Configuring urpf, Urpf overview, What is urpf – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 34: How urpf works
26
Configuring URPF
URPF configuration is available only in the web interface.
URPF overview
What is URPF
Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding (URPF) protects a network against source address spoofing attacks.
Attackers launch such attacks by sending a large number of packets with forged source addresses. For
applications using IP-address-based authentication, this type of attacks allows unauthorized users to
access the system in the name of authorized users, or even access the system as the administrator. Even
if the attackers cannot receive any response packets, the attacks are still disruptive to the attacked target.
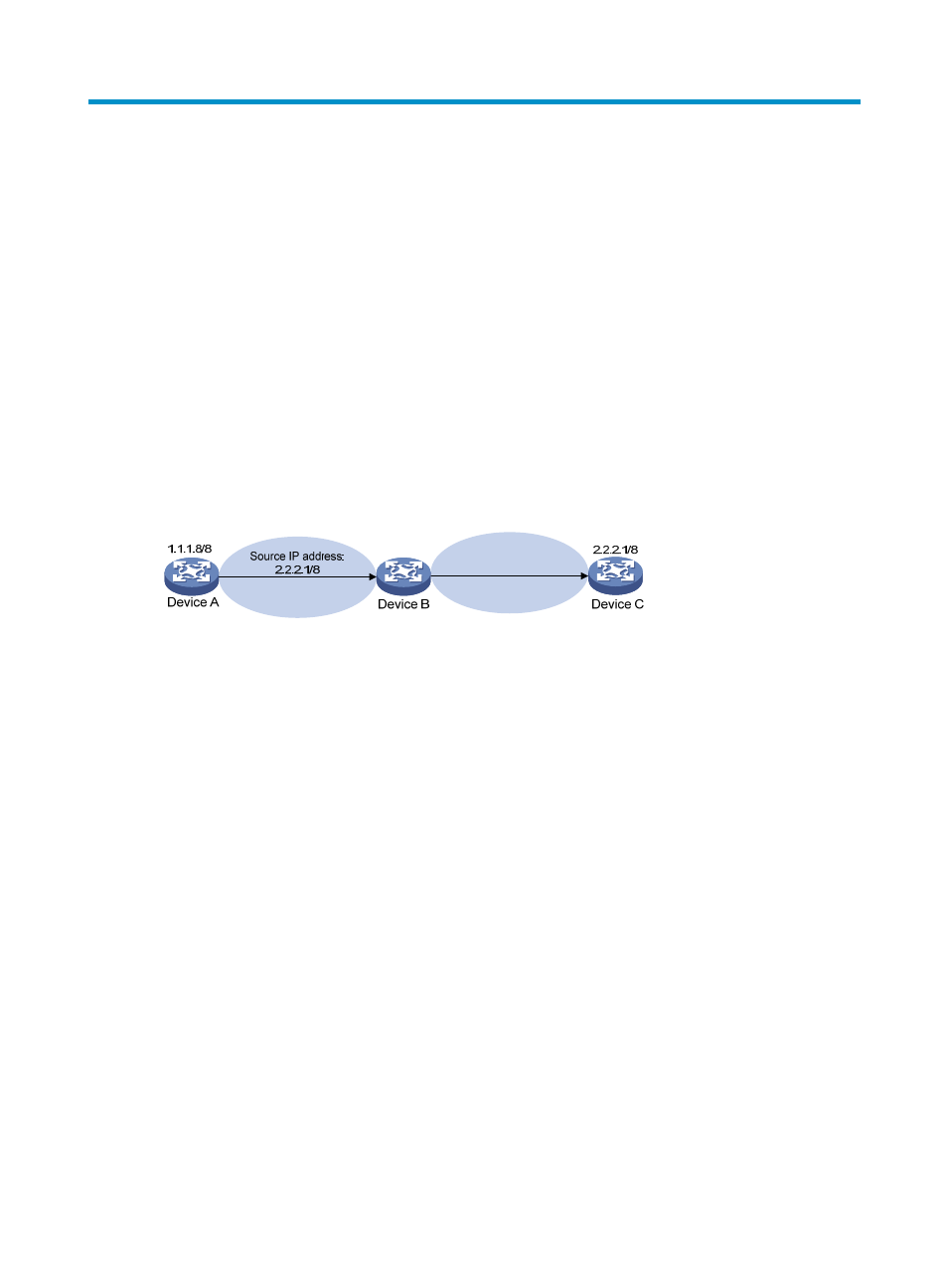
Figure 28 Source address spoofing attack
As shown in
, Device A sends a request with a forged source IP address of 2.2.2.1/8 to the
server (Device B), and Device B sends a packet to Device C at 2.2.2.1/8 in response to the request.
Consequently, this packet affects the communication between Device B and Device C.
URPF can prevent source address spoofing attacks.
How URPF works
URPF provides two check modes: strict and loose. In addition, it supports ACL check, link layer check,
and default route check.
URPF works as follows:
1.
First, URPF checks the source address validity, and then:
{
Discards packets with a broadcast source address.
{
Discards packets with an all-zero source address but a non-broadcast destination address. (A
packet with source address 0.0.0.0 and destination address 255.255.255.255 might be a
DHCP or BOOT packet, and thus is not discarded.)
2.
If the source address of an incoming packet is found in the FIB table:
{
In strict approach, URPF does a reverse route lookup for routes to the source address of the
packet. If at least one outgoing interface of such a route matches the receiving interface, the
packet passes the check. Otherwise, the packet is rejected.
{
In loose approach, the packet passes the check.
3.
If the source address is not found in the FIB table, URPF makes a decision based on the default
route and the allow-default-route option.
- H3C SecPath F5000-A5 Firewall H3C SecPath F1000-A-EI H3C SecPath F1000-E-SI H3C SecPath F1000-S-AI H3C SecPath F5000-S Firewall H3C SecPath F5000-C Firewall H3C SecPath F100-C-SI H3C SecPath F1000-C-SI H3C SecPath F100-A-SI H3C SecBlade FW Cards H3C SecBlade FW Enhanced Cards H3C SecPath U200-A U200-M U200-S H3C SecPath U200-CA U200-CM U200-CS
