On/off control, Pid control, Remote setpoint – Red Lion DLC User Manual
Page 18: On/off control - reverse or direct acting figures, On/off control - heat/cool output figures, Typical pid response curve
18
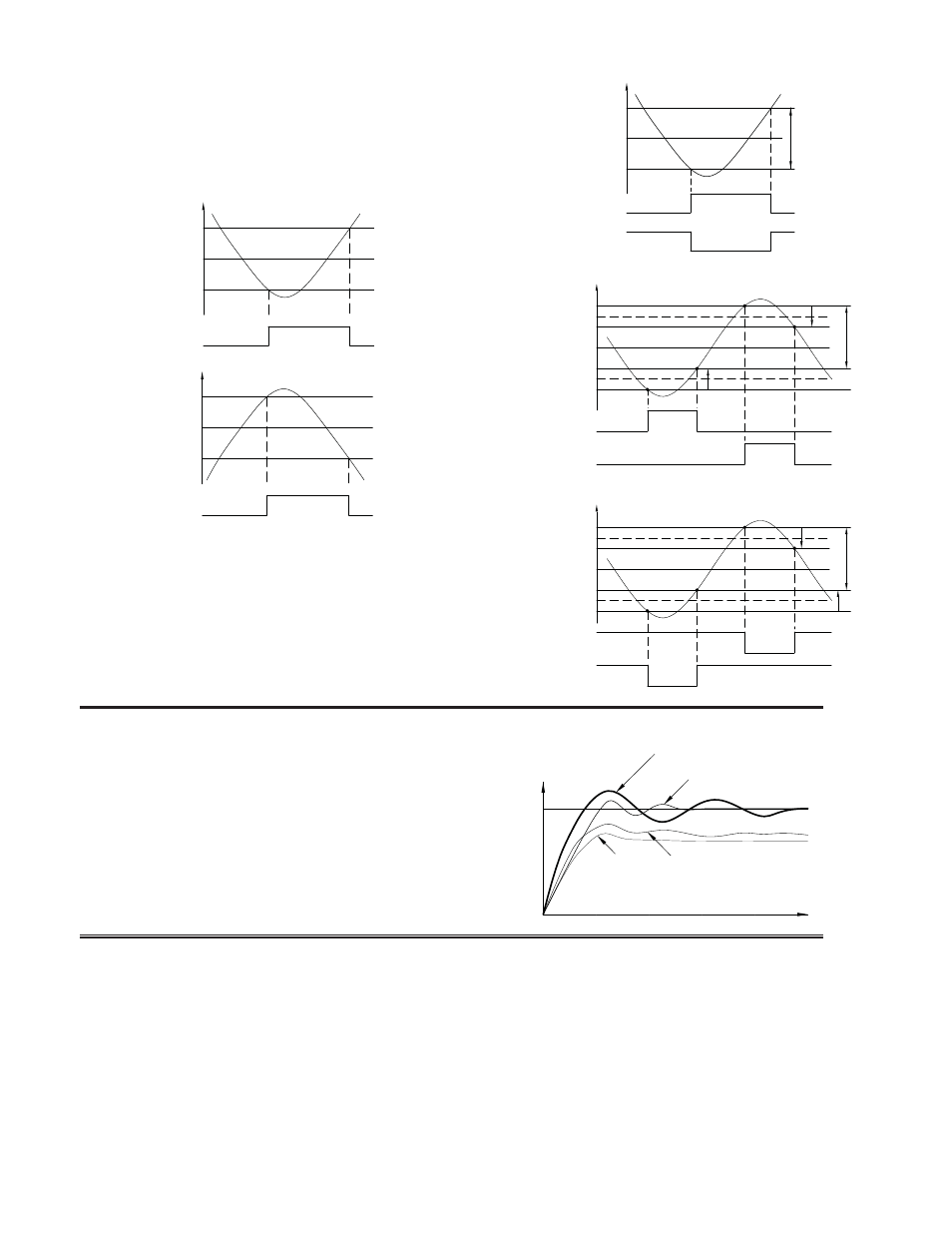
ON/OFF CONTROL
The controller operates in On/Off Control when the Proportional Band is set
to 0.0%. In this control, the process will constantly oscillate around the setpoint
value. The On/Off Control Hysteresis (balanced around the setpoint) can be
used to eliminate output chatter. Output OP1 Control Action can be set to
reverse for heating (output on when below the setpoint) or direct for cooling
(output on when above the setpoint) applications.
