4 fn_or example, 5 fn_compare example – Echelon i.LON 100 e2 Internet Server User Manual
Page 149
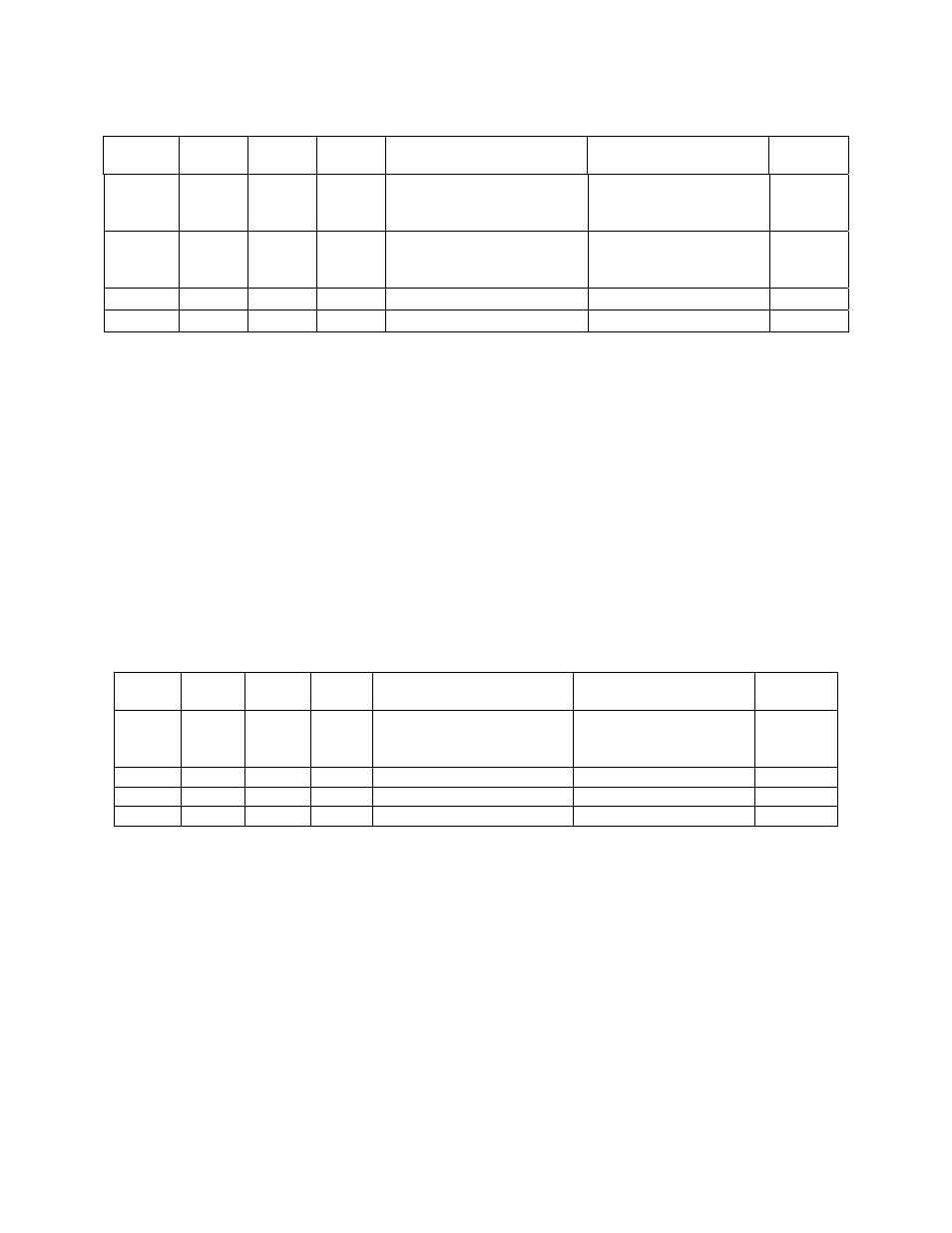
Table 48 FN_AND Examples
Input 1 Input
2
Input
3
Input
4
Value of Compare
Data Point
UCPTtrueThreshold Output
9 11
12
13
10 0.0
0
Does not matter since
defined.
20 30 40 50
10 100.0
1
Does not matter since
defined.
20 30 40 50
35
EMPTY 0.0
0
70 80 40 50
EMPTY 100.0
1
9.2.1.2.4 FN_OR Example
Because the output function is FN_OR, and the comparison function is FN_LT, one of the
values of the data inputs must be less than the value of the compare data point, or the
in the comparison.
Table 49 lists several case scenarios that show when these two functions might evaluate to
True.
Input
1
Input
2
Input
4
Value of Compare
Data Point
35
In this example, there are four input data points and one compare data point, all of the type
SNVT_count. There is one output data point, of the type SNVT_switch.
Table 49 FN_OR Examples
Input
3
UCPTtrueThreshold Output
9
11
12
13
Does not matter since
defined.
10 100.0
1
30 40 50
35
EMPTY
0.0
0
20 30 40 50
35
EMPTY
100.0
1
20 30 40 50
35
EMPTY
100.0
1
9.2.1.2.5 FN_COMPARE Example
20
In this example, there are four input data points and one compare data point, all of the type
SNVT_count. There is one output data point, of the type SNVT_switch.
Because the
and compare data points must return True in order for the output data point to be set to
True. The comparison function selected is FN_EQ, so this means the values of the input data
points must match the value of the compare data point, or the
i.
LON 100 Internet Server Program
9-12
mer’s Reference
