One power supply (middle-connected), Example using thick cable, X (0.005))] x i – Rockwell Automation DeviceNet Media Design Installation Guide User Manual
Page 101
Publication DNET-UM072C-EN-P - July 2004
Determine Power Requirements 4-23
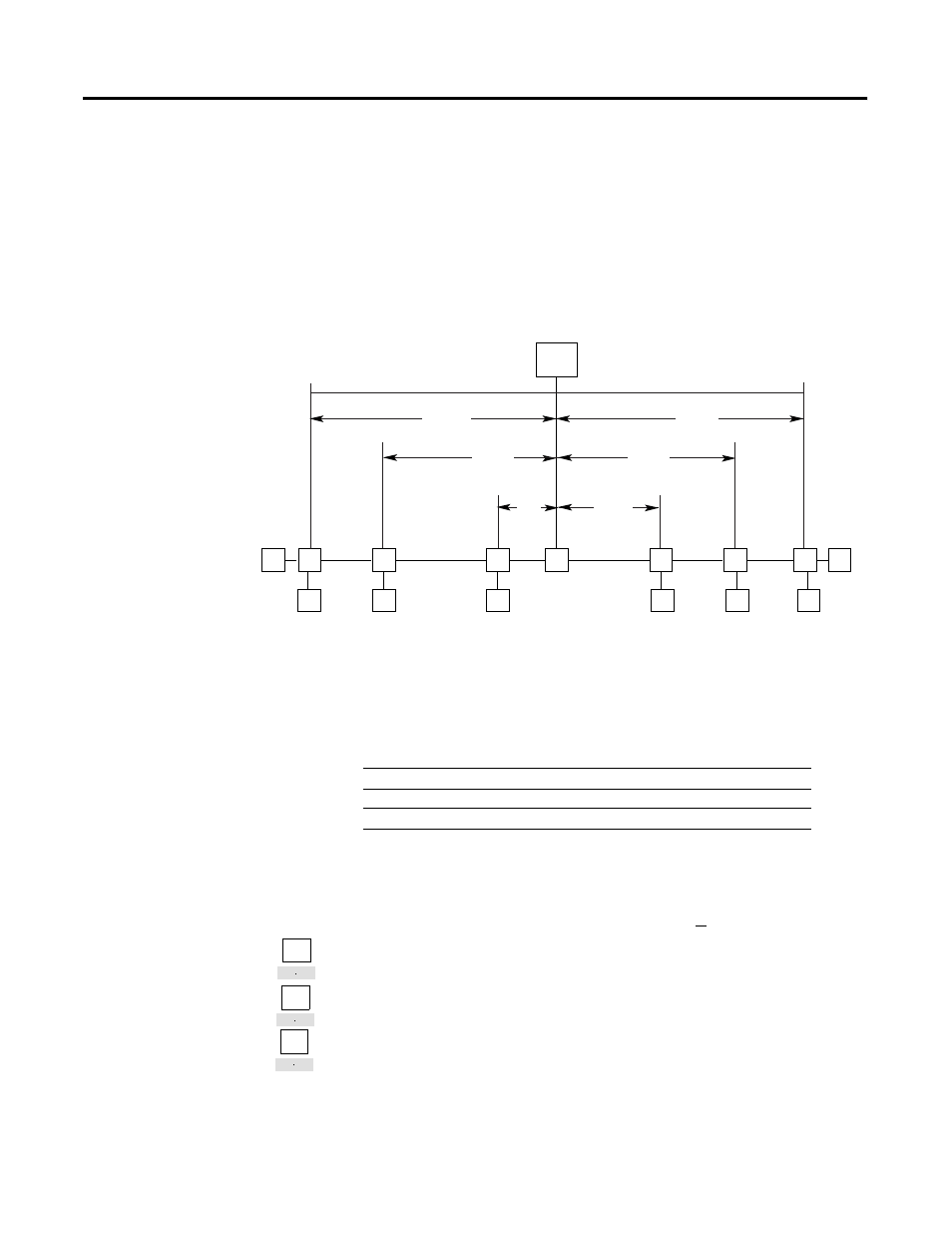
One power supply (middle-connected)
Example using thick cable
This example is used to check loading on both sides of a middle-connected
supply on a thick cable trunk line. Keep the loads, especially the higher ones,
close to the power supply. If the device location is fixed, put the power supply
in the center of the highest current concentration.
According to the look-up method, section 1 is operational while section 2 is
overloaded.
1. Find the voltages for each device in section 1 using the equation for
thick cable.
SUM {[(L
n
x (0.0045)) + (N
t
x (0.005))] x I
n
} < 4.65V.
A.[(100 x (0.0045)) + (1 x (0.005))] x 0.25 = 0.12V
B.[(400 x (0.0045)) + (2 x (0.005))] x 0.25 = 0.45V
C.[(800 x (0.0045)) + (3 x (0.005))] x 0.25 = 0.90V
2. Add each device’s voltage together to find the total voltage for section 1.
0.12V + 0.45V + 0.90V = 1.47V
power
supply
D3
PT
T
TR
TR
T
T
T
T
T
section 1
244 m
(800 ft)
122 m
(400 ft)
section 2
D2
D1
D4
D5
D6
30 m
(100 ft)
60 m
(200 ft)
122 m
(400 ft)
244 m
(800 ft)
0.25A
0.25A
0.25A
0.25A
1.5A
0.5A
TR = terminating resistor T = T-Port tap
PT = Power Tap D = device
31515-M
Value of
Section 1
Section 2
Total maximum current
1.25A (approximately)
1.25A (approximately)
Total current required
0.75A
2.25A
D1
0.25A
D2
0.25A
D3
0.25A
