4 protective functions, Protective functions -8, Fig. 4.1-7 – Rockwell Automation Low-Voltage Switchgear and Controlgear User Manual
Page 116
motors for example, the measurement from the rotor to the stator is very costly. Line conductor
protection via temperature measurement is hardly practical for various reasons.
0
50
100
150
200
250
0
5
10
15
t [s]
Δδ [K]
Δδ
W-S
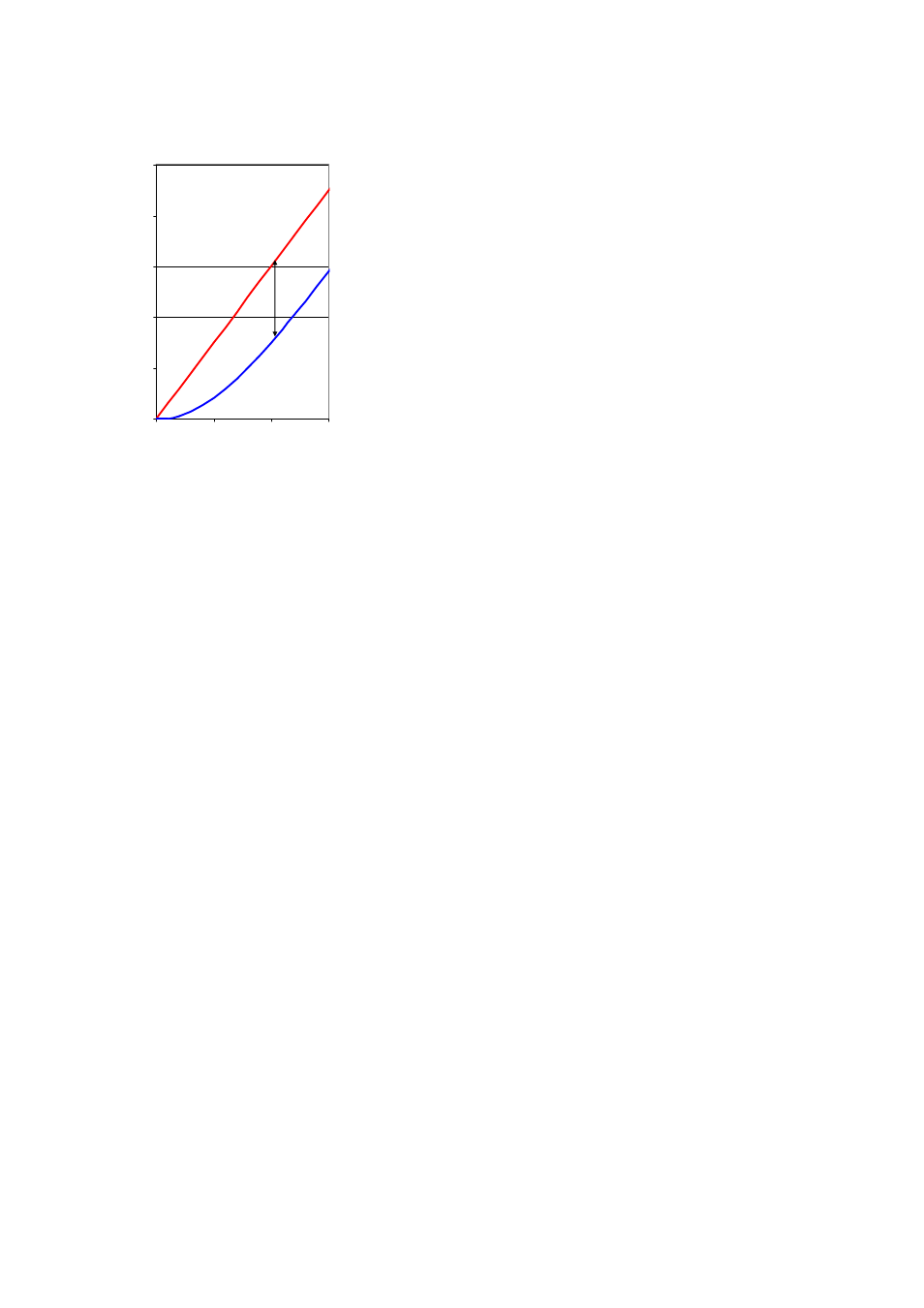
Fig. 4.1-7
Thermal delay of a PTC sensor integrated in the stator coil with rapid temperature rises (for example with
a locked rotor)
Δδ
=
Temperature difference above the coolant temperature of 40 °C
Δδ
W-S
=
Temperature difference winding – sensor
t
=
Time in s
The measurement of the load current by the protective device has proven reliable and economic
in the majority of normal applications, even if the full exploitation of the actual load capacity of
the electrical equipment is often not possible. Current measurement offers specifically for the
protection of motors the option for functions that cannot be measured via the temperature as the
current contains important information about the operating status of the motor and its exposition
to potential damage. Temperature measurement by means of sensors integrated in the
windings is usually used as a complementary method.
4.1.2.4 Protective
functions
Due to their differing modes of operation, various types of protective devices offer a variety of
functions and properties.
provides a summary of the most important protective
functions and their availability by technology, specifically considering motor protection.
LVSAM-WP001A-EN-P - April 2009
4-8
