Routed vs. bridged pdus, Routed vs, Bridged pdus – Paradyne Hotwire Routers User Manual
Page 30
Configuring the DSL Router
3-10
6371-A2-GB20-10
August 2000
Routed vs. Bridged PDUs
The DSL router supports both the VNET model and the 1483 Routed model
(derived from RFC 1483) for the transportation of PDUs (Protocol Data Units)
from the DSL router to the router in the core network. When operating in
Standard mode, the DSL router supports both routed and bridged PDUs. When
operating in VNET mode, the DSL router supports bridged PDUs only.
NOTE:
Standard mode vs. VNET mode is configured on the DSL card at the
DSLAM/GranDSLAM chassis.
Both ends of the network (e.g., the DSL router and the DSL line card or the core
router) must be configured to operate the same way (i.e., routed or bridged).
If Using This Network Model . . .
Then These DSL Cards Can Be Used . . .
1483 Routed or Bridged
(Standard Mode)
Model 8303 24-port IDSL
Model 8344 24-port SDSL
Model 8374 12-port RADSL
1483 Bridged (VNET Mode)
Models 8303/8304 24-port IDSL
Models 8343/8344 24-port SDSL
Models 8373/8374 12-port RADSL
Model 8510 12-port RADSL
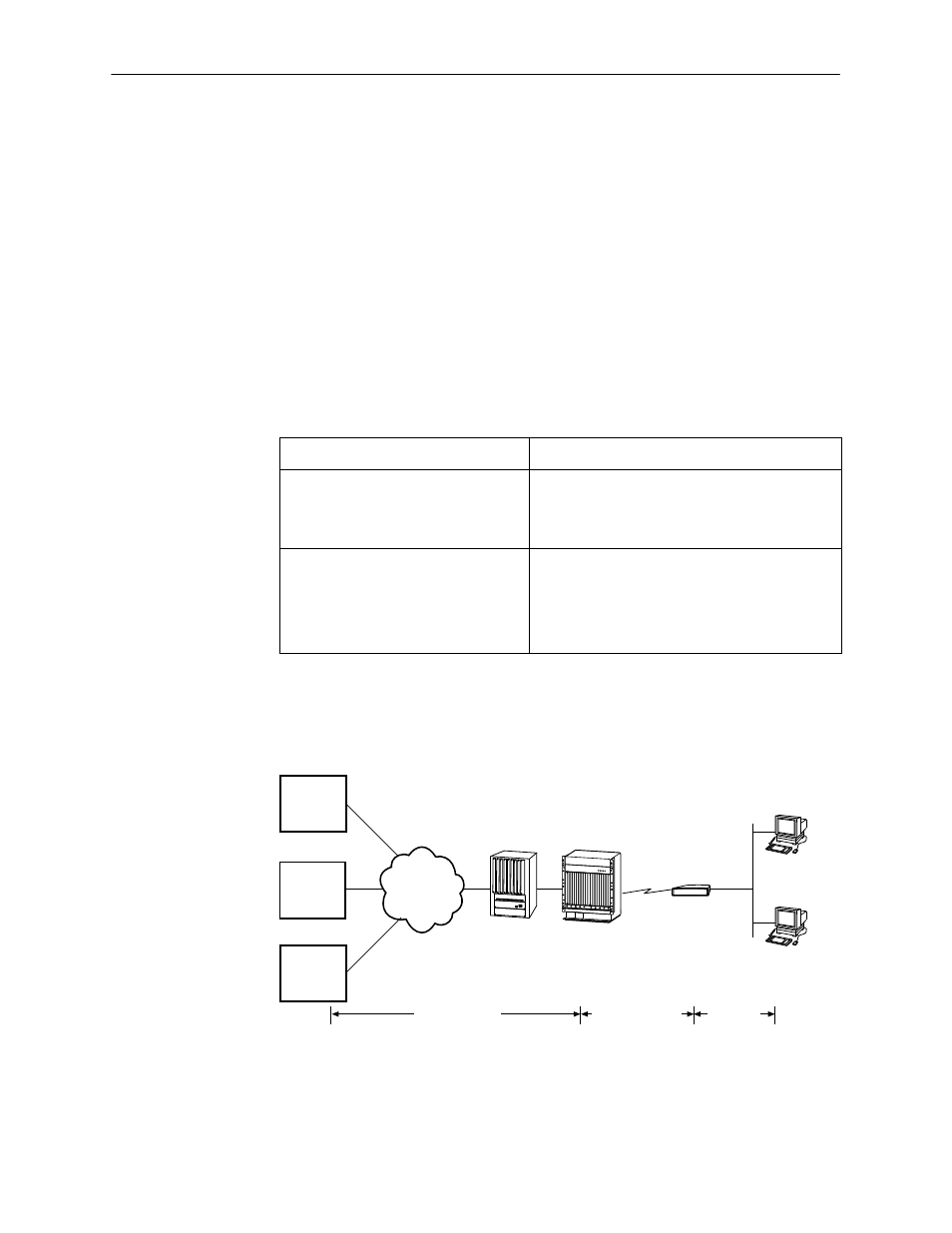
The following diagram illustrates the 1483 Routed model (Standard mode) in the
network.
O I
ALARMS
Major Minor
Fan
B
A
POWER
IPC
Hotwire
GranDSLAM
DSL
Router
Client
NSP's
Access
Device
NAP's
Core
Router
NAP's ATM
Network
Client
IP/MAC
IP/1483/FUNI
IP/1483/ATM
00-16802
NSP's
Access
Device
Figure 3-1.
1483 Routed Network Model (Standard mode)
