3 virtual ip addresses, 4 a simple example of vrrp fail over – Allied Telesis AT-WR4500 User Manual
Page 251
AT-WR4500 Series - IEEE 802.11abgh Outdoor Wireless Routers
251
RouterOS v3 Configuration and User Guide
11.1.3
Virtual IP addresses
Submenu level: /ip vrrp address
Property Description
address (IP address) - IP address belongs to the virtual router
broadcast (IP address) - broadcasting IP address
interface (name; default: default) - interface, where to put the address on (may be different form the
interface this VRRP instance is running on)
default - put this address on the interface the given VRRP instane is working on
network (IP address) - IP address of the network
virtual-router (name) - VRRP router's name the address belongs to
The virtual IP addresses should be the same for each node of a virtual router.
To add a virtual address of 192.168.1.1/24 to the vr1 VRRP router:
[admin@AT-WR4562] ip vrrp> address add address=192.168.1.1/24 \
\... virtual-router=vr1
[admin@AT-WR4562] ip vrrp> address print
Flags: X - disabled, A - active
# ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INSTANCE INTERFACE
0 192.168.1.1/24 192.168.1.0 192.168.1.255 vr1 default
[admin@AT-WR4562] ip vrrp>
11.1.4
A simple example of VRRP fail over
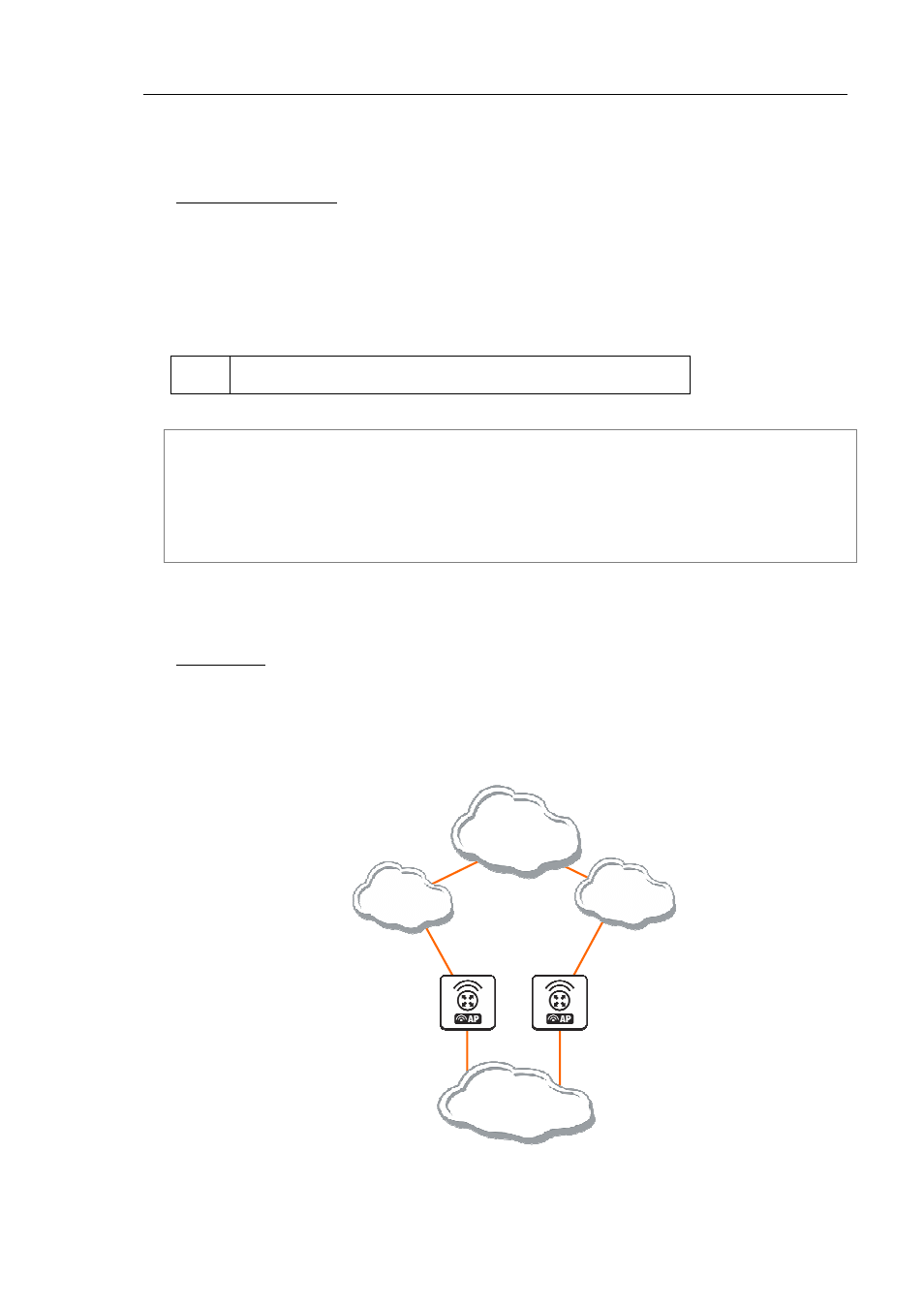
Description
VRRP protocol may be used to make a redundant Internet connection with seamless fail-over. Let us
assume that we have 192.168.1.0/24 network and we need to provide highly available Internet connection
for it. This network should be NATted (to make fail-over with public IPs, use such dynamic routing
protocols as BGP or OSPF together with VRRP). We have connections to two different Internet Service
Providers (ISPs), and one of them is preferred (for example, it is cheaper or faster).
Internet
ISP1
ISP2
LAN
192.168.1.0/24
192.168.1.1
Figure 35: Simple VRRP fail over example
