Internal operation modes of the bridge ports, None – RAD Data comm 10/100BaseT to STM-1/OC-3 Converter RIC-155 User Manual
Page 78
Appendix B Traffic Separation
RIC-155 Installation and Operation Manual
B-4
Port-Based/VLAN-Based Traffic Separation
Internal Operation Modes of the Bridge Ports
All VLAN information is kept in the VTU (VLAN Translation Unit) table. The bridge
ports operate in the following internal modes:
• Secure – only frames with VIDs that are registered in the VTU table are
forwarded according to the VTU rules. The management and host ports
operate in the secure mode only.
• Fallback – untagged frames and tagged frames with VIDs that are not
registered in the VTU table are forwarded according to the port-based
procedures only.
The internal port operation modes depend on the port access mode and
forwarding mode of the bridge, as detailed in
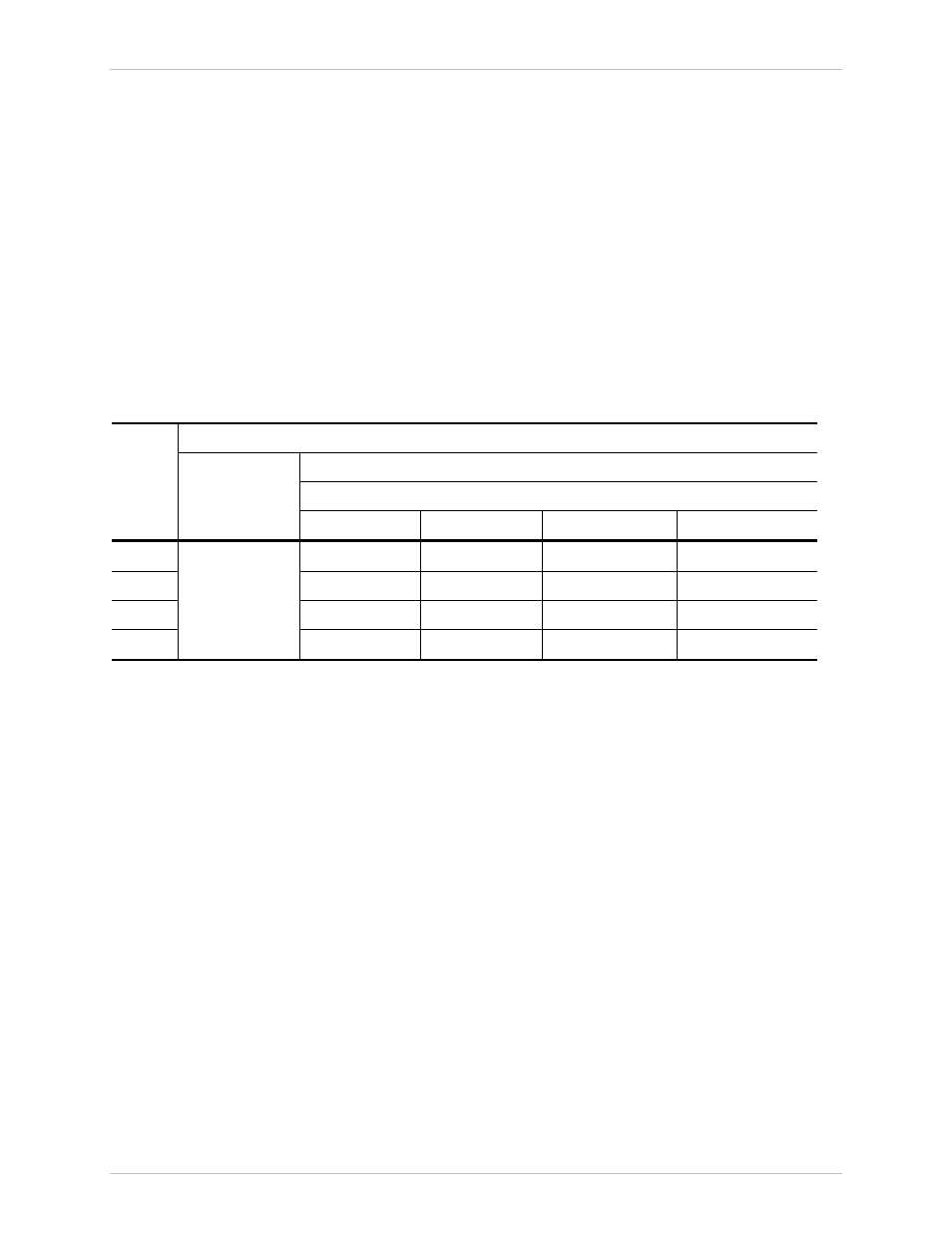
Table B-2. Internal Port Operation Modes
Forwarding Mode
Filter Tagged
Management Access Mode
Port
Filter
None MNG
Only
All Local
MNG
Only
MNG Disabled
Secure
Secure
Secure
Data
Fallback Fallback Fallback Fallback
Host
Secure Secure Secure Secure
Uplink
Disabled
Fallback Fallback Fallback Fallback
Traffic Separation according to the Management Access and VLANs
The following diagrams illustrate how RIC-155 separates between the management
and user traffic according to the port access mode and bridge port VLANs
(management port VID is set to 1, data port VID is set to 2). Numbers 1 and 2 inside
the bridge indicate the management and data frame routes inside the bridge.
None
When the port access mode is set to None, the management port is disabled.
Frames coming from the local data port can reach the local uplink port only, and
remote data frames can reach the local data port only. Remote management
frames are forwarded to the local host port only.
In the None access mode, the host port checks the source port of the incoming
frames and drops those that do not originate from the management port.
