Fractionation by solubility/hydrophobicity, Fractionation by protein charge, Fractionation by pi – Bio-Rad GS-900™ Calibrated Densitometer User Manual
Page 14
Products for Fractionation by
Solubility/Hydrophobicity
Products for Fractionation by
Protein Charge
■
■
ReadyPrep sequential extraction kit is based on
a published method (Molloy et al. 1998) that uses
sequentially more highly solubilizing chaotrope
and detergent mixtures. Applying each extracted
fraction to a separate gel allows the resolution of
more protein spots
■
■
ReadyPrep protein extraction kit (soluble/insoluble)
uses a different set of detergents to fractionate
proteins on the basis of their solubility in detergents
The ReadyPrep sequential extraction kit and the
ReadyPrep protein extraction kit (soluble/insoluble)
can be used either independently or sequentially for
even greater depth of coverage.
For prefractionation in a convenient kit format,
Aurum
™
AEX (anion exchange) and CEX (cation
exchange) mini kits and columns employ ion
exchange chromatography in an easy-to-use spin
column format for fractionating and concentrating
acidic and basic proteins from small sample volumes
(<1 ml). Micro Bio-Spin 6 columns are included for
salt removal from the fractionated samples.
Requiring only 15–20 min operating time, Aurum
ion exchange mini spin columns provide a quick,
convenient, and reproducible sample preparation
tool for 2-D electrophoresis, and their use can
improve detection of low-abundance proteins
(Liu and Paulus 2008).
2
Liquid IEF introduces ampholytes that must be removed, for example
with the ReadyPrep 2-D cleanup kit, before IEF in IPG strips.
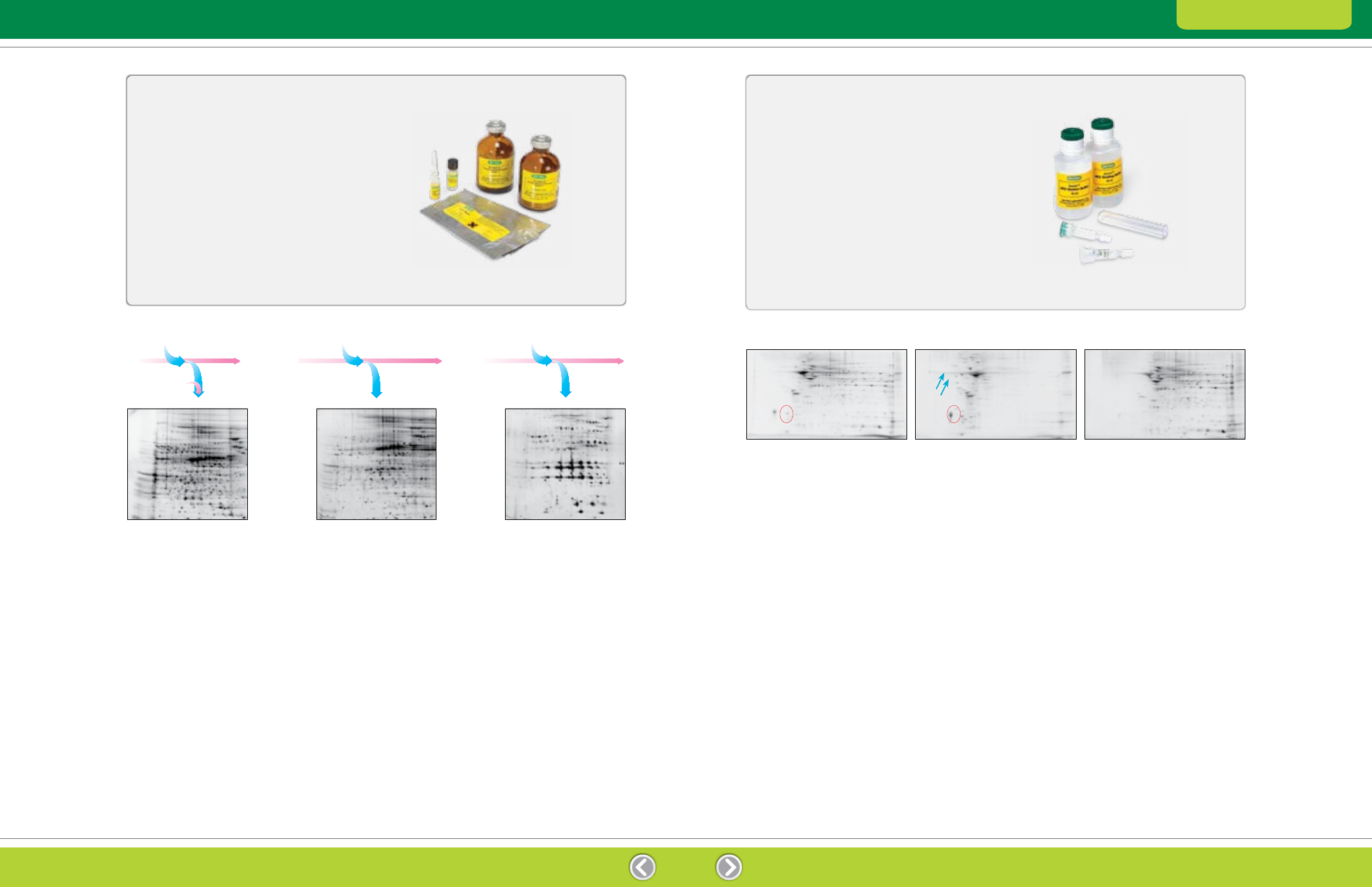
Fig. 2.5. Distribution of proteins based on differential solubility using the ReadyPrep sequential extraction kit. The generation of three
fractions provides increased resolution of proteins on 2-D gels.
