0 compressor maintenance and replacement (cont'd) – Reznor MAPSII Series REDA Users Manual User Manual
Page 16
Form O-MAPS II, P/N 209179 R7, Page 16
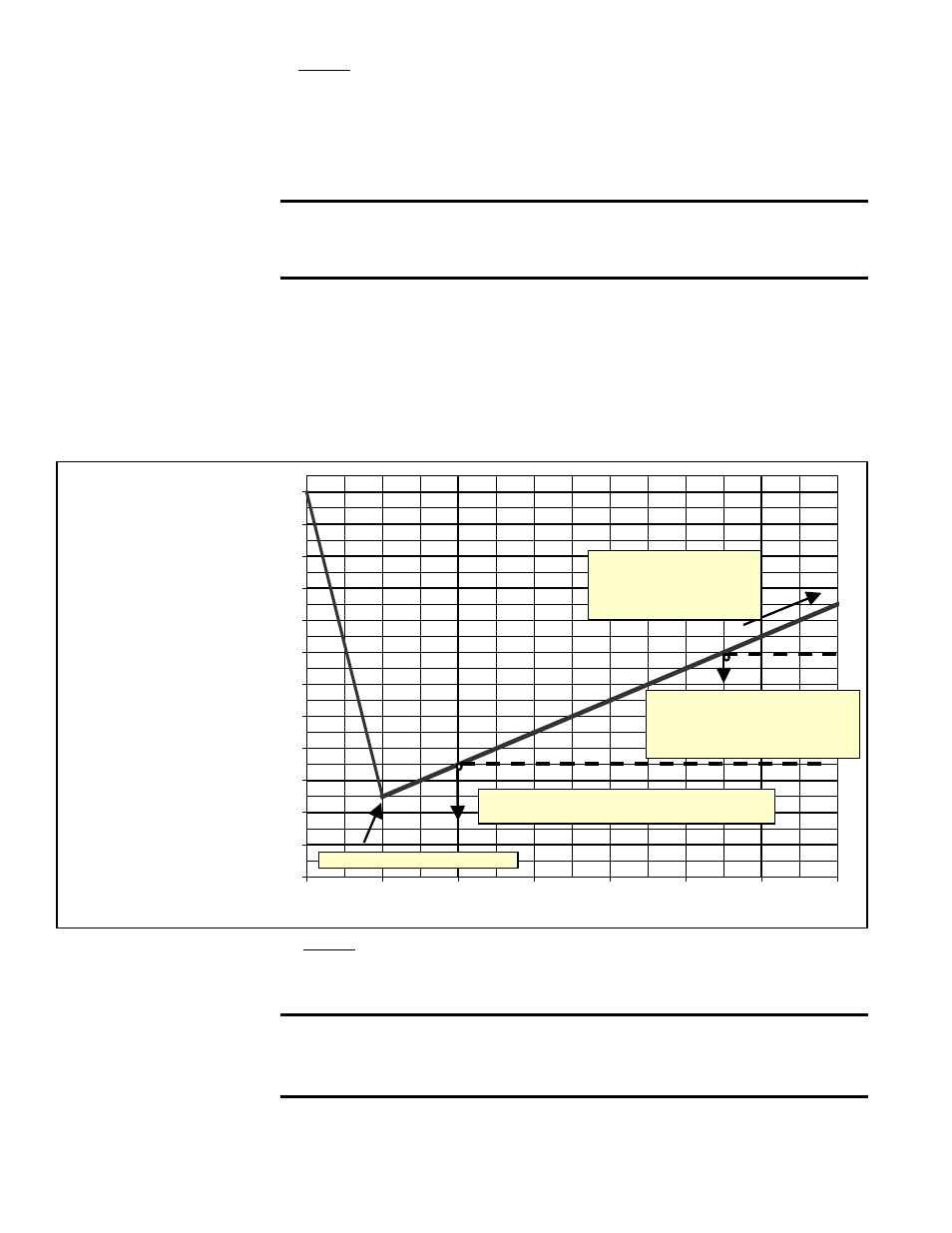
FIGURE 9 -
Pressure Rise
vs Time
IMPORTANT
NOTE:
Always check
gauge hose
connections
for leaks prior
to evacuation.
Step 8. Check the Electrical System
While the system is being evacuated, connect the electrical plug to the
compressor. It is a normal practice to replace all starting components any
time a compressor is changed.
WARNING: Voltage should not be applied to the compressor
when the terminal plug is removed as personal injury could
result.
Compressor
Maintenance
Checklist,
Steps 1-13 (cont'd)
If there is a crankcase heater, connect it. The crankcase heater is ener-
gized continuously and is extremely important to proper compressor oper-
ation and long life.
0
200
400
600
800
1,000
1,200
1,400
1,600
1,800
2,000
2,200
2,400
-20
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
Time (minutes)
Pressure (microns)
Evacuate to 500 microns or lower.
If system holds a vacuum at or below 700 microns,
the system is sufficiently dry and has no leaks.
If system holds a steady vacuum in
this region, there are no leaks. But
the system is not sufficiently dry. Re-
evacuate to remove excess moisture.
If system pressure continues
to rise, the system has leaks.
The leaks must be found and
sealed prior to re-evacuating.
Time varies by moisture level.
Step 7. Evacuate the System
Use a vacuum pump rated for a minimum capacity of 6 cfm. Vacuum must
be pulled on both the discharge (high) and suction (low) sides of the sys-
tem. Evacuate to 500 microns or lower.
Moisture and air are harmful to the system because they increase the con-
densing temperature, raise the discharge gas temperature, cause forma-
tion of acids, and cause oil breakdown.
CAUTION: Do not use the replacement compressor as an
evacuation assist and never apply voltage to a compressor while
it is in a vacuum.
Acids are corrosive to the components in the refrigeration system. This
includes the piping, refrigerant specialties, and the compressor’s mechani-
cal and electrical components. The elevated temperatures can cause cop-
per plating resulting in premature mechanical failure of the compressor.
To establish that the unit is leak-free and moisture-free, a standing vacuum
test is recommended. The maximum allowable rise over a 18-minute
period is 200 microns. If
the rise exceeds this, either there is a leak or
moisture still exists in the system. See the chart in
FIGURE 9.
7.0 Compressor
Maintenance
and
Replacement
(cont'd)
