Typical dsl router system – Paradyne Hotwire Routers User Manual
Page 12
Introduction to Hotwire DSL Routers
1-2
6371-A2-GB20-10
August 2000
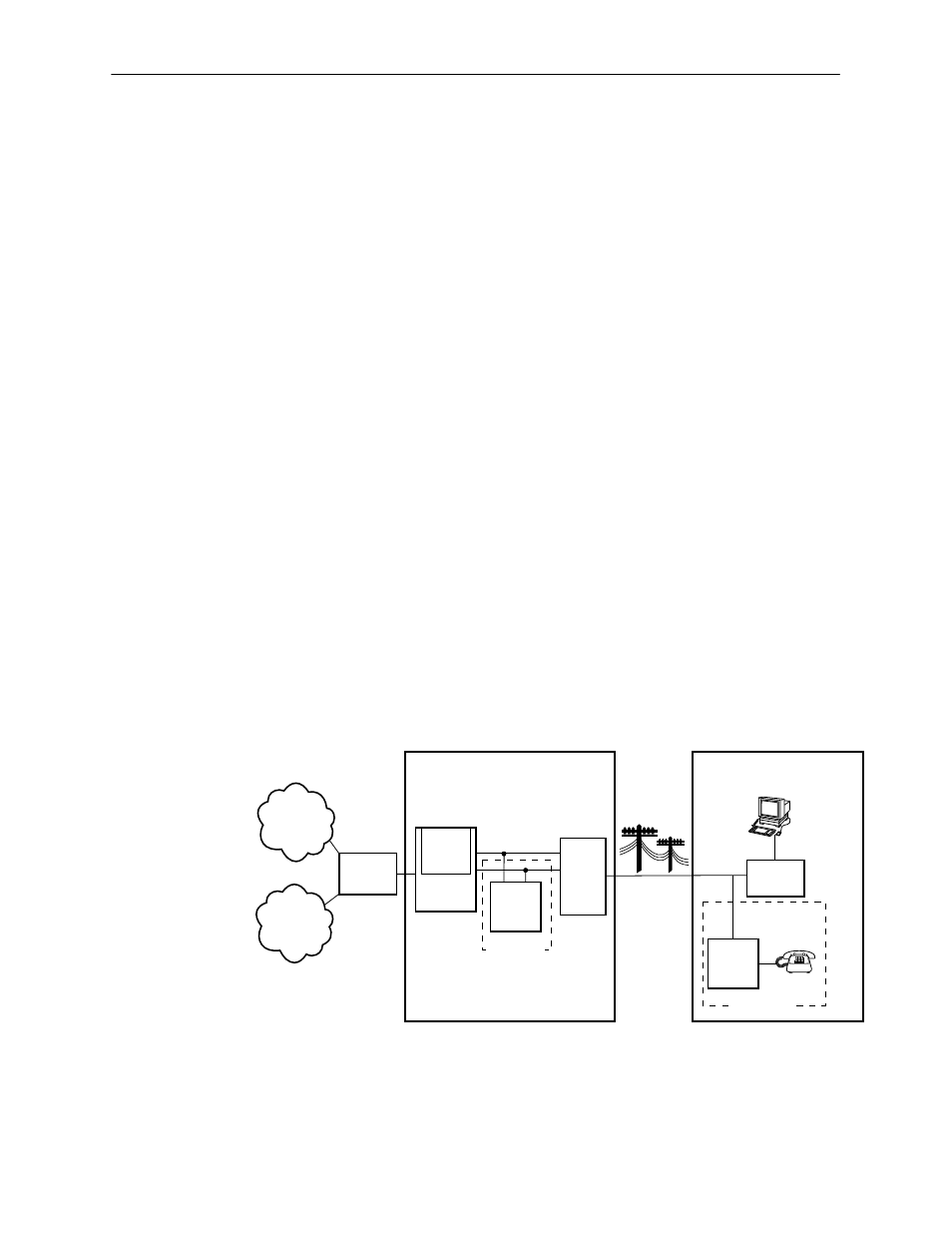
Typical DSL Router System
DSL is a local loop technology that uses standard twisted-pair copper wire to
support high-speed access over a single pair of twisted copper wires. DSL
applications are point-to-point, requiring DSL devices at the central site and at the
end-user site.
The Hotwire DSL routers interoperate with the following types of Hotwire IP DSL
cards (at the DSLAM/GranDSLAM chassis) to deliver applications at high speeds
in support of packet services over a DSL link:
H
The Hotwire 8303 or 8304 IP IDSL Cards interoperate with two Hotwire IDSL
Routers:
— Hotwire 6301 IDSL Router with one Ethernet port
— Hotwire 6302 IDSL Router with a 4-port Ethernet hub
H
The Hotwire 8343 or 8344 SDSL Cards interoperate with two Hotwire
Symmetric DSL Routers:
— Hotwire 6341 SDSL Router with one Ethernet port
— Hotwire 6342 SDSL Router with a 4-port Ethernet hub
H
The Hotwire 8510, 8373, and 8374 IP RADSL Cards interoperate with the
Hotwire 6371 RADSL Router with one Ethernet port
The following illustration shows a typical Hotwire system with a Hotwire DSL
Router. All Hotwire DSL routers transport data. The Hotwire 6371 RADSL Router
can transport data and POTS simultaneously.
Legend: DSL – Digital Subscriber Line
POTS – Plain Old Telephone Service
MDF – Main Distribution Frame
* 6371 RADSL Router Only
IP DSL
Line
Card
DSLAM
Central Office (CO)
00-16576-02
Customer Premises (CP)
DSL
Router
CP
POTS
Splitter
CO
POTS
Splitter
MDF
POTS/DSL
Core
Router
Data
Interface
POTS
*
Network
Service
Provider
Optional
Optional
Corporate
Intranet
Network Access Provider (NAP)
Service Subscriber
