Scsi bus differences – HP B180L User Manual
Page 187
173
SCSI Connections
SCSI Bus Differences
SCSI Bus Differences
A Small Computer Systems Interface (SCSI) bus is an IEEE standard bus for
connecting your workstation to internal and external SCSI devices running
at different speeds, singly or in combination. Examples of these SCSI
devices are 4-mm DDS-format tape drives, CD-ROM drives, and Winches-
ter hard disk drives.
There are three types of SCSI buses available with this workstation - a nar-
row single-ended SCSI (NSE SCSI) bus, and a fast, wide differential SCSI
(FWD SCSI) bus or an ultra, wide, single-ended SCSI bus. Table 17 shows
the specification differences between these SCSI buses, and Table 18 shows
the SCSI addresses, ID numbers, and arbitration priorities for each.
CAUTION:
Do not mix single-ended, fast, wide and ultra, wide-SE SCSI devices on any one bus
type. Doing this will cause a system failure.
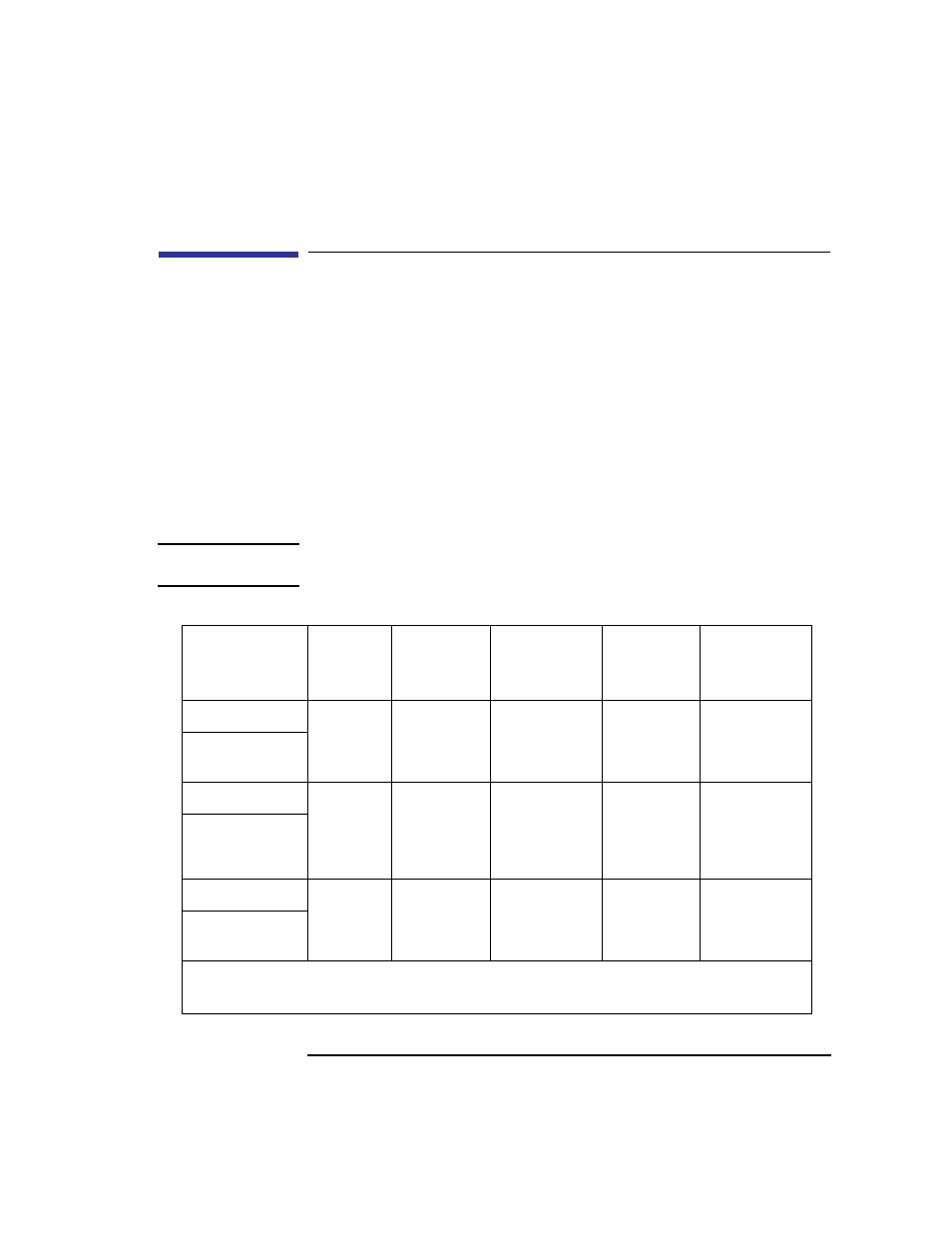
Table 17
SCSI Bus Differences
Transfer Rate
Data Bus
Width
Maximum
Addresses*
Maximum
Cable Length
Device
Physical
Location
Controller
Embedded
or Optional
Single-Ended
8 bits
8
6.0 meters
(19.6 feet)
Internal and
external
Embedded
Up to 5 Mbytes
per second
Fast, Wide
16 bits
16
25 meters
(82 feet)
Internal
and
external
Optional
Up to 20 Mbytes
per second
Ultra, Wide-SE
16 bits
16**
2.0 meters
(6.56 feet)
Internal
and
external
Embedded
Up to 40 Mbytes
per second
* Address 7 is reserved for host controller use on both buses.
** Only 2 external devices allowed (total of 4 devices).
