Disk tab – HP Matrix Operating Environment Software User Manual
Page 120
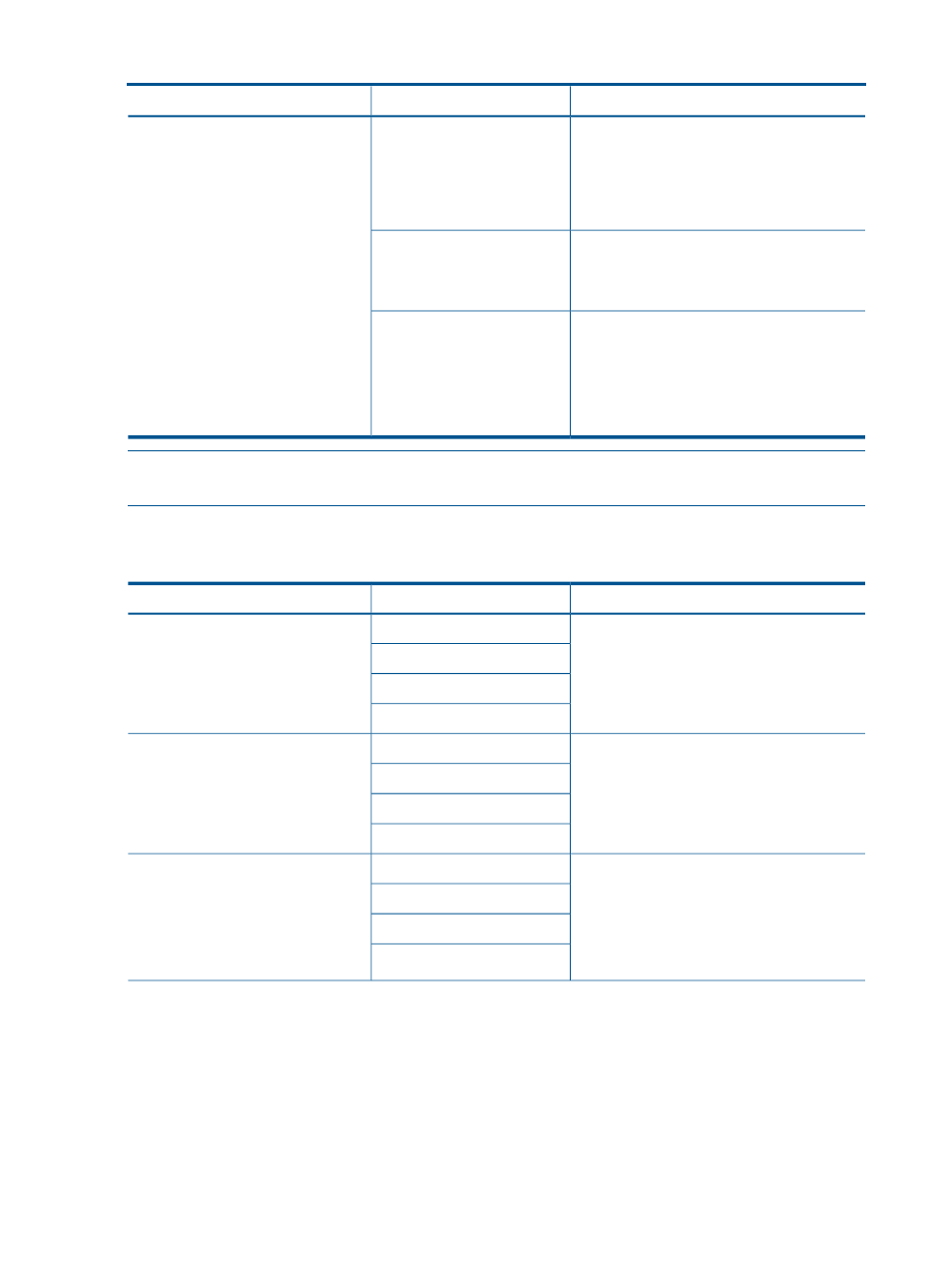
Table 18 Attributes available for use in analysis queries: Network Tab (continued)
Description
Attribute Name
Section
The system's network I/O capacity as defined
by the user. If a user value was not explicitly
entered for the system, then the maximum
observed capacity or 100 Mb/s, whichever is
higher, is used to estimate capacity. See Net
HWM (Mb/s) below.
Net I/O Cap (Mb/s)
Network Capacity
The observed high water mark for network
utilization. This is the peak network utilization
over the history of the server, not just the
selected interval.
Net HWM (Mb/s)
The headroom percentage indicates how much
the demand for the network I/O could grow
before violating the system's network I/O
utilization limits.
This metric is capped at 3100% to avoid
dividing by zero or other small numbers.
Network I/O Headroom
NOTE:
Peak, 15-minute sustained, 90th percentile, and average values are available as separate
attributes. See
Disk Tab
Table 19 Attributes available for use in analysis queries: Disk Tab
Description
Attribute Name
Section
Percentage of the available bandwidth being
utilized, measured in megabytes per second
(MB/s).
For more information see
Peak Disk I/O (%)
Disk I/O Utilization (%)
15–Min Disk I/O (%)
90%ile Disk I/O (%)
Avg Disk I/O (%)
Total data being transferred, measured in
MB/s.
For more information see
Peak Disk I/O (MB/s)
Disk I/O Utilization (MB/s)
15–Min Disk I/O (MB/s)
90%ile Disk I/O (MB/s)
Avg Disk I/O (MB/s)
The number of data disk transfers per second,
measured in Input/Output Operations per
Second (IOPS). Each disk block that is read or
written counts as an I/O operation.
This metric is only collected from physical Linux
and Windows systems.
Peak Disk I/O (IOPS)
Disk I/O Utilization (IOPS)
15–Min Disk I/O (IOPS)
90%ile Disk I/O (IOPS)
Avg Disk I/O (IOPS)
120 Using Capacity Analysis
