Time proportioning (tp), Distributed zero crossing (dzc), Analog outputs – Watlow ANASOFT User Manual
Page 71
Appendix A: PID Tuning and
ANASOFT User’s Guide 61
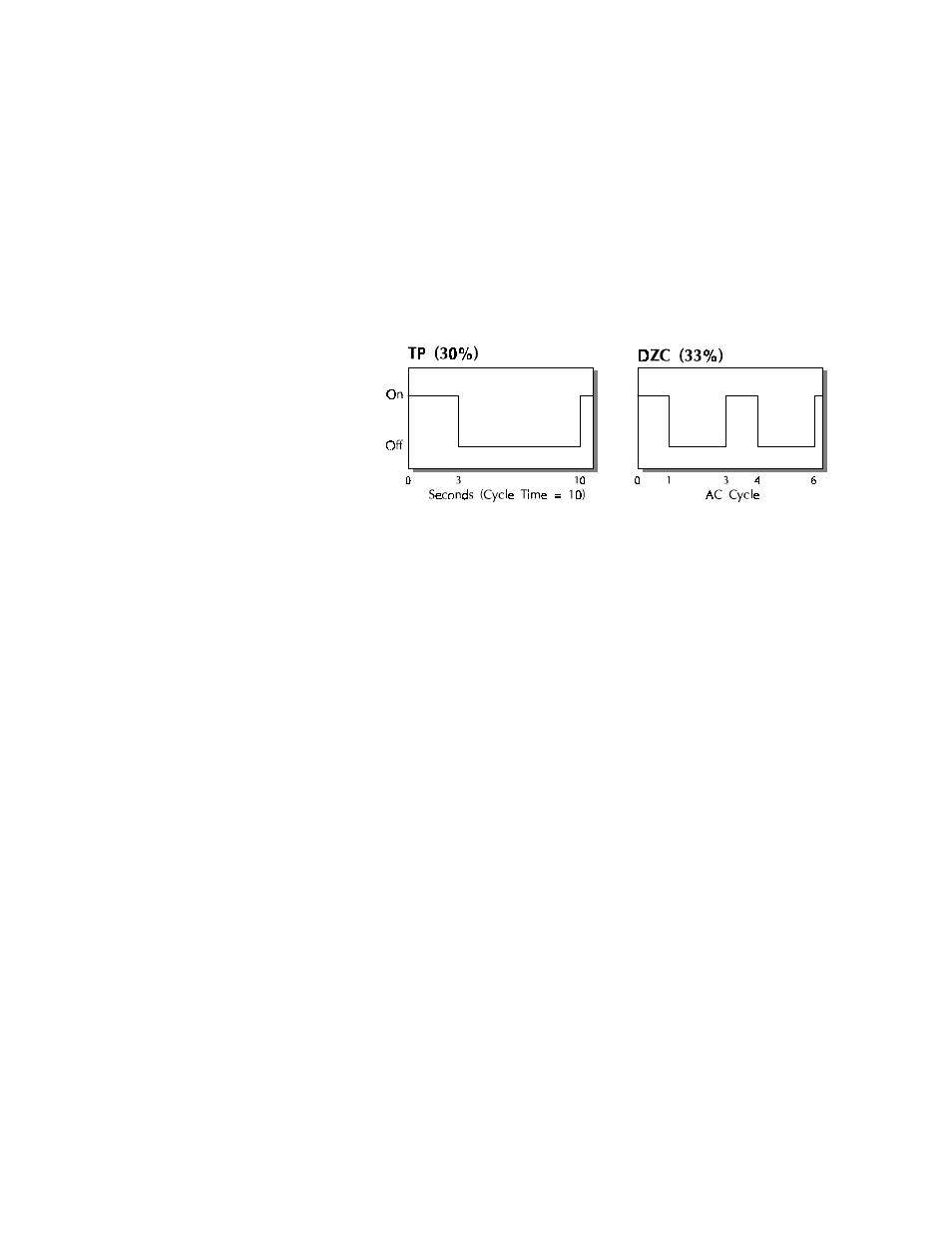
Time Proportioning (TP)
Time Proportioning attempts to digitally simulate an analog output
percentage by turning the output on or off for each time step so that the
cumulative average of the output is the desired setting. You must enter a
cycle time for TP outputs. The cycle time is the time over which the
output is proportioned, and it can be any value from 1 to 255 seconds.
For example, if the output is 30% and the Cycle Time is 10 seconds,
then the output will be on for 3 seconds and off for seven seconds. The
figure below shows typical TP and DZC graphs.
Distributed Zero Crossing (DZC)
DZC output is essentially a Time Proportioning output. However, for
each AC line cycle the controller decides whether the power should be
On or Off. There is no Cycle Time since the decision is made for each
line cycle. Since the time period for 60 Hz power is 16.6 ms, the
switching interval is very short and the power is applied uniformly.
Switching is done only at the zero crossing of the AC line, which helps
reduce electrical “noise”.
DZC output is primarily used for very fast acting electrical heating loads
using Solid State Relays (SSRs). For instance, the open air heater coil is
an example of a fast acting load. Do not use DZC output for
electromechanical relays.
The combination of DZC output and a solid state relay can
inexpensively approach the effect of analog phase angle fired control.
Analog Outputs
The Serial DAC is an optional analog output module for the CLS. It lets
the controller output precision analog voltages or currents--typically for
precision open-loop control, motor or belt speed control, or phase angle
fired control. To use it, set the output type for the appropriate loop to
SDAC.