ON/OFF CONTROL - REVERSE OR DIRECT ACTING FIGURES
For heat and cool systems, OP1 Control Action is set to reverse (heat) and the
Alarm 2 Action is set to cooling (OP2). The Proportional Band is set to 0.0 and
the Relative Gain in Cooling to 0.0. The Deadband in Cooling sets the amount
of operational deadband or overlap between the outputs. The setpoint and the
On/Off Control Hysteresis applies to both OP1 and OP2 outputs. The hysteresis
is balanced in relationship to the setpoint and deadband value.
ON/OFF CONTROL - HEAT/COOL OUTPUT FIGURES
OFF
Output 1 (OP1) :
OFF
SP
ON
INPUT
REVERSE ACTING
SP+1/2 HYS
SP-1/2 HYS
OFF
Output 1 (OP1) :
SP
OFF
INPUT
DIRECT ACTING
SP-1/2 HYS
SP+1/2 HYS
ON
ON
Output 2 (OP2) :
ON
SP
OFF
INPUT
HEAT/COOL DEADBAND VALUE (db) = 0
SP + 1/2 HYS
SP - 1/2 HYS
OFF
OFF
Output 1 (OP1) :
ON
HYS
SP
SP + 1/2 (db) - 1/2 HYS
SP + 1/2 (db) + 1/2 HYS
SP - 1/2 (db) + 1/2 HYS
SP - 1/2 (db) - 1/2 HYS
HEAT/COOL DEADBAND VALUE (db) < 0
db
HYS
HYS
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
Output 1 (OP1) :
Output 2 (OP2) :
ON
ON
INPUT
SP + 1/2 (db)
SP - 1/2 (db)
db
Output 1 (OP1) :
Output 2 (OP2) :
SP - 1/2 (db) + 1/2 HYS
SP - 1/2 (db) - 1/2 HYS
OFF
SP
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
HYS
OFF
HEAT/COOL DEADBAND VALUE (db) > 0
SP + 1/2 (db) - 1/2 HYS
SP + 1/2 (db) + 1/2 HYS
HYS
INPUT
SP + 1/2 (db)
SP - 1/2 (db)
PID CONTROL
In PID Control, the controller processes the input and then calculates a
control output power value by use of a modified Proportional Band, Integral
Time, and Derivative Time control algorithm. The system is controlled with the
new output power value to keep the process at the setpoint. The Control Action
for PID Control can be set to reverse for heating (output on when below the
setpoint) or direct for cooling (output on when above the setpoint) applications.
For heat and cool systems, the heat (OP1) and cool (OP2) outputs can be used
together in the PID Control. The PID parameters can be Auto-Tune or Manual
Tune to the process.
TYPICAL PID RESPONSE CURVE
SP
TIME
P & I
P & I & D
P only
P & D
INPUT
REMOTE SETPOINT
Channel B can operate as a Remote Setpoint Input to Channel A. Channel B
PID control is not functional when the input is assigned as a Remote Setpoint.
This mode of operation enables Cascade control (external), Ratio control, and
Temperature Setpoint Slave control, among others.
The Remote Setpoint value used internally by the controller is:
Remote Setpoint = (Scaled CHB Input * Remote Setpoint Ratio Multiplier)
+ Remote Setpoint Bias Offset
where Ratio Multiplier
= 0.0001 to 3.2000
Bias Offset
= -32000 to 32000
The Ratio Multiplier and Bias Offset parameters offer on-line scaling of the
Remote Setpoint to adjust control ratios or biases among related processes.
The Remote Setpoint is restricted to the setpoint low and high limit values for
channel B. These parameters may be used to limit the range of the Remote
Setpoint to a safe or more stable control range. For Remote Setpoint signal
sources that change wildly or are too sensitive to process upsets, the CHA
Setpoint Ramp Rate parameter (40110) can be used to ramp (rate limit) the
Remote Setpoint reading. This can subsequently reduce the fluctuations of the
secondary control loop.
Note: HYS in the On/Off Control Figures refers to the On/Off Control Hysteresis.
