2 voltage ramp, 3 kickstart, Voltage ramp -24 – Rockwell Automation Low-Voltage Switchgear and Controlgear User Manual
Page 100: Kickstart -24, Produced, Fig. 3.9-1
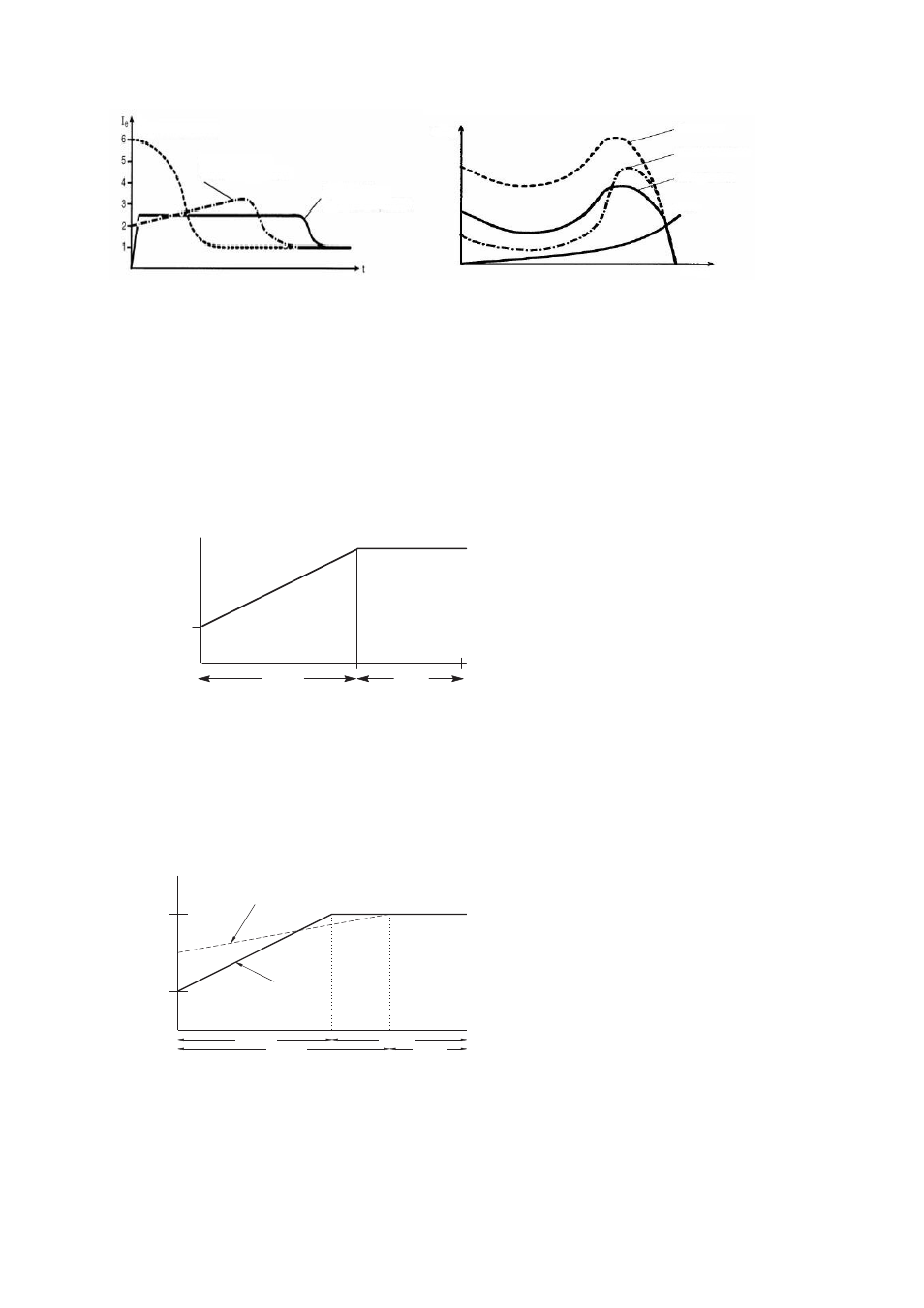
Direct start
Current at direct
start
T/T
e
Current limit
Current at soft start
with voltage ramp
Current at soft start
with current limit
Voltage ramp
Load
n/n
s
Fig. 3.9-1
Current and torque characteristics for starting
In the following a more detailed discussion of the characteristics of various available soft starter
functions is presented.
3.9.2 Voltage
ramp
The voltage across the motor is linearly increased during a settable time, starting from an
adjustable initial value (
). The starting current and the starting torque, and hence the
acceleration, adjust themselves in accordance with the voltage ramp and the torque characteris-
tic of the load. This method is especially suitable for load-free start-ups and for working ma-
chines with increasing torque requirement at increasing speed (drives with larger inertial
masses, fans etc.).
100%
Percent
Voltage
Initial
Torque
Start
Run
Time (seconds)
Fig. 3.9-2
Soft start with voltage ramp
For drives with variable loading at the start – for example processing machines that normally
start up in a load-free condition, but which can be under load due to a fault – soft starters with
two voltage ramps are available (
). The initial voltages and starting times of ramps are
separately adjustable and hence can be adapted to both operating states. It is possible to
switch between both ramps as required.
Ramp #2
Ramp #1
Start #1
Start #2
Run #1
Run #2
Time (seconds)
Percent
Voltage
100%
Initial Torque
#2
Initial Torque
#1
Fig. 3.9-3
Soft starter with changeable voltage ramp for various loading states at start.
3.9.3 Kickstart
Many drives have a high breakaway torque at rest, because for example bearings surfaces may
generate high initial friction. This requires a short period of increased starting voltage at the
LVSAM-WP001A-EN-P - April 2009
3-24
