X2 multiplying encoder mode, Ab quadrature encoder 1734-vhsc input a input b, A input b input x1 count x2 count x4 count – Rockwell Automation 1734-VHSC24 Very High-Speed Counter Modules User Manual User Manual
Page 14: Forward rotation reverse rotation input z, Z (store count) (gate / reset )
Publication 1734-UM003B-EN-P - August 2005
1-4 About the Modules
Absolute encoders typically have higher speed requirements (200 KHz
typical) for motion control applications. An absolute encoder has a
unique code associated with each position, so the exact position is
always known, even if the system power is turned off.
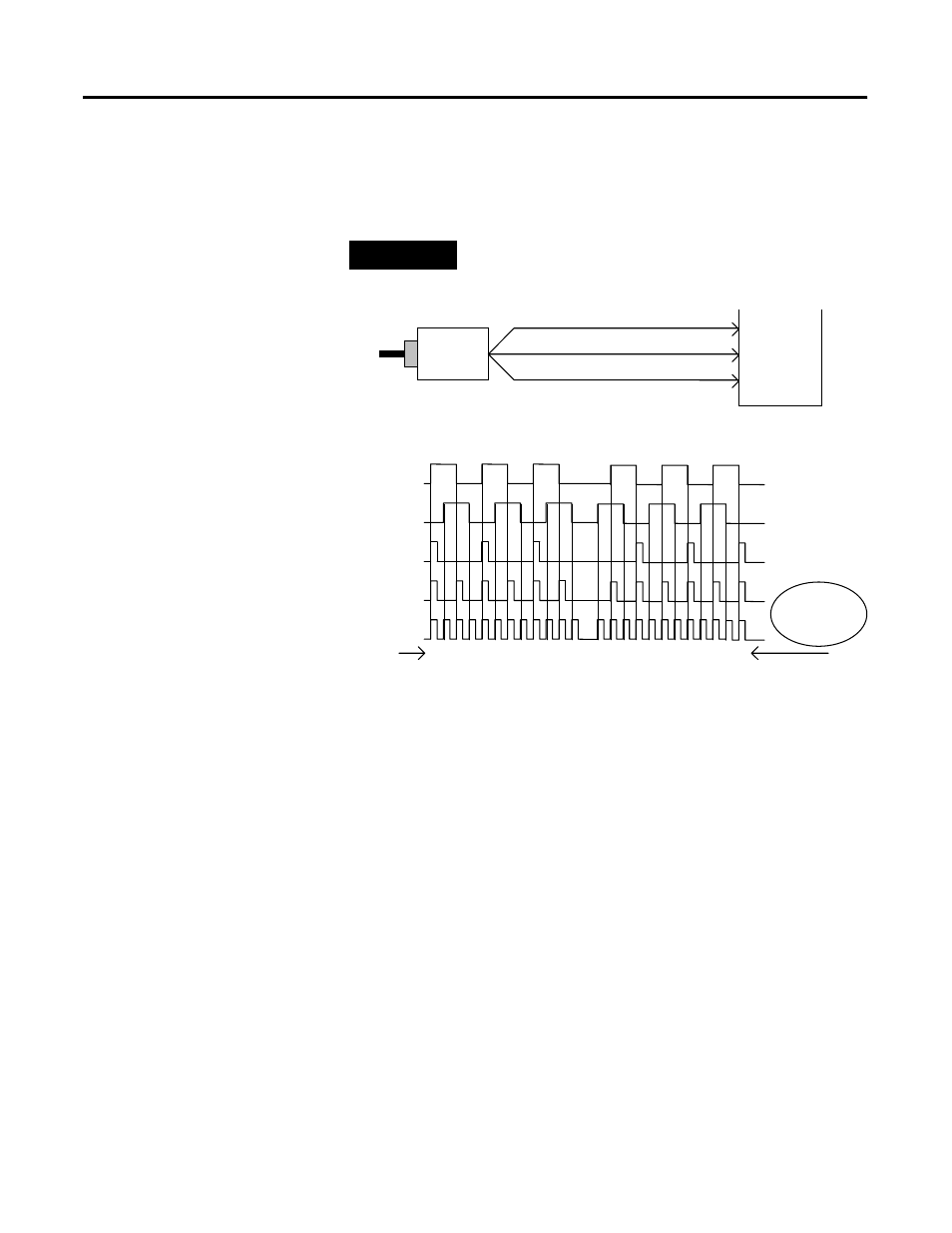
EXAMPLE
Example of Multiplying Encoder Mode X1, X2 and X4
X1 Multiplying Encoder Mode
Quadrature input signals are used to count on the leading (up
direction) or trailing (down direction) edge of A for a bidirectional
count, and channel B is used to determine the direction.
[ B = leads A, Count = Down; B = follows A, Count = Up ]
X2 Multiplying Encoder Mode
Quadrature input signals are used to count on leading and trailing
edges of A for a bidirectional count, and channel B is used to
determine the direction.
[ B = leads A, Count = Down; B = follows A, Count = Up ]
A
B
Quadrature Encoder
1734-VHSC
Input A
Input B
1
2
3
1
3
5
2
4
6
1
3
5
2
4
6
7
10
9
8
12
11
A Input
B Input
X1 Count
X2 Count
X4 Count
2
1
0
5
3
1
4
2
0
11
9
7
10
8
6
5
2
3
4
0
1
Forward Rotation
Reverse Rotation
Input Z
Outputs
Updated
Continuously
Z (Store Count)
(Gate / Reset )
