ZyXEL Communications NBG4115 User Manual
Page 225
Appendix C IP Addresses and Subnetting
User’s Guide
225
By convention, subnet masks always consist of a continuous sequence of ones
beginning from the leftmost bit of the mask, followed by a continuous sequence of
zeros, for a total number of 32 bits.
Subnet masks can be referred to by the size of the network number part (the bits
with a “1” value). For example, an “8-bit mask” means that the first 8 bits of the
mask are ones and the remaining 24 bits are zeroes.
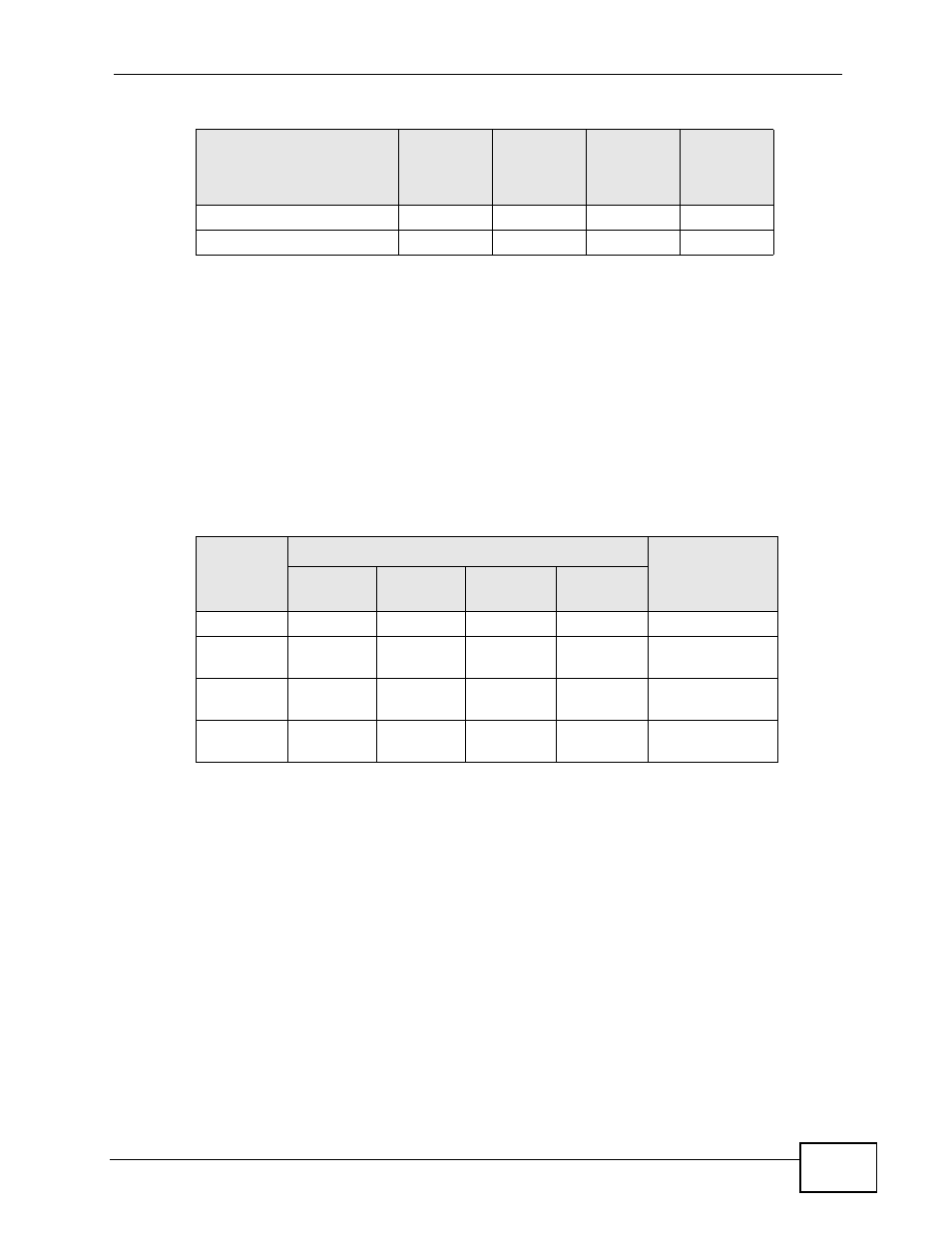
Subnet masks are expressed in dotted decimal notation just like IP addresses. The
following examples show the binary and decimal notation for 8-bit, 16-bit, 24-bit
and 29-bit subnet masks.
Network Size
The size of the network number determines the maximum number of possible
hosts you can have on your network. The larger the number of network number
bits, the smaller the number of remaining host ID bits.
An IP address with host IDs of all zeros is the IP address of the network
(192.168.1.0 with a 24-bit subnet mask, for example). An IP address with host
IDs of all ones is the broadcast address for that network (192.168.1.255 with a
24-bit subnet mask, for example).
Network Number
11000000 10101000 00000001
Host ID
00000010
Table 71 Subnet Masks
BINARY
DECIMAL
1ST
OCTET
2ND
OCTET
3RD
OCTET
4TH
OCTET
8-bit mask 11111111
00000000
00000000
00000000
255.0.0.0
16-bit
mask
11111111
11111111
00000000
00000000
255.255.0.0
24-bit
mask
11111111
11111111
11111111
00000000
255.255.255.0
29-bit
mask
11111111
11111111
11111111
11111000
255.255.255.24
8
Table 70 Subnet Mask - Identifying Network Number
1ST
OCTET:
(192)
2ND
OCTET:
(168)
3RD
OCTET:
(1)
4TH
OCTET
(2)
