Scotsman Prodigy Plus D Series Service Manual User Manual
Page 29
N0422, F0522, N0622, F0822, N0922, F1222, N1322, F1522
Air, Water or Remote Service Manual
December 2014
Page 29
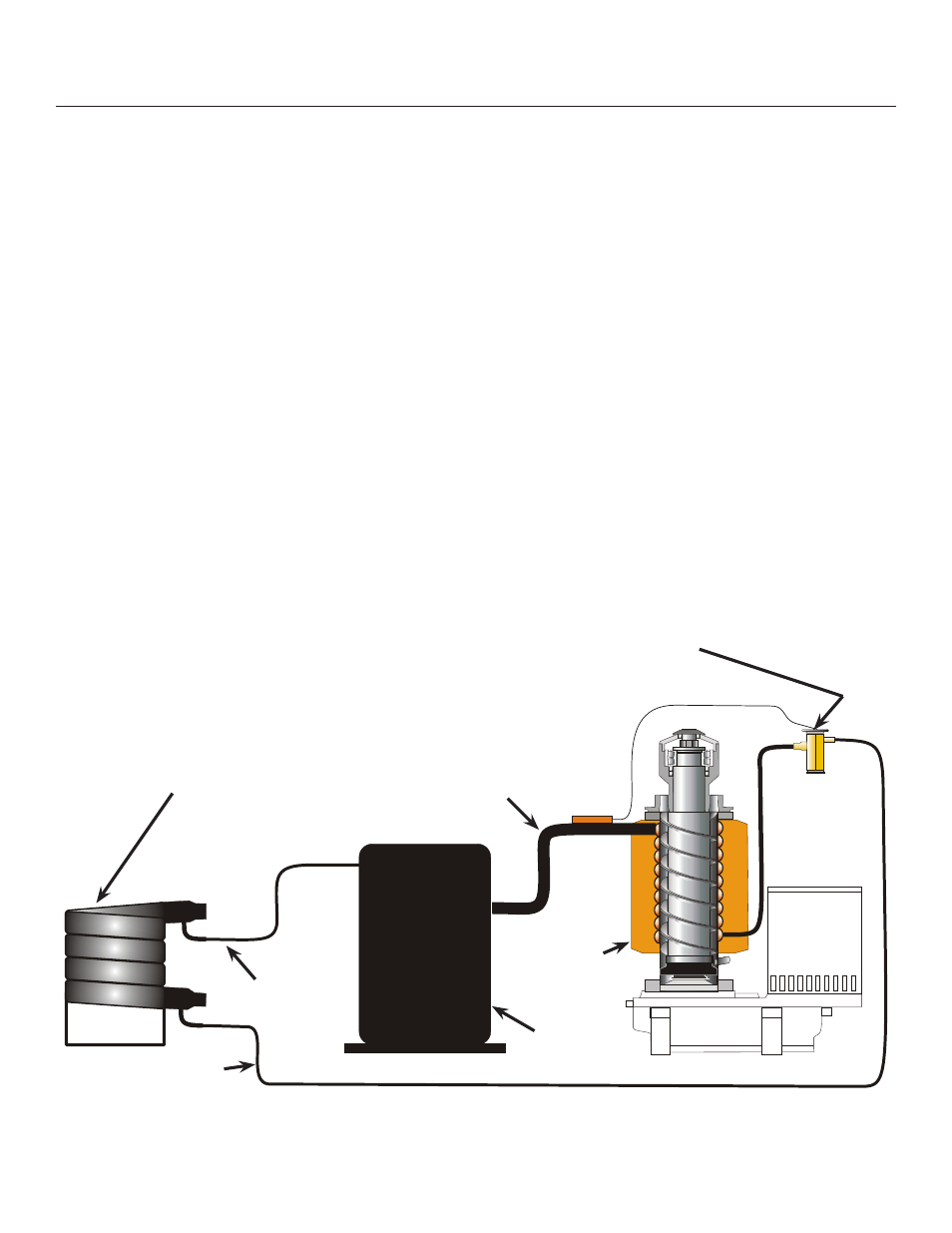
Water Cooled Refrigeration
The compressor concentrates the heat from ice
making into high pressure, hot discharge gas. The
high pressure forces the gas to the water cooled
condenser.
At the condenser, refrigerant gas and water flow
through connected parallel tubes, but in opposite
directions. Heat moves from the hotter discharge gas
to the cooler water, and the refrigerant condenses into
a liquid. The water flows out of the condenser warmed
up to about 110
o
F. Water flow is controlled by a water
regulating valve on the inlet of the condenser's water
circuit.
From the condenser the high pressure liquid
refrigerant flows through the liquid line to the metering
device - a thermostatic expansion valve.
At the expansion valve, liquid refrigerant passes from
a high pressure zone to one of relatively low pressure,
and in the low pressure zone it evaporates.
The low pressure zone where the refrigerant
evaporates is the evaporator. The evaporator is a
vertical metal tube surrounded by a coil of tubing,
where the refrigerant flows through. When the
refrigerant evaporates in the coil, it absorbs heat from
the metal parts of the evaporator and the water inside
it. As the auger inside the evaporator turns, ice is
continuously forced out of the evaporator and make
up water flows in.
From the evaporator, the refrigerant, carrying the
heat from ice making, flows back to the compressor
through the suction line, and the cycle continues.
Refrigeration Schematic
Evaporator
Compressor
TXV
Discharge Line
Suction Line
Liquid Line
Water Cooled
Condenser
