2 effects of and dangers in case of short-circuits, Ak short-circuit current) is produced, Fig. 4.1-17 – Rockwell Automation Low-Voltage Switchgear and Controlgear User Manual
Page 125
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
kA
1
2
u
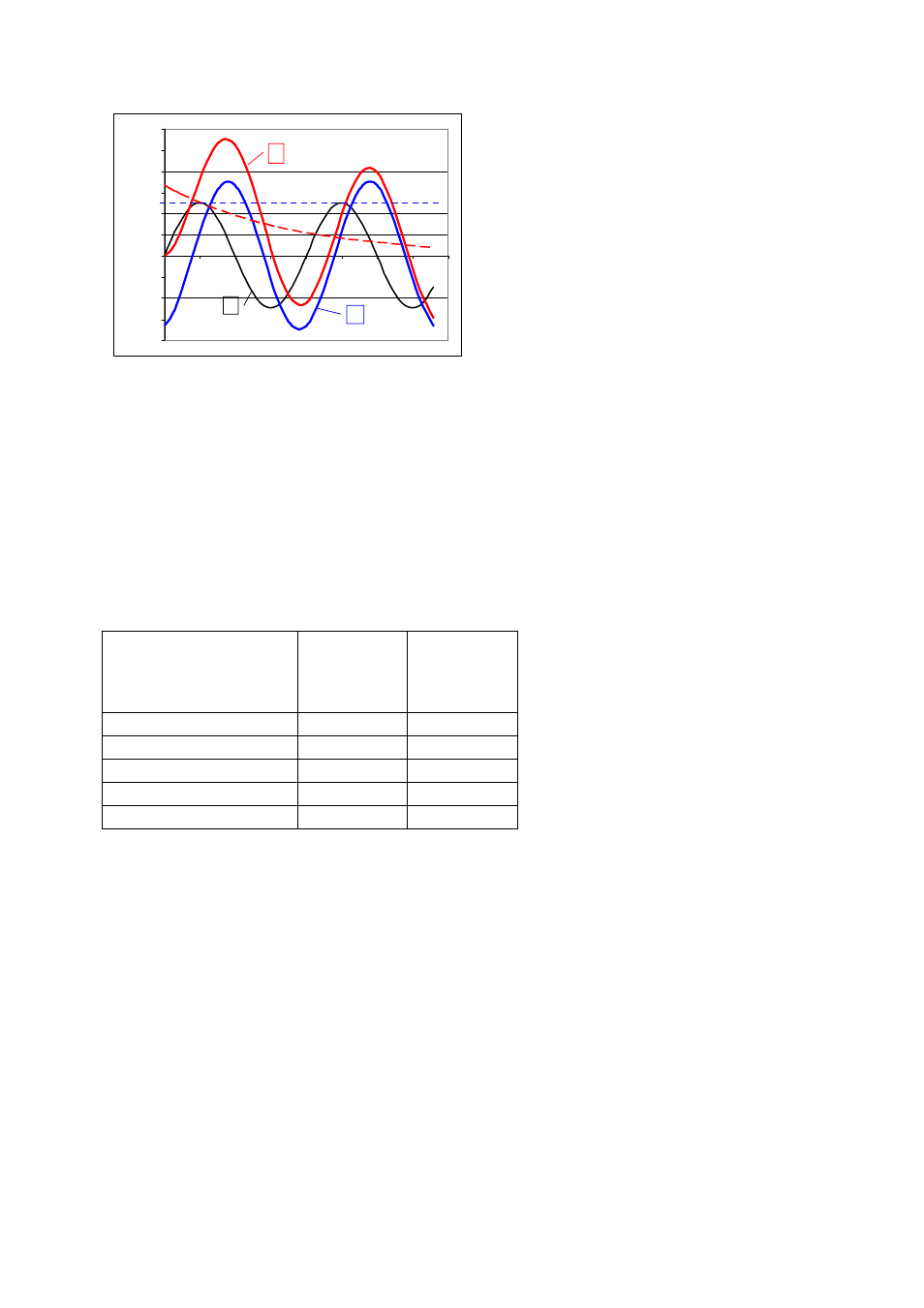
Fig. 4.1-17
Depending on the time of occurrence of a short-circuit and because of the high inductance of the short-
circuit loop, an overshoot and a high initial current peak are produced.
1
Symmetrical short-circuit current (as an example 50 kA
eff
)
2
Characteristic of the current when switching on at voltage – zero crossover
(most adverse point in time)
u Driving
voltage
This overshoot is taken into account in the regulations by the factor n that should be taken into
account when designing switchgear assemblies with respect to the short-circuit withstand
capacity of the installation and of short-circuit switchgear with respect to its making capacity.
The factor n is depending on the power of the power supply system and therefore on the
prospective short-circuit current (
r.m.s. value of the
prospective
short-circuit current
[kA]
Power
factor
cos
φ
Factor n
I
≥ 5
0.7
1.5
5 < I
≥ 10
0.5
1.7
10 < I
≥ 20
0.3
2.0
20 < I
≥ 50
0.25
2.1
50 < I 0.2
2.2
Tab. 4.1-6
Standard values for the factor n in accordance with IEC 60439-1 for determining the electrodynamic
short-circuit withstand capacity of switchgear assemblies. The r.m.s. value of the prospective short-circuit
current should be multiplied by the factor n in order to determine the peak value of the prospective short-
circuit current.
4.1.3.2
Effects of and dangers in case of short-circuits
The high currents during short-circuits stress the components in the shorted circuit by high
dynamic forces and strong heat generation in the current-carrying parts.
The forces developed are proportional to the square of the current flowing. Therefore the peak
value of the short-circuit current is highly significant. The heat generation, too, is proportional to
the square of the current.
Usually an electric arc is developing at the location of the short-circuit that can result in serious
injuries to persons through burns, blinding or electric shock as well as it can lead to the damage
or destruction of installation components.
LVSAM-WP001A-EN-P - April 2009
4-17
