Pseudo-differential (pd), Fully-differential (diff) – Measurement Computing ADAC/5500 Series User Manual
Page 21
ADAC Series PCI Boards
795
- 16 -
ADAC/5500 Series User Manual
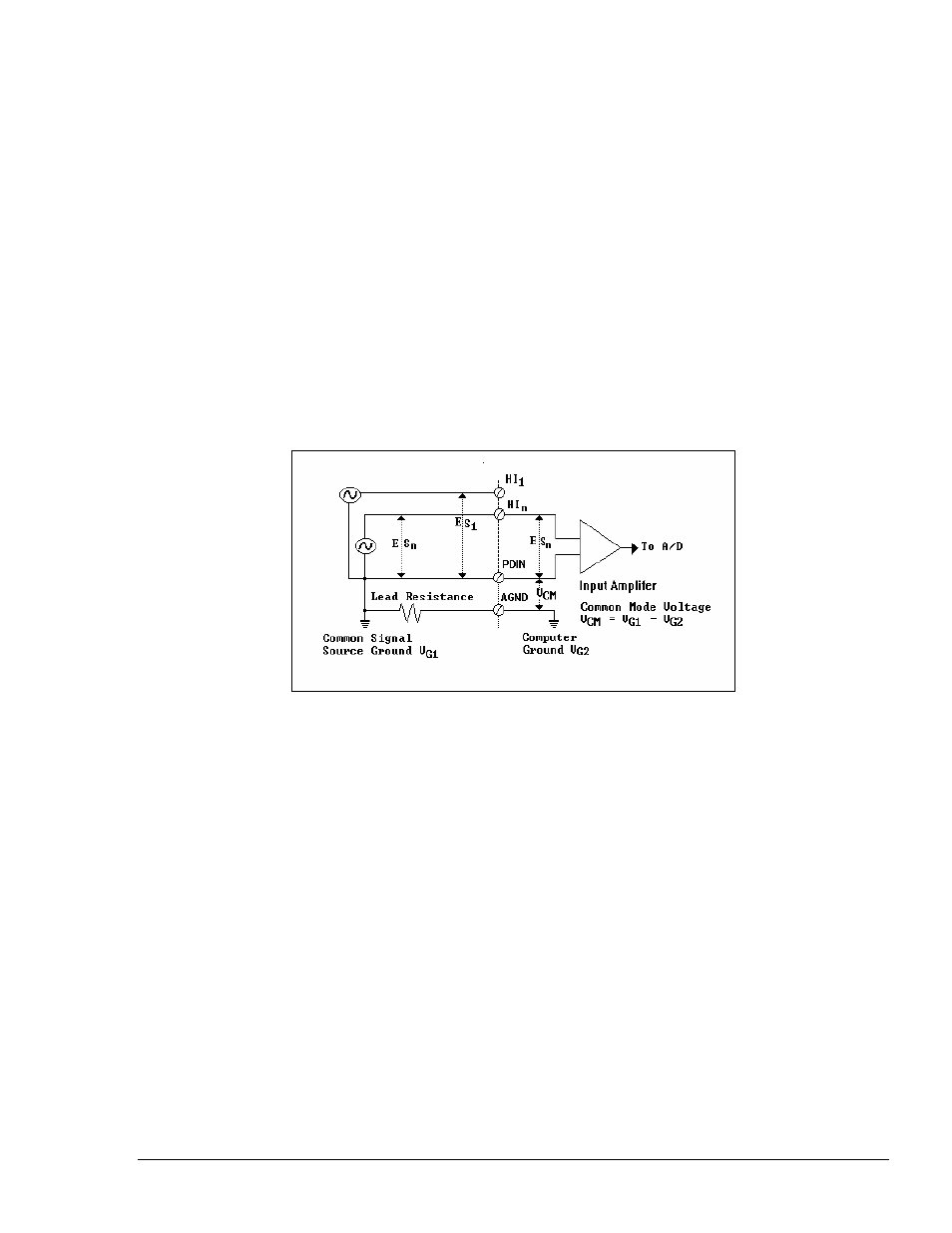
4.1.2.2 Pseudo-Differential (PD)
For multiple signal sources that share a common ground (signals must be local to one another), the Pseudo-
Differential mode may be the most desirable. The Pseudo-Differential configuration is similar to Single-
Ended, but the analog low side of each signal is isolated from analog ground (AGND) by a 10 M
Ω resistor and
a capacitor. All input returns are tied together to PDIN. Pseudo-Differential configuration allows the system to
reject any common-mode voltage difference that may exist.
Pseudo Differential configuration should be used when:
• Common Mode Voltage exists
• Common Mode Noise does not exist
• Each Source has a local ground
• Input signals are greater than 1 V (High Level)
• Signal leads are longer than 12 feet
Figure 4.2 shows proper wiring for Pseudo-Differential configuration.
Figure 4.2
Pseudo-Differential Configuration
4.1.2.3 Fully-Differential (DIFF)
In installations where each Ground Referenced Source signal has a local ground (signal located remote from
one another), the Fully-Differential configuration must be used. Since the Fully-Differential configuration
only responds to the difference in a signal between its high and low voltages, any Common Mode Voltage will
be cancelled out. In addition, Fully-Differential configuration provides the best performance of the three
configurations in an electrically noisy environment.
The Fully-Differential configuration should be used when any of the following exists:
• Each source has a local ground
• Signal sources are remote from one another
• Common Mode Voltage exists
• Common Mode Noise exists
• Signal sources are low-level (less than 1 V)
• Signal source leads are longer that 12 feet
928
