Casio SERIES FX-9860G User Manual
Page 160
20070201
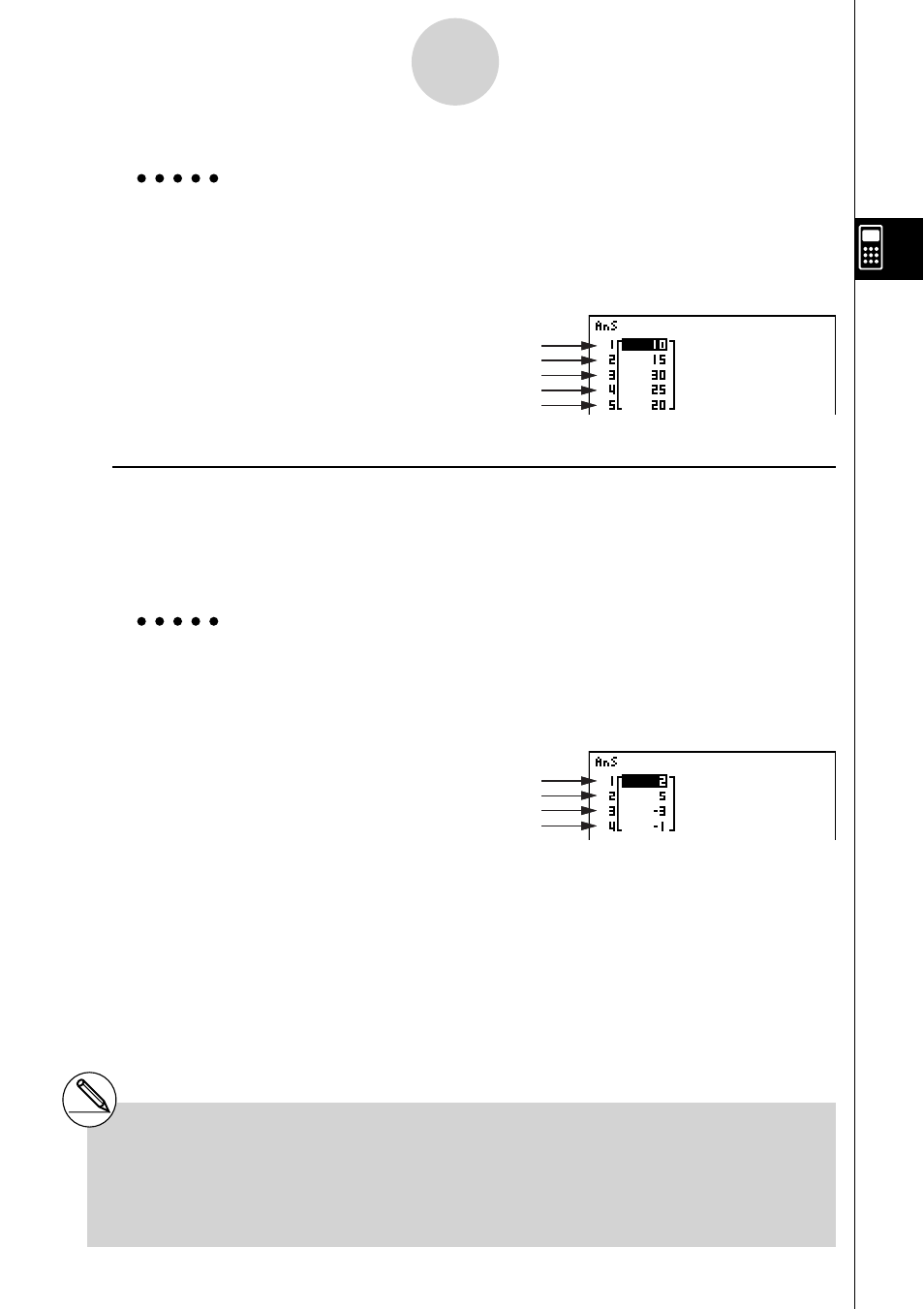
Example
To calculate the percentage represented by each data item in List 1
(2, 3, 6, 5, 4)
AK1(LIST)6(g)6(g)4(%)
6(g)1(List)bw
u To calculate the differences between neighboring data inside a list
[OPTN]-[LIST]-[
A
]
K1(LIST)6(g)6(g)5(A)w
• The result of this operation is stored in ListAns memory.
Example
To calculate the difference between the data items in List 1
(1, 3, 8, 5, 4)
AK1(LIST)6(g)6(g)5(A)
bw
Ч 100 =
2/(2+3+6+5+4)
3/(2+3+6+5+4)
Ч 100 =
6/(2+3+6+5+4)
Ч 100 =
5/(2+3+6+5+4)
Ч 100 =
4/(2+3+6+5+4)
Ч 100 =
Ч 100 =
2/(2+3+6+5+4)
3/(2+3+6+5+4)
Ч 100 =
6/(2+3+6+5+4)
Ч 100 =
5/(2+3+6+5+4)
Ч 100 =
4/(2+3+6+5+4)
Ч 100 =
3 – 1 =
8 – 3 =
5 – 8 =
4 – 5 =
3 – 1 =
8 – 3 =
5 – 8 =
4 – 5 =
3-2-8
Manipulating List Data
# You can specify the storage location in list
memory for a calculation result produced by a
list calculation whose result is stored in ListAns
memory. For example, specifying “
AList 1 → List
2” will store the result of
AList 1 in List 2.
# The number of cells in the new
AList is one
less than the number of cells in the original list.
# An error occurs if you execute
AList for a list
that has no data or only one data item.