Protein
sample
ReadyPrep
reagent 1
Step 1
Insoluble pellet
from reagent 1
Collect supernatant 1
ReadyPrep
reagent 2
Step 2
Insoluble pellet
from reagent 2
Collect supernatant 2
ReadyPrep
reagent 3
Step 3
Insoluble pellet
from reagent 3
Collect supernatant 3
Reagent 2
Fig. 2.6. Fractionation of rat brain tissue using Aurum ion exchange mini columns. Rat brain total protein extracts (3 ml) were loaded onto
an Aurum AEX column and eluted. The unfractionated and fractionated samples were then treated with the ReadyPrep reduction alkylation
and 2-D cleanup kits and separated by 2-D electrophoresis. Red circles indicate a group of protein spots with increased intensities after
fractionation. Blue arrows show two representative spots detected only in the gels of the AEX bound fraction.
Total Protein
pH 3
pH 10
AEX bound fraction
pH 3
pH 10
AEX unbound fraction
pH 3
pH 10
ReadyPrep Sequential Extraction Kit
Aurum Ion Exchange Kit
24
25
2-D Electrophoresis Guide
Theory and Product Selection
Chapter 2: Sample Preparation
Fractionation by Protein Charge
Ion exchange chromatography has been used to
reduce proteome complexity, enrich low-abundance
proteins, and improve peptide mass fingerprints
(Butt et al. 2001). This technique separates proteins
according to their charge at various pHs. It is based
on the reversible adsorption of proteins to a solid
phase containing charged chemical groups.
Cationic (+) or anionic (-) resins (Figure 2.6) attract
molecules of opposite charge in the solvent. A variety
of systems and media are available for ion exchange
chromatography, but because elution involves gradient
elution by washing the column with buffers of gradually
increasing ionic strength or pH, a subsequent
cleanup step must be included.
Fractionation by pI
Fractionation by pI, for example by liquid-phase IEF,
may seem counterintuitive as a fractionation technique
upstream of the first-dimension IEF separation. It can,
however, improve downstream sample loading and
separation on narrow- and micro-range IPG strips by
eliminating proteins outside the pH region of interest
(Figure 2.7). This unique separation method can also
be coupled to analytical or preparative SDS-PAGE for
a powerful, complementary first-dimension separation
and enrichment strategy for high molecular weight,
membrane, hydrophobic, or other proteins that
are often underrepresented in IPG-based 2-D gels
(Davidsson 2002, Hansson et al. 2004, Brobey
and Soong 2007)
2
.
Fractionation by Solubility/Hydrophobicity
Proteins can be separated according to their
solubility in different reagents using either chemical
or chromatographic methods. Sequential extraction
under different solvent conditions can be used to
fractionate a protein sample based on solubility,
and this strategy has also been used to prepare
discrete fractions for analysis by 2-D electrophoresis
(Lenstra and Bloemendal 1983, Weiss et al. 1992).
Extraction using different detergents can also
yield different protein fractions (Figure 2.5), and
chromatographic methods that can be used include
reverse-phase (Van den bergh and Arckens 2008)
and hydrophobic interaction chromatography
(McNulty and Annan 2009).
