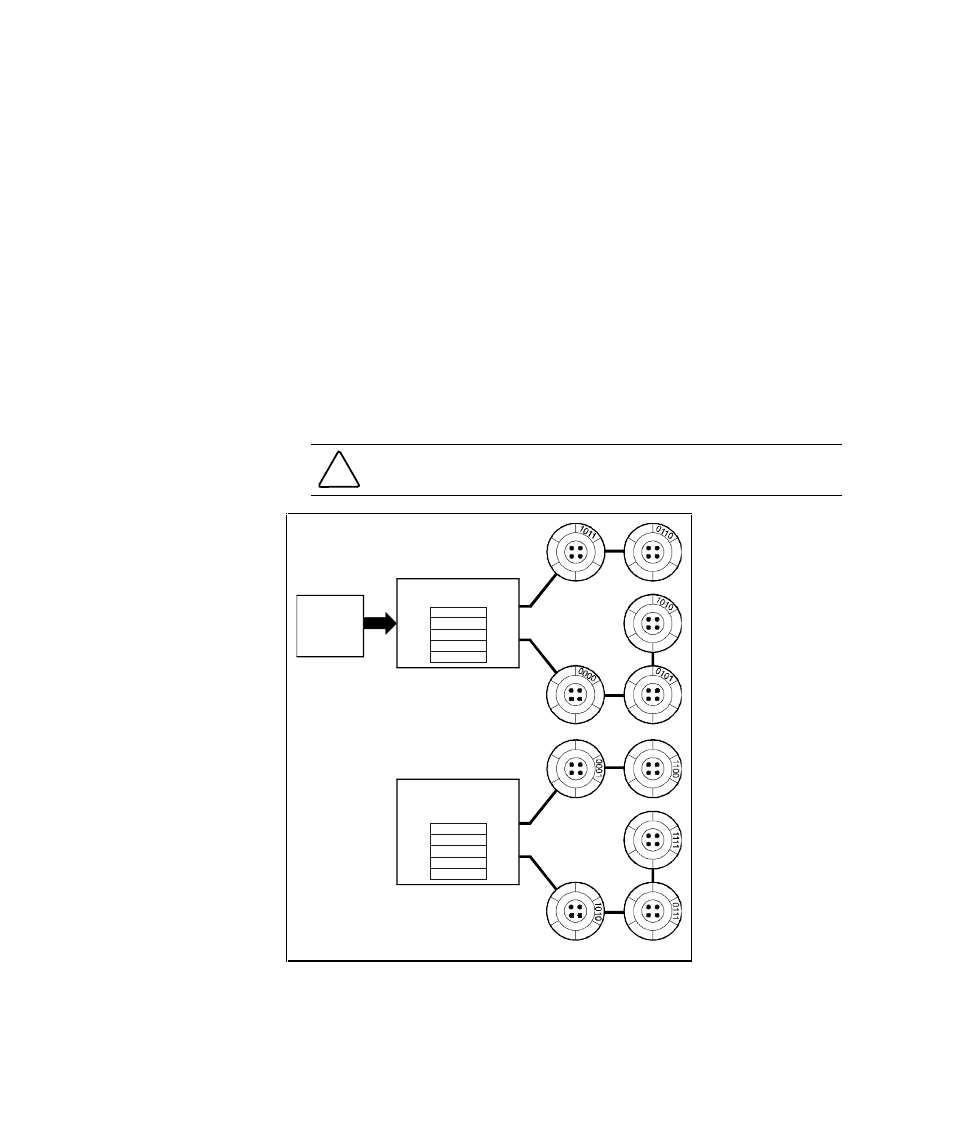
RAID 0
RAID 0 breaks up data into smaller chunks and writes each chunk to a
different drive in the array. The size of each chunk is determined by the
controller’s chunk size parameter, which you set in the course of creating a
RAID set.
The advantage of RAID 0 is its high bandwidth. By breaking up a large block
of data into smaller chunks, the controller can use multiple drive channels to
write the chunks to the disk drives. Furthermore, RAID 0 involves no parity
calculations to complicate the write operation. Likewise, a RAID 0 read
operation employs multiple drives to assemble a single, large data block. This
makes RAID 0 ideal for applications such as graphics, video, and imaging that
involve the writing and reading of large, sequential blocks. Figure 2– 5 shows a
diagram of a RAID 0 write.
CAUTION: The lack of parity means that a RAID 0-disk array offers no
redundancy and thus cannot recover from a drive failure.
1011
0110
1010
0101
0000
0001
1100
1111
0111
1010
Host Data
Controller divides the
data into chunksized units
There is still data left
so the Controller
repeats the process
1011
0001
0110
1100
1010
1111
0101
0111
0000
1010
Striped data
written to the array
Striped data
written to the array
SHR-1054
Figure 2-5. RAID 0 write
