SATEC C192PF8-RPR User Manual
Page 26
Chapter 4 Setup Menus
21
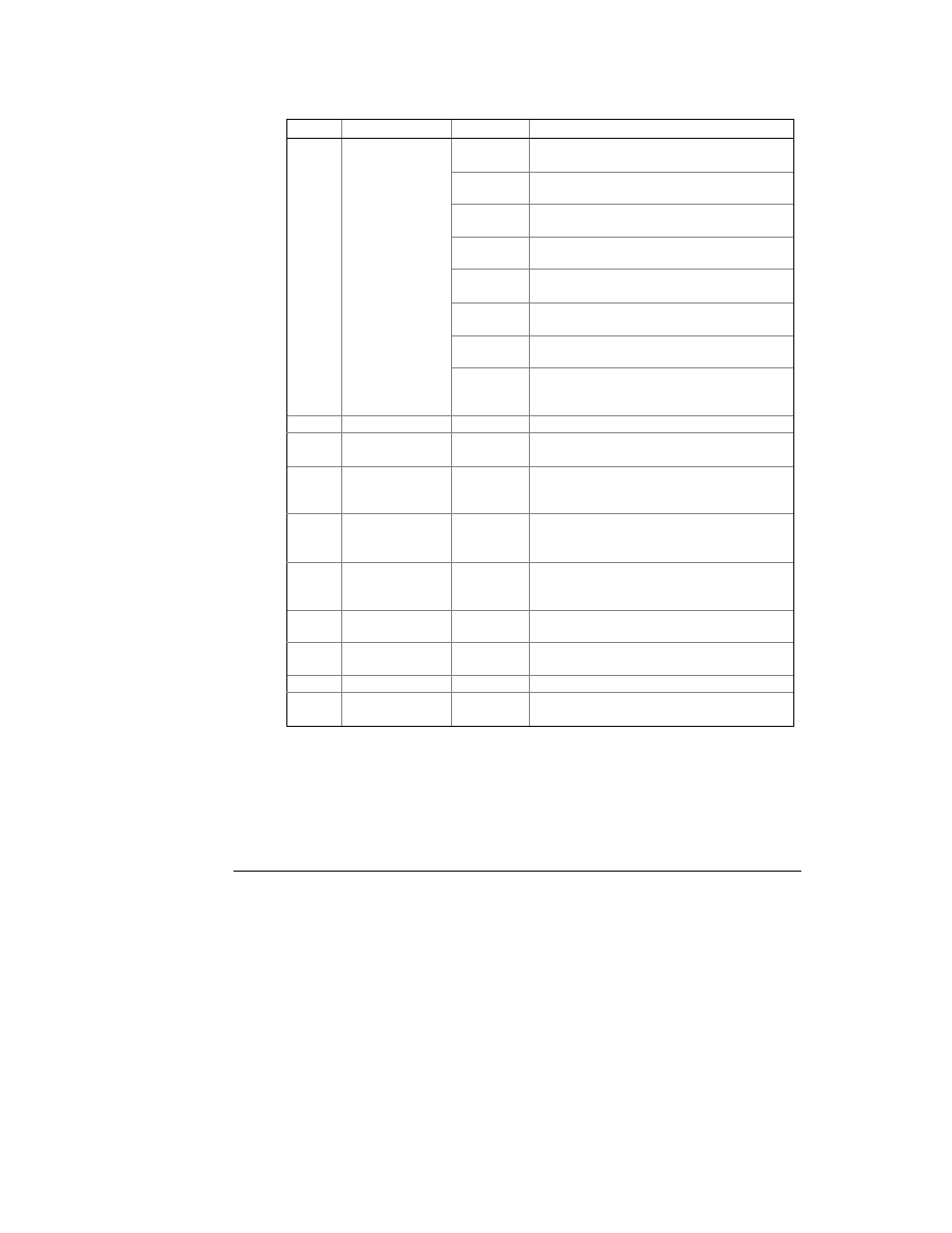
Table 4-1 Basic Setup Options (
∗
default setting)
Code
Parameter Options
Description
3OP2
3-wire open delta using 2 CTs
(2 element)
4Ln3
∗
4-wire Wye using 3 PTs (3 element), line to
neutral voltage readings
3dir2
3-wire direct connection using 2 CTs (2
element)
4LL3
4-wire Wye using 3 PTs (3 element), line to
line voltage readings
3OP3
3-wire open delta using 3 CTs
(2½ element)
3Ln3
4-wire Wye using 2 PTs (2½ element), line to
neutral voltage readings
3LL3
4-wire Wye using 2 PTs (2½ element), line to
line voltage readings
ConF
Wiring mode
2LL1
3-wire/4-wire connection using the current
from one phase (1 CT) and the L-L voltage
from the two other phases
Pt
PT ratio
1.0*-6,500.0 The phase potential transformer ratio
Ct
CT primary current 1-6,500A
(5
∗
)
The primary rating of the phase current
transformer
d.P
Power demand
period
1, 2, 5, 10,
15*, 20, 30,
60, E
The length of the demand period for power
demand calculations, in minutes. E = external
synchronization
n.dp
Number of power
demand periods
1-15
(1*)
The number of demand periods to be averaged
for sliding window demands
1 = block interval demand calculation
A.dP
Ampere/Volt
demand period
0-1800 s
(900*)
The length of the demand period for
volt/ampere demand calculations
0 = measuring peak current
buF
Averaging buffer
size
8
∗
,16,32
The number of measurements for RMS sliding
averaging
rSt
Reset
enable/disable
diS
∗
, En
Protects all reset functions, both via the front
panel or communications.
Freq
Nominal frequency 50, 60 Hz
The nominal power utility frequency
LoAd
Maximum demand
load current
0-6,500A
(0
∗
)
The maximum demand load current used in
TDD calculations (0 = CT primary current)
When the power demand period is specified in minutes, synchronization of the demand
interval can be made through communications (see the C192PF8-RPR Modbus
Reference Guides) or via the front panel (see Section 4.11). If the power demand period
is set to External Synchronization, an external synchronization pulse denoting the start
of the next demand interval can be provided through a digital input or can be simulated
by using the synchronization command sent via communications.
60 Hz default for North America; elsewhere, default is 50Hz.
