Mdio addressing, Figure 9-2, Figure 9-3 – Xilinx 1000BASE-X User Manual
Page 117: Write transaction, Read transaction, Physical address (phyad)
Ethernet 1000BASE-X PCS/PMA or SGMII v9.1
117
UG155 March 24, 2008
MDIO Management Interface
R
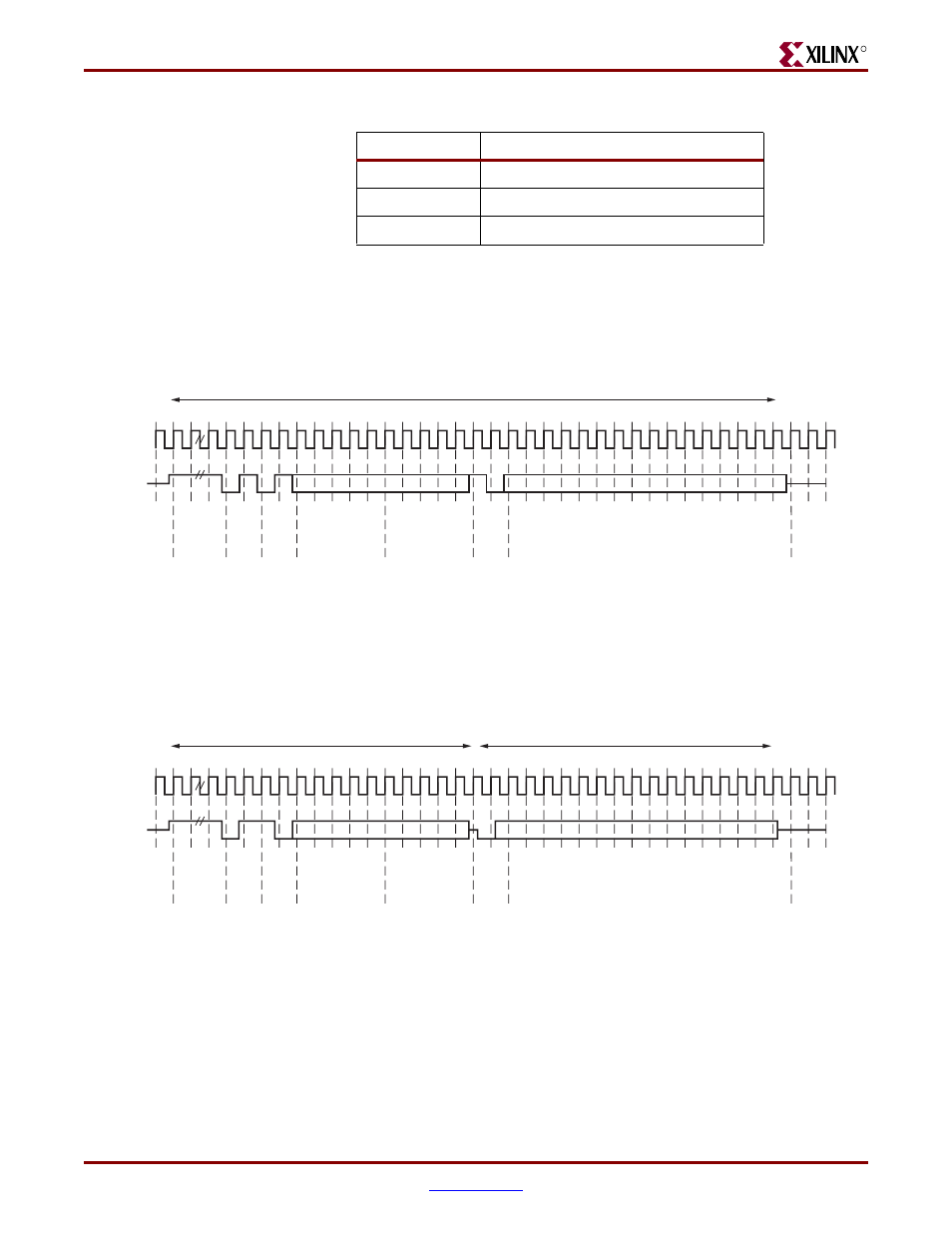
Write Transaction
shows a write transaction across the MDIO, defined as OP=”01.” The addressed
PHY device (with physical address PHYAD) takes the 16-bit word in the Data field and
writes it to the register at REGAD.
Read Transaction
shows a read transaction, defined as OP=”10.” The addressed PHY device (with
physical address PHYAD) takes control of the MDIO wire during the turnaround cycle and
then returns the 16-bit word from the register at REGAD
MDIO Addressing
MDIO Addresses consists of two stages: Physical Address (PHYAD) and Register Address
(REGAD).
Physical Address (PHYAD)
As shown in
, two PHY devices are attached to the MDIO bus. Each of these has
a different physical address. To address the intended PHY, its physical address should be
PHYAD
Physical address
REGAD
Register address
TA
Turnaround
Table 9-1:
Abbreviations and Terms (Continued)
Abbreviation
Term
Figure 9-2:
MDIO Write Transaction
Z
1 1 1 0
0 1 P4 P3 P2 P1 P0 R4 R3 R2 R1 R0 1 0 D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D9
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
1
Z
Z
Z
mdc
mdio
IDLE
IDLE
32 bits
PRE
ST
OP
PHYAD
REGAD
TA
16-bit WRITE DATA
STA drives MDIO
Figure 9-3:
MDIO Read Transaction
Z
1 1 1 0
1 0 P4 P3 P2 P1 P0 R4 R3 R2 R1 R0 Z 0 D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D9
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
1
Z
Z
Z
mdc
mdio
IDLE
IDLE
32 bits
PRE
ST
OP
PRTAD
REGAD
TA
16-bit READ DATA
STA drives MDIO
Addressed MMD drives MDIO
