Rockwell Automation 20-COMM-R Remote I/O Adapter User Manual
Page 70
5-12
Using Block Transfer Messaging
20-COMM-R Remote I/O Adapter User Manual
Publication 20COMM-UM004D-EN-P
Response and Control Data to Write to Drive Parameter 41 (Hex)
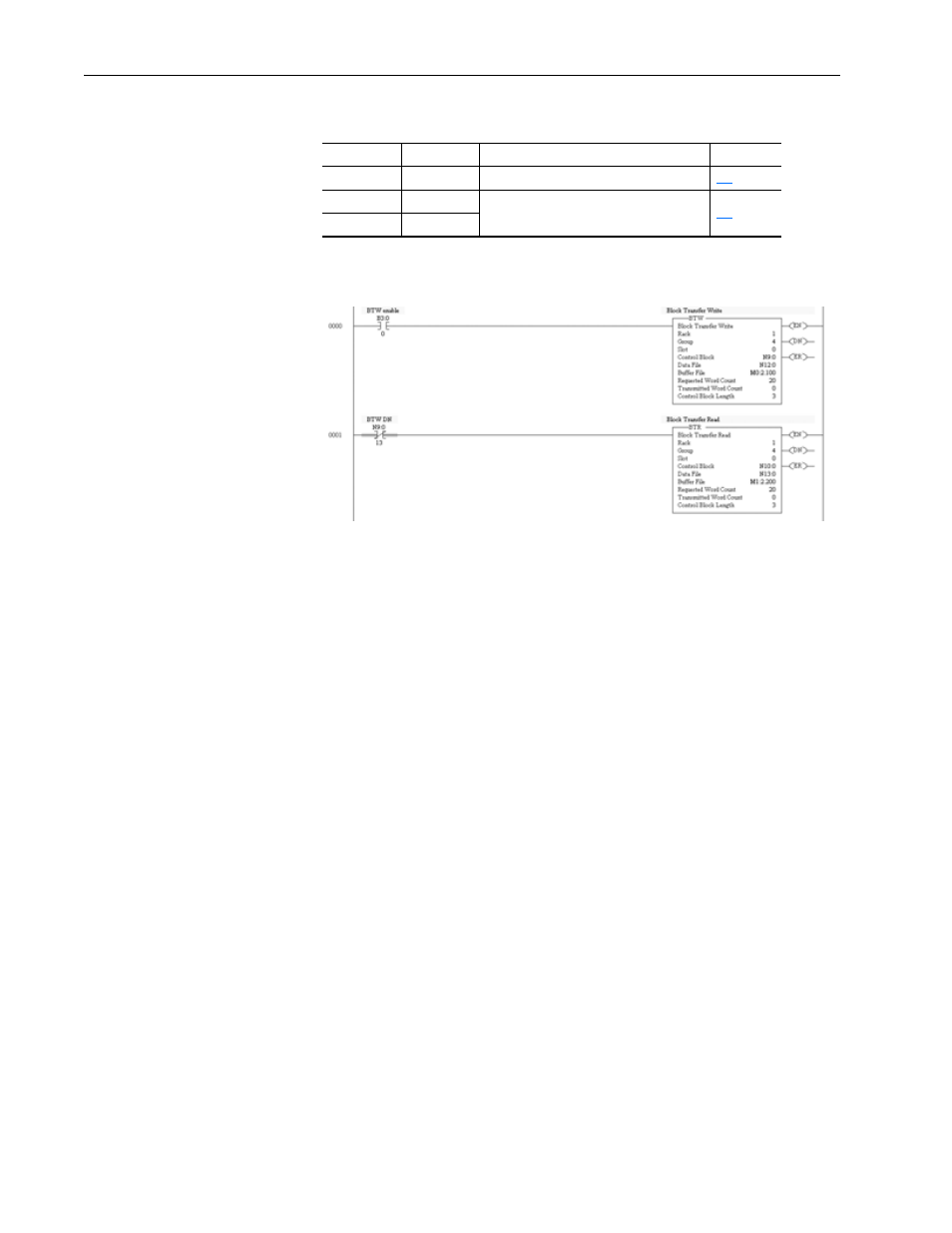
Figure 5.5 SLC 500 Series C, FRN 3.xx and Higher, Example Ladder Logic for
Block Transfer Read and Block Transfer Write
The following data is used for this example.
• Rack 1
• Group 4 (upper half rack)
• Slot 0 (always 0)
• Control Block N9:0 and N10:0 (user defined)
• Data File N12:0 and N13:0 (user defined)
• Buffer File M0:x.100 and M1:x.200 (Block Transfer Writes always with
start M0 and Block Transfer Reads always start with M1, where x is the
slot in which the 1747-SN scanner card is in. In this example, the
1747-SN card is in slot 2.)
• Requested Word Count is 20, 40, or 60
• Transmitter Word Count (always 0)
• Control Block Length (always 3)
Important: Each Block Transfer needs to be offset by 100 (M1:x.100) and
the default is 3300 words, so you can perform up to 33 Block
Transfers. See the advanced configuration for your 1747-SN
scanner card under channel configuration.
The Block Transfer Write is transmitted first, and then the
Block Transfer Read is executed. (The BTW requests the data,
and the BTR reads back the data requested.)
Address
Value (hex)
Description
See Page
N13:0
0002
Length of Message = 2 bytes
N13:1
0000
The Message was Successful
N13:2
0000
