Active serial programming, User-programmable epcs64 device – Altera Cyclone II EP2C35 PCI Development Board User Manual
Page 31
Altera Corporation
Core Version 4.0.0
3–5
May 2005
Cyclone II EP2C35 PCI Development Board Reference Manual
Using the Board
lists the advantages and disadvantages of both methods.
Active Serial Programming
This section provides active serial programming steps for both the
user-programmable and preloaded, factory-programmed EPCS64
devices.
User-Programmable EPCS64 Device
This section provides the steps to program the user-programmable
EPCS64 device’s serial flash memory via the active serial programming
method.
To program the user-programmable EPCS64 device’s serial flash memory
using the Quartus II software, follow these steps:
1.
Write your custom programmer object file (.pof) into flash memory.
f
For instructions on either writing a POF to flash memory or creating a
POF, refer to Quartus II Help.
2.
Choose Programmer (Tools menu). The Chain1.cdf window
displays.
3.
Scroll to Active Serial Programming in the Mode field.
4.
To select the user-programmable EPCS64 device, set the switch (J3)
to the Down position.
If the switch (J3) is in the Up position (factory-programmed), the
factory-programmed design will be overwritten.
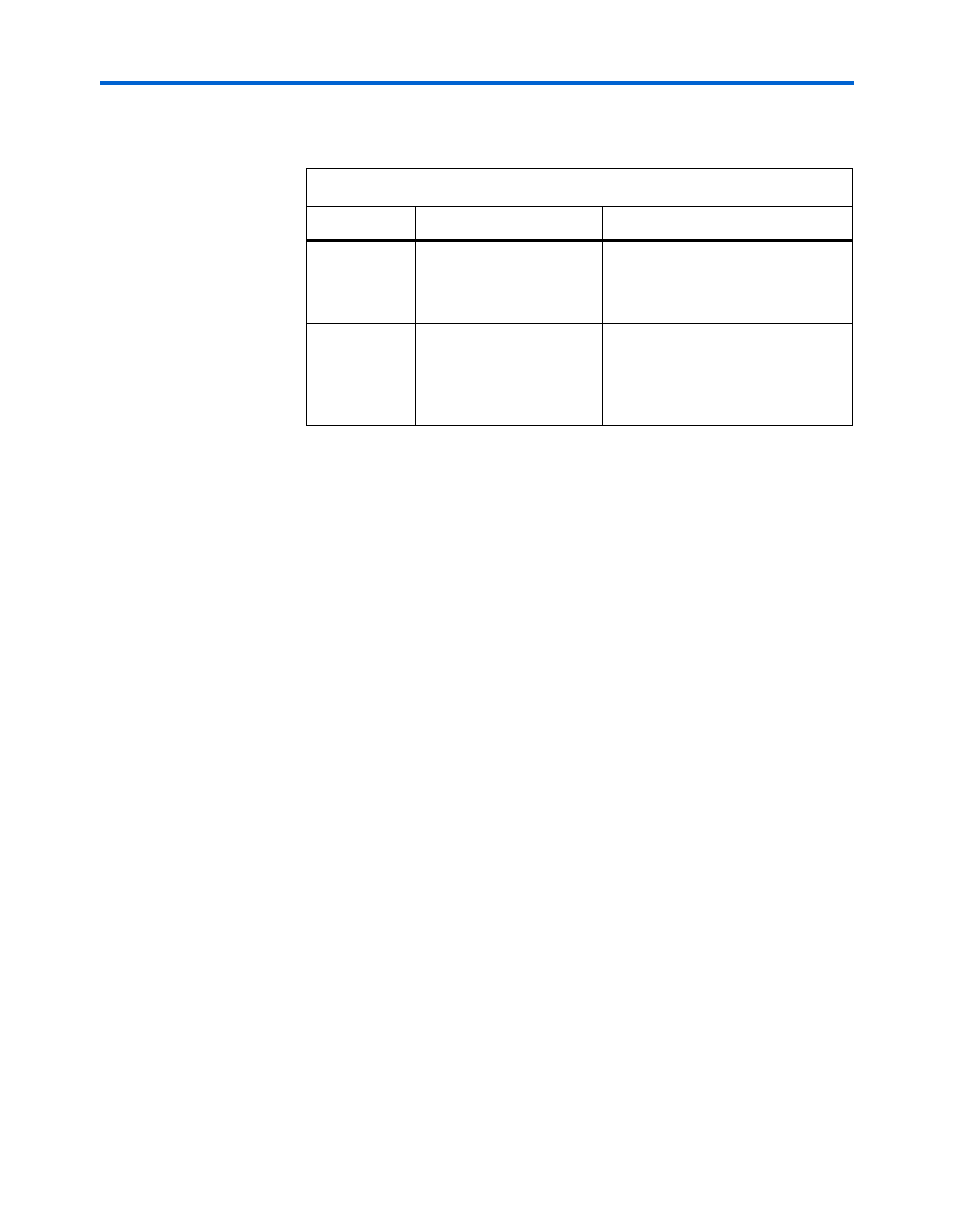
Table 3–1. Advantages & Disadvantages
Method
Advantage
Disadvantage
Conventional
Simple and fast
Requires separate programming
interface to configure FPGAs and
program serial configuration
devices.
SFL solution
Able to configure the
FPGA and program serial
configuration devices
using the same JTAG
interface
Slow because the SFL solution
needs to configure the FPGA before
programming serial configuration
devices.
