Rockwell Automation Low-Voltage Switchgear and Controlgear User Manual
Page 49
tures. The rated loading values refer from a thermal view point to continuous duty at a certain
ambient temperature (see Section
). IEC 60034-1 defines the continuous duty of motors at
the rated operational current until the steady-state temperature is reached as the rated service
type S1.
In practice in addition to the continuous duty there is a large number of loading situations with
changing loads. In intermittent operation, load-phases and de-energized breaks alternate in
regular sequences. The load periods and intervals are so short that the components of the
switchgear (and of the load) do not reach their thermal equilibrium neither during the warming
nor the cooling phases. For motors the three rated service types S3, S4 and S5 are defined for
intermittent operation in IEC 60034-1 (S3…constant load; S4…with additional starting load;
S5…with additional starting and braking load).
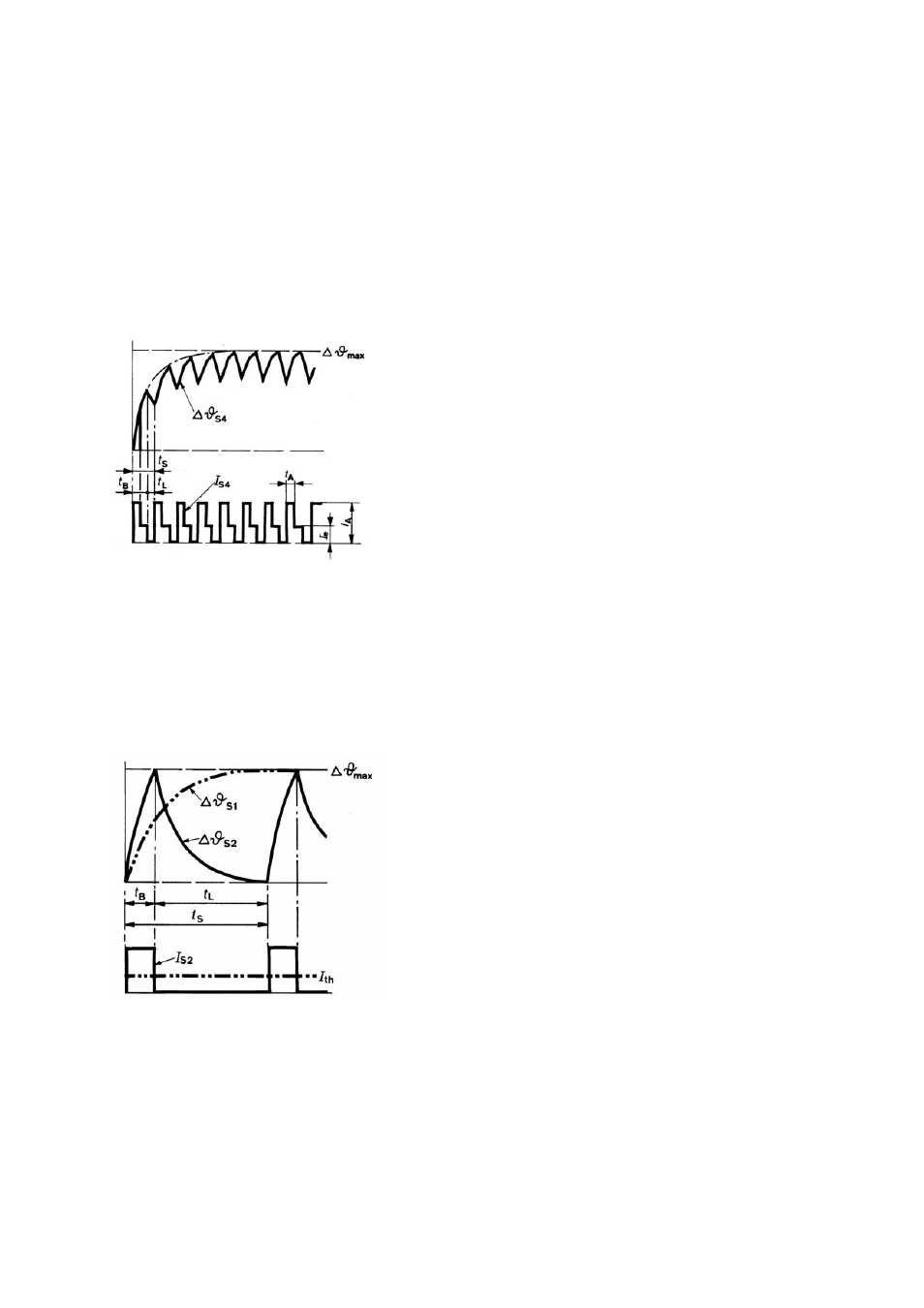
Fig. 2.3-10
Current loading and temperature rise during intermittent duty
I
S4
Current loading during intermittent duty S4
Δ
δ
S4
Heating and cooling during intermittent duty S4
For meaning of other symbols see
In short-time duty the current flows for a limited time so that steady-state temperature is not
reached. The de-energized interval after the load-period is however so long that the devices can
nearly cool down to the ambient temperature. In IEC 60034-1 the short-time duty for motors is
named rated service type S2.
Fig. 2.3-11
Current loading and temperature rise in short-time duty S2
t
B
Load
duration
t
B
L
De-energized
interval
t
S
Duration of a switching cycle
I
th
Thermal continuous current
I
S2
Current loading with short-time duty
Δδ
max
Maximum permissible temperature rise
Δδ
S1
Temperature rise with thermal continuous current
Δδ
S2
Heating and cooling with short-time duty
Comment: In short-time duty a higher temperature than in continuous duty is permitted!
LVSAM-WP001A-EN-P - April 2009
2-21
