D-Link DES-3225G User Manual
Page 34
24-port NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
24
Switch Management Concepts
♦
Tagging
The act of putting 802.1Q VLAN information into the header of a packet. Tagging ports will put the VID
number, priority, and other VLAN information into all packets that flow out it. If a packet has previously been tagged,
the port will not alter the packet, thus keeping the VLAN information intact. Tagging is used to send packets from one
802.1Q-compliant device to another.
♦
Untagging
The act of stripping 802.1Q VLAN information out of the packet header. Untagging ports will take all
VLAN information out of all packets that flow out of a port. If the packet doesn’t have a VLAN tag, the port will not
alter the packet, thus keeping the packet free of VLAN information. Untagging is used to send packets from an 802.1Q-
compliant switch to a non-compliant device.
♦
Ingress port
A port on a switch where packets are flowing into the switch. If an ingress port has the Ingress Filter
enabled, the switch will examine each packet to determine whether or not it is a VLAN member and then take one of
two actions: if the port is not a member of a VLAN, the packet will be dropped; if the port is a member of a VLAN, then
the packet will be forwarded. Otherwise, if the Ingress Filter is disabled, then the switch will process any packet
received at this port in its normal fashion.
♦
Egress port
A port on a switch where packets are flowing out of the switch, either to another switch or to an end
station, and tagging decisions must be made. If an egress port is connected to an 802.1Q-compliant device, tagging
should be enabled so the other device can take VLAN data into account when making forwarding decisions (this allows
VLANs to span multiple switches). If an egress connection is to a non-compliant switch or end-station, tags should be
stripped so the (now normal Ethernet) packet can be read by the receiving device.
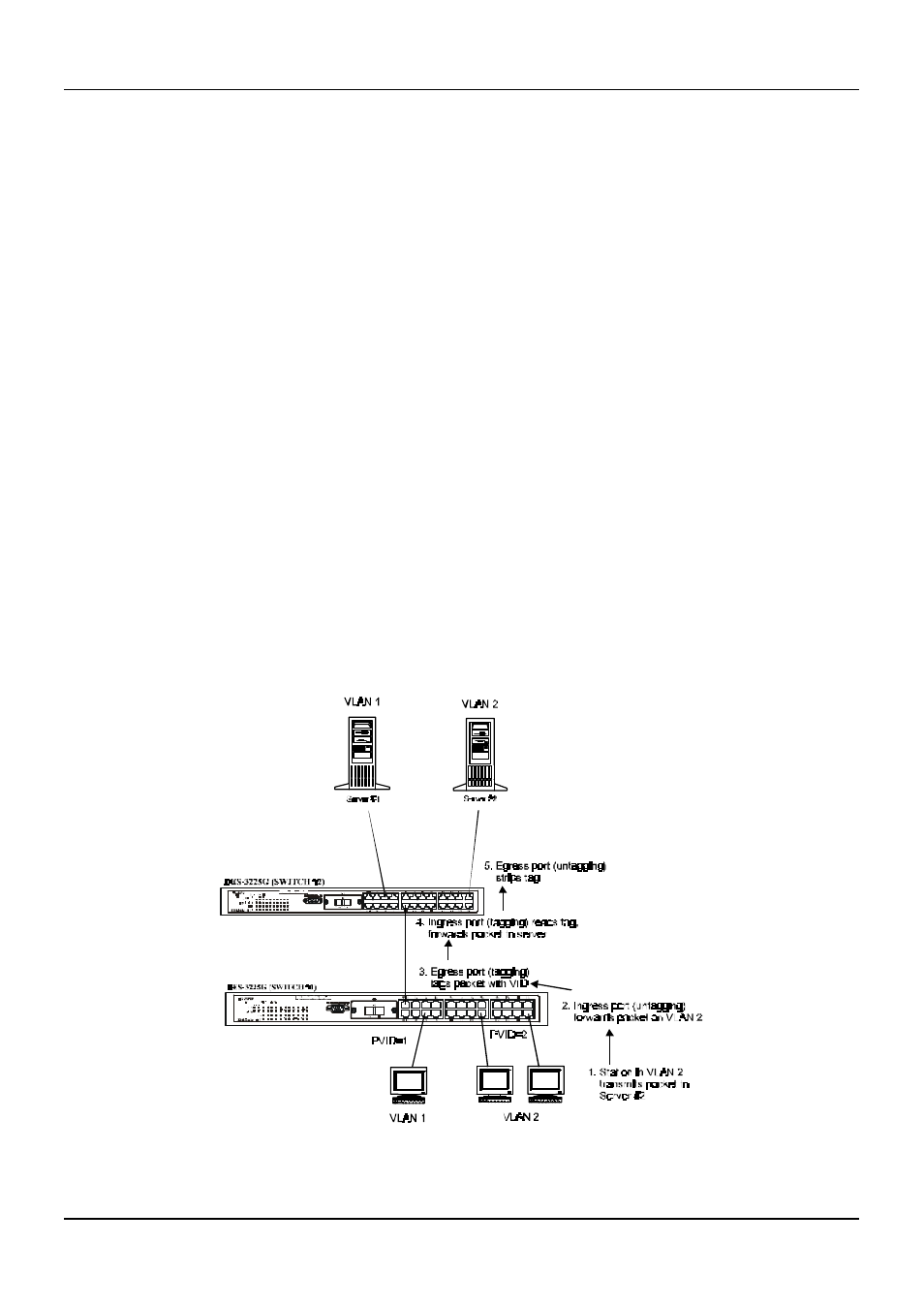
VLANs Over 802.1Q-compliant Switches
When switches maintaining the same VLANs are 802.1Q-compliant, it is possible to use tagging. Tagging puts 802.1Q
VLAN information into each packet header, enabling other 802.1Q-compliant switches that receive the packet to know how
to treat it. Upon receiving a tagged packet, an 802.1Q-compliant switch can use the information in the packet header to
maintain the integrity of VLANs, carry out priority forwarding, etc.
Data transmissions between 802.1Q-compliant switches take place as shown below.
Figure 5-5. Data transmissions between 802.1Q-compliant Switches
