Figure 1. block diagram – Rainbow Electronics DS28DG02 User Manual
Page 6
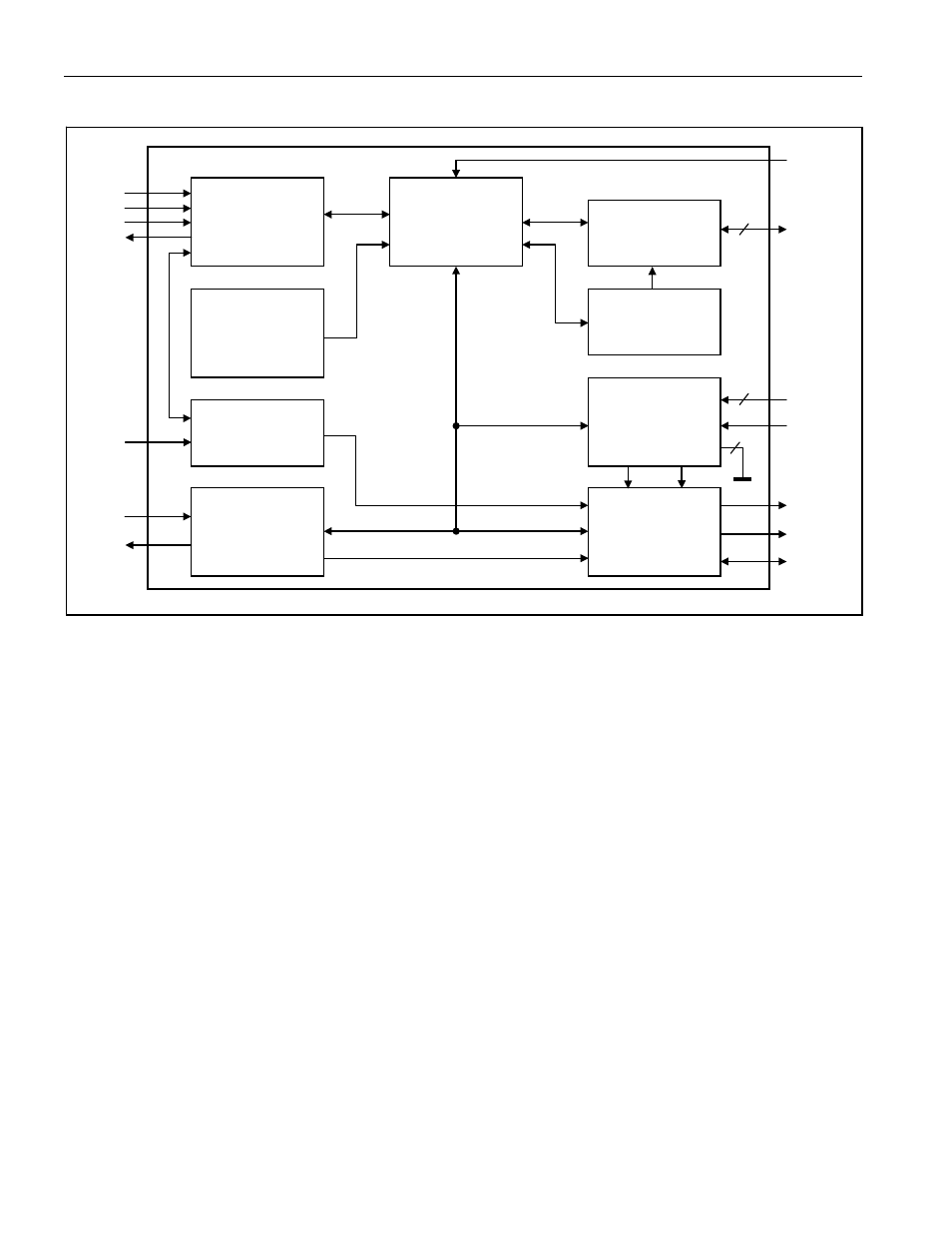
DS28DG02: 2kb SPI EEPROM with PIO, RTC, Reset, Battery Monitor, and Watchdog
6 of 33
Figure 1. Block Diagram
SPI
Communication
Interface
64-bit Unique
Registration
Number
Watchdog
Timer
Real-Time
Clock, Calendar
and RTC Alarm
Memory
Function Buffer
and Control
PIO Function
Control
2kb
EEPROM Array
Voltage Monitors
and Power
Distribution
Alarm Control
Logic, RSTZ
Debounce
CSZ
SCK
SI
SO
X1
X2
WDI
ALMZ
WDOZ
RSTZ
V
CC
V
BAT
GND
PIOn
WPZ
12
BATA VCLA
WDA
CLKA
2
2
The PIO configuration and setup of RTC/calendar with alarm are part of the Detailed Register Description. This
section also includes specifics of the Multifunction Control/Setup register, which enables/disables several device
functions, and the Alarm/Status register. For detailed information on the operation of the V
CC
monitor/power-fail
reset and the battery monitor see the Monitoring Functions section. The SPI Interface description explains the
communication protocol for memory and register access and the use of the watchdog function. The PIO
Read/Write Access
section illustrates the behavior of the PIOs, in particular the address generation and timing in
low- and high-current mode.
The DS28DG02 memory map (Figure 2) begins with 256 bytes of general-purpose user EEPROM, organized as
four blocks of 64 bytes. Additional EEPROM is set aside to store power-on defaults for PIO state (high, low, in
output mode), data direction (in, out), read-inversion (true, false), port output type (push-pull, open-drain), and
output mode (high current, low current). Once powered up, the PIO settings can be overwritten through SRAM
registers without affecting the power-on defaults. PIO state, direction, and read-inversion can be set for individual
ports. The output type is set for groups of four PIOs and the selected output mode applies to all PIOs in output
mode. The RTC/calendar, associated Alarm registers and the Multifunction Control/Status registers are kept
nonvolatile through battery backup. Write-protection, if enabled, is available for all four EEPROM blocks, blocks 2
and 3 only, or block 3 only and for all writeable registers from address 120h and higher.
