Using the cgroup command – HP XP P9500 Storage User Manual
Page 90
•
FREEZE: When CGROUP is issued with the FREEZE option, the MCU:
Blocks the logical path(s) between the specified MCU CU and RCU CU to stop all
Continuous Access Synchronous Z update copy operations to the R-VOLs in the specified
RCU.
◦
◦
Presents state change pending (SCP) with extended long busy status to host I/O requests,
which causes the host to queue I/Os for the M-VOLs. SCP is indicated until the
CGROUP/RUN command is issued or until the SCP time expires.
◦
Suspends all Continuous Access Synchronous Z pairs with M-VOLs on the specified MCU
CU.
After all logical MCU RCU paths are established, make sure to specify the desired SCP time
(0 600 seconds) for the MCU using the CU Option dialog box.
If the specified MCU does not have any Continuous Access Synchronous Z M-VOLs, the FREEZE
command is executed without performing any operations (paths are not blocked, SCP is not
indicated).
•
RUN: When CGROUP is issued with the RUN option, the MCU:
Presents a state change interrupt (SCI) to the host(s), so that the host(s) re issue the I/Os
that were waiting while the M-VOLs were in the SCP state.
◦
◦
Changes the Continuous Access Synchronous Z M-VOL fence level to Never (PPRC
CRIT=NO), so that the suspended M-VOLs accept host write I/O operations.
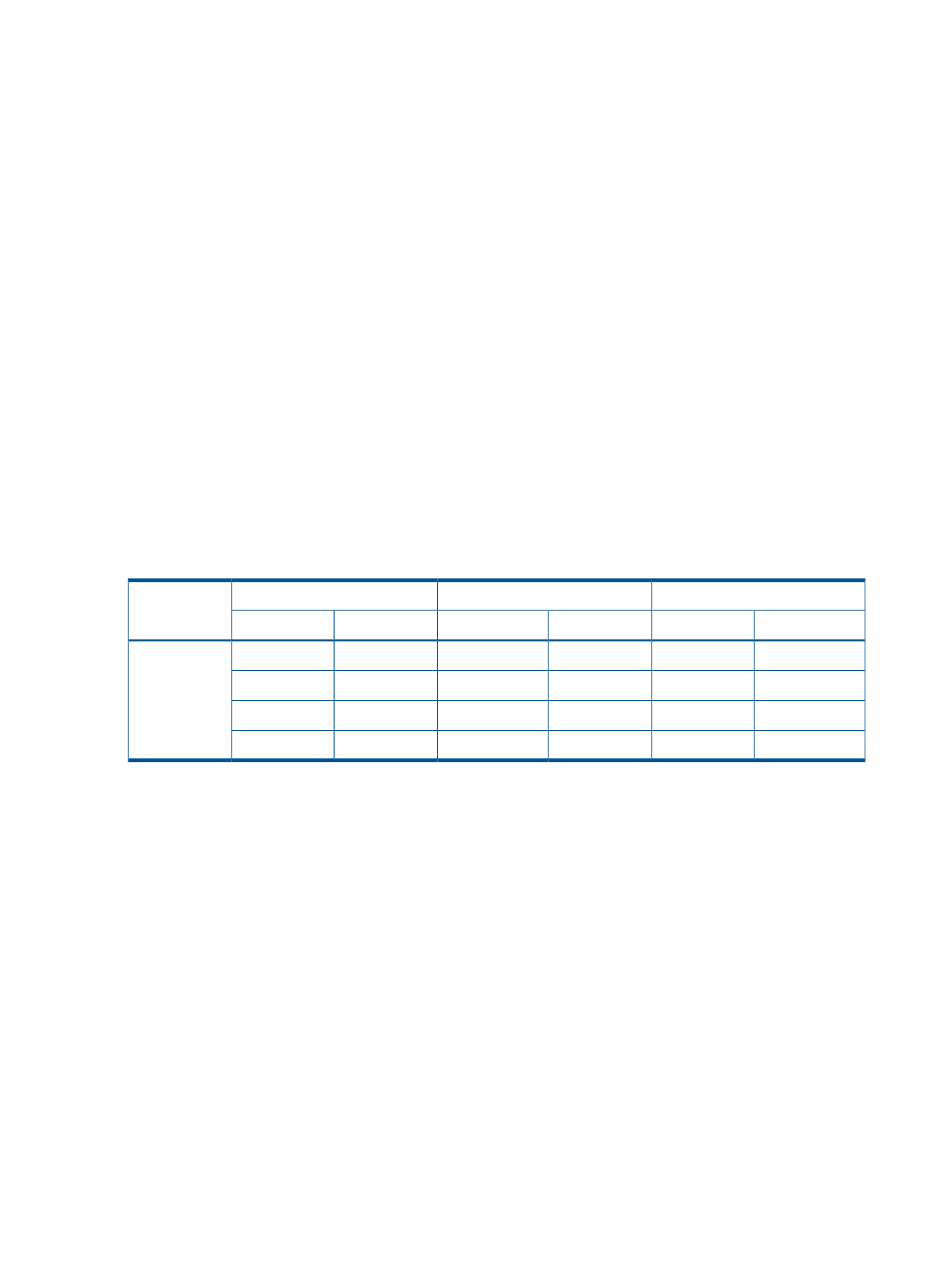
shows the Continuous Access Synchronous Z pair status for Continuous Access
Synchronous Z M-VOLs and R-VOLs during CGROUP (FREEZE/RUN) operations.
Table 38 Pair status during CGROUP (FREEZE/RUN) operations
After CGROUP/RUN
After CGROUP/FREEZE
Before CGROUP (FREEZE/RUN)
R-VOL
M-VOL
R-VOL
M-VOL
R-VOL
M-VOL
—
Simplex
—
Simplex
—
Simplex
Continuous
Access
Pending
Suspended
Pending
Suspended
Pending
Pending
Synchronous Z
pair status
Duplex
Suspended
Duplex
Suspended
Duplex
Duplex
Suspended
Suspended
Suspended
Suspended
Suspended
Suspended
Using the CGROUP command
shows a simplified operational example of the CGROUP (FREEZE/RUN)
command implemented in a GDPS environment. The CGROUP (FREEZE/RUN) TSO command can
be issued by the user or through automation (such as GDPS) to perform the following sequence of
actions:
1.
Suspend host updates to all Continuous Access Synchronous Z M-VOLs on the specified MCU.
2.
Block the specified MCU RCU path to stop update copy operations to the R-VOLs.
3.
Change all Continuous Access Synchronous Z M-VOLs on the specified MCU to suspended.
4.
Resume host updates to the suspended M-VOLs.
5.
The add RCU operation (CESTPATH) must be performed to reestablish the blocked logical
paths. After the MCU RCU path is reestablished, the resynchronize pair operation
(CESTPAIR/RESYNC) must be performed to resynchronize the suspended pairs.
90
Using PPRC commands for Continuous Access Synchronous Z
