Pre-operational containment testing, Required equipment, Containment tightness and continuity test – Franklin Fueling Systems TS-550/TS-5000 consoles Secondary Containment Monitoring User Manual
Page 17
14
Pre-Operational Containment Testing
Pre-operational containment tests determine the tightness of the entire SCM system, including TS-SCCM and inter-
connect tubing. These tests consist of two separate procedures: Containment Tightness Tests and STP Siphon Tests. The
first procedure, Containment Tightness Testing, will determine whether the containment areas chosen to be monitored are
tight. The second, STP Siphon Testing, will determine if the STP is capable of creating enough vacuum for proper SCCM
operation.
The Containment Tightness Testing procedure assumes that all STP’s and pump controllers have been installed, wired,
calibrated, and are operational and in accordance with their respective installation and operation procedures. It also
assumes that all T5 FMS console programming has been completed.
Warning
DO NOT apply vacuum or pressure until consulting the containment manufacturer on the maximum
allowed vacuum or pressure levels.
Warning
DO NOT use equipment that is not explosion proof in classified areas. Keep vacuum pumps
outside class 1, division 1, and class 2 areas. Refer to NFPA 30A, chapter 8.
Caution
DO NOT proceed to the Learn Process until each containment successfully completes
pre-operational testing. Failure to perform these tests or ignoring any failed tests may prevent the
SCM application from detecting a containment fault.
Note: State and/or local laws may require a separate, more stringent containment tightness test. ALWAYS verify and
comply with local regulations.
Note: The STP connected to the SCCM being tested will need to be activated by lifting the appropriate product dispenser
handle. Verify that all STP’s and pump controllers are installed, calibrated and operational.
Required Equipment
• Vacuum Pump (or other vacuum source)
• In-line Regulator
• Shut-off / Isolation Ball Valve
• Two 0" to -30" Hg Vacuum Gauge (2" Hg max. graduation marks)
• T-Fittings (where applicable)
In-Line
Regulator
To Containment
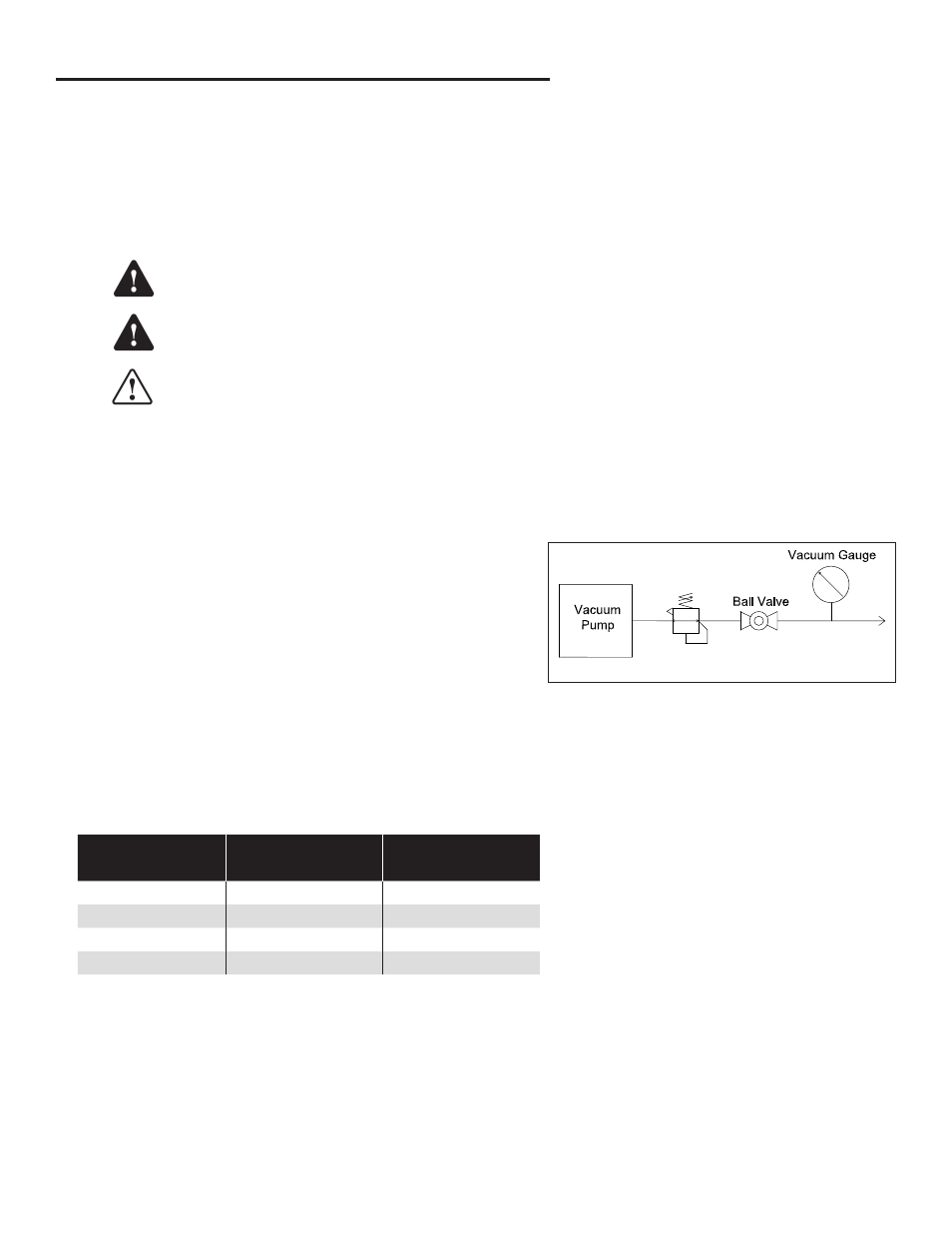
Figure 7 – Vacuum Pump Setup Diagram
Containment Tightness and Continuity Test
Perform the following steps for each SCCM channel.
1. Calculate the approximate containment volume for each area. Consult the secondary containment equipment
manufacturer’s manuals, data sheets, or other official references.
APT SC Pipe Size
Interstitial Volume
(gal/ft)
Interstitial Volume
(gal/100 ft)
1.00" (XP-100-SC)
0.006
0.600
1.50" (XP-150-SC)
0.008
0.800
1.75" (XP-175-SC)
0.009
0.900
2.00" (XP-200-SC)
0.010
1.000
2. Vacuum Gauge Installation
• For Individual DW Turbine and Tank Sump Containments,
connect the vacuum gauge as shown in Figure 7.
• For SC Pipe and Multiple Jumpered Containments,
in addition to the setup shown in Figure 7, connect a vacuum
gauge to the end of the last interstitial space or pipe test boot.
