Creating disk groups, Disk drive activity indicator – HP 3000 Enterprise Virtual Array User Manual
Page 40
•
The disk drives should be distributed evenly across the disk enclosures. The number of disks of
a given type in each enclosure should not differ by more than one. For example, no enclosure
should have seven disks until all the other enclosures have at least six. A minimum of four disks
are required to be populated in every disk enclosure.
•
Disk drives should be installed in vertical columns within the disk enclosures. Add drives vertically
in multiples of eight, completely filling columns if possible. Disk groups are more robust if filled
with the same number of disk drives in each enclosure. See
for an example.
NOTE:
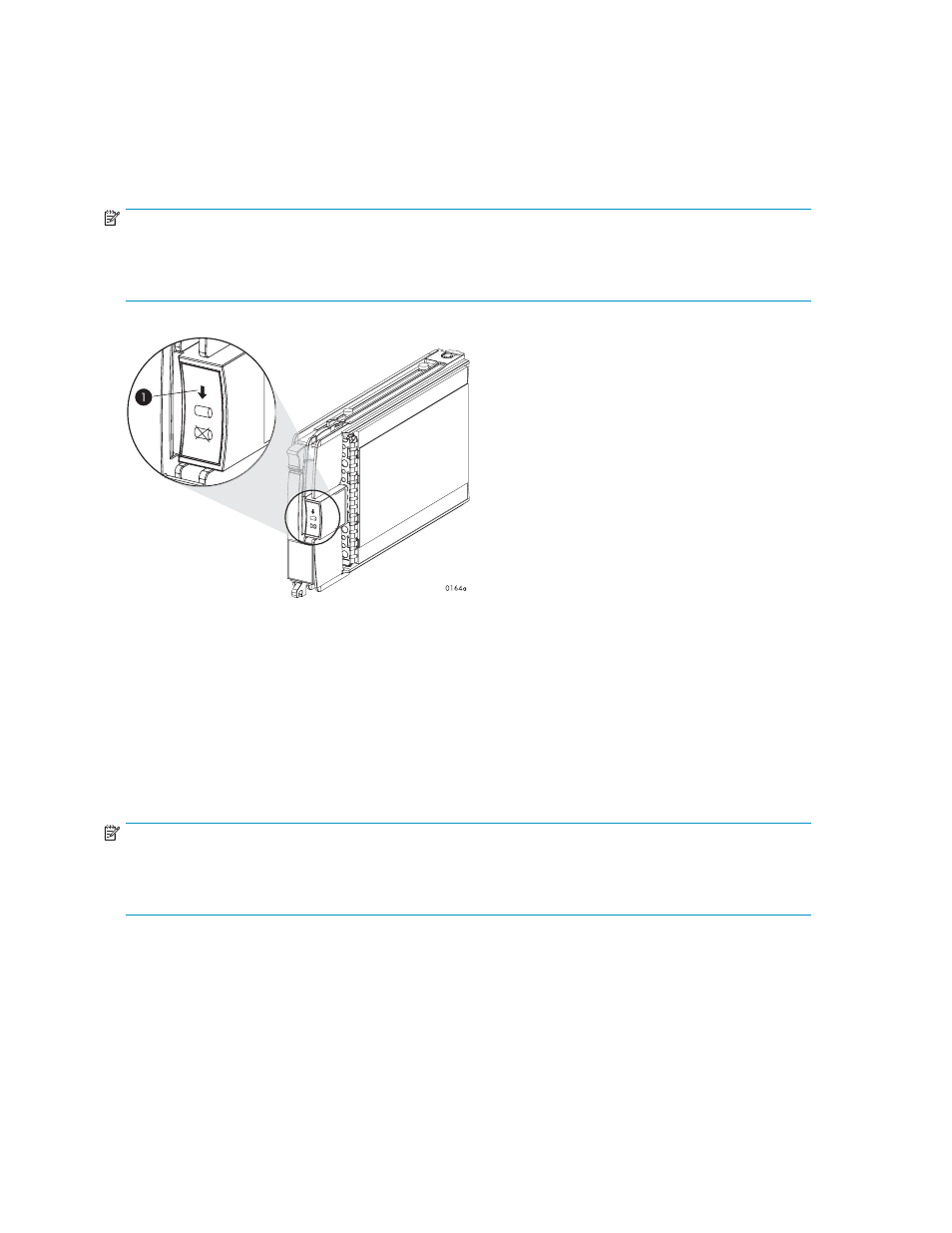
When adding multiple disk drives, add a disk and wait for its activity indicator (1) to stop flashing
(up to 90 seconds) before installing the next disk (see
). This procedure must be followed to
avoid unexpected EVA system behavior.
Figure 5 Disk drive activity indicator
Creating disk groups
The new disks you add will typically be used to create new disk groups. Although you cannot select
which disks will be part of a disk group, you can control this by building the disk groups sequentially.
Add the disk drives required for the first disk group, and then create a disk group using these disk drives.
Now add the disk drives for the second disk group, and then create that disk group. This process gives
you control over which disk drives are included in each disk group.
shows the sequential
building of vertical disk groups.
NOTE:
Standard and FATA disk drives must be in separate disk groups. Disk drives of different capacities and
spindle speeds can be included in the same disk group, but you may want to consider separating
them into separate disk groups.
40
Enterprise Virtual Array operation
