Custom query examples, Background, Requirements – HP Matrix Operating Environment Software User Manual
Page 122: Background requirements, Example
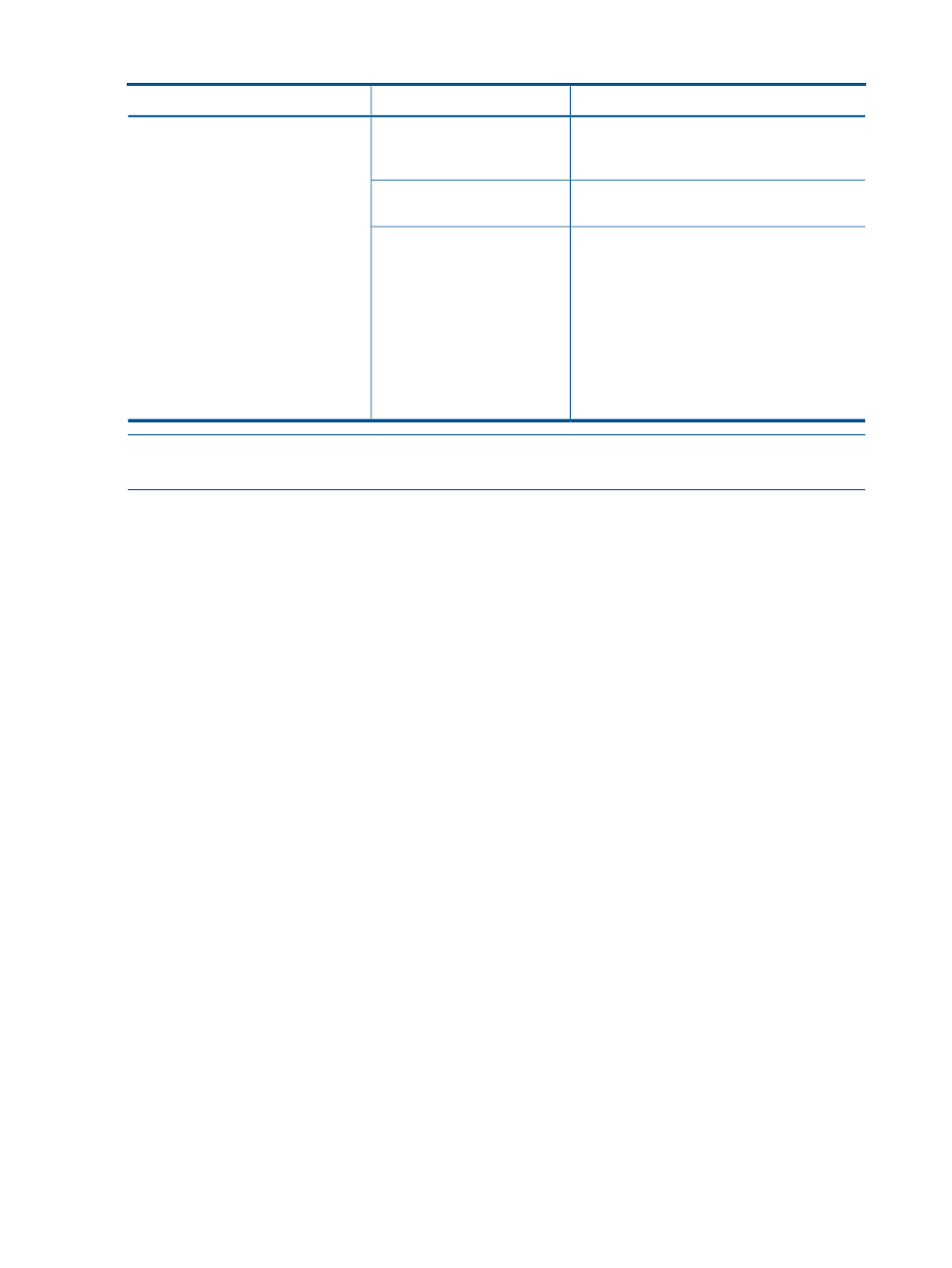
Table 20 Attributes available for use in analysis queries: Power Tab (continued)
Description
Attribute Name
Section
The system's estimated peak power
consumption when all resources are fully
consumed.
Max Power (W)
Power Capacity
The system's estimated power consumption
while idle.
Min Power (W)
This value indicates whether the system's
minimum and maximum power consumption
values are known. The minimum and maximum
power consumption values have been tested
via Integrated Lights-Out (iLO) or manually
entered for the system.
See
“Calibrating power on actual systems”
for information on setting the power
calibration on systems where this value is
false
.
Power Calibrated
NOTE:
Peak, 15-minute sustained, 90th percentile, and average values are available as separate
attributes. See
Custom query examples
Example: Finding large underused VMs that could be replaced with medium or small
VMs
Background
In this example, the data center has three sizes of Hyper-V virtual machines — small, medium, and
large. A medium VM has two vCPUs and 4 GB of RAM. A large VM has four vCPUs and 8 GB
of RAM. Most applications in the data center start to have performance issues if the CPU utilization
is greater than 80%, or if the memory use is within 1 GB of the capacity.
As administrator, you want to locate large, underused VMs that could be replaced by smaller VMs.
Requirements
To find the oversized VMs, you need to develop a query to find systems that:
•
Are Hyper-V VMs
•
Have four cores
•
Use less than 1.6 cores most of the time
•
Use less than 3 GB of RAM most of the time
Using the Capacity Analysis query language, this query can be expressed as follows:
Match ALL of:
Type = MICROSOFT HYPERV VMGUEST
Core count = 4
15-Min CPU (cores) <= 1.6
15-Min Memory (GB) <= 3
122
Using Capacity Analysis
