Rockwell Automation 1747-ASB Remote I/O Adapter User Manual
Page 52
Publication 1747-UM006B-EN-P - June 2003
3-16 Addressing
When discrete mode is selected, specialty I/O modules are discretely
mapped or block transfer mapped, depending on:
•
the specialty I/O module's image size
•
the addressing mode selected (2-slot, 1-slot, or 1/2-slot)
When discrete mode is selected, a specialty I/O module is discretely
mapped if its image fits into the image space assigned to its slot pair.
For example, if the specialty I/O module such as the 1746-NIO4I and
-NIO4V requires two words of input and output image, and the
1747-ASB module is configured for 1-slot addressing, the specialty I/O
module is discretely mapped . However, if four words of input or
output image are required, the specialty I/O module such as the
1746-NI4, -NO4V, -NO4I, and -HS, are block transfer mapped.
Due to the module's image size, some specialty I/O modules are
always block transfer mapped.
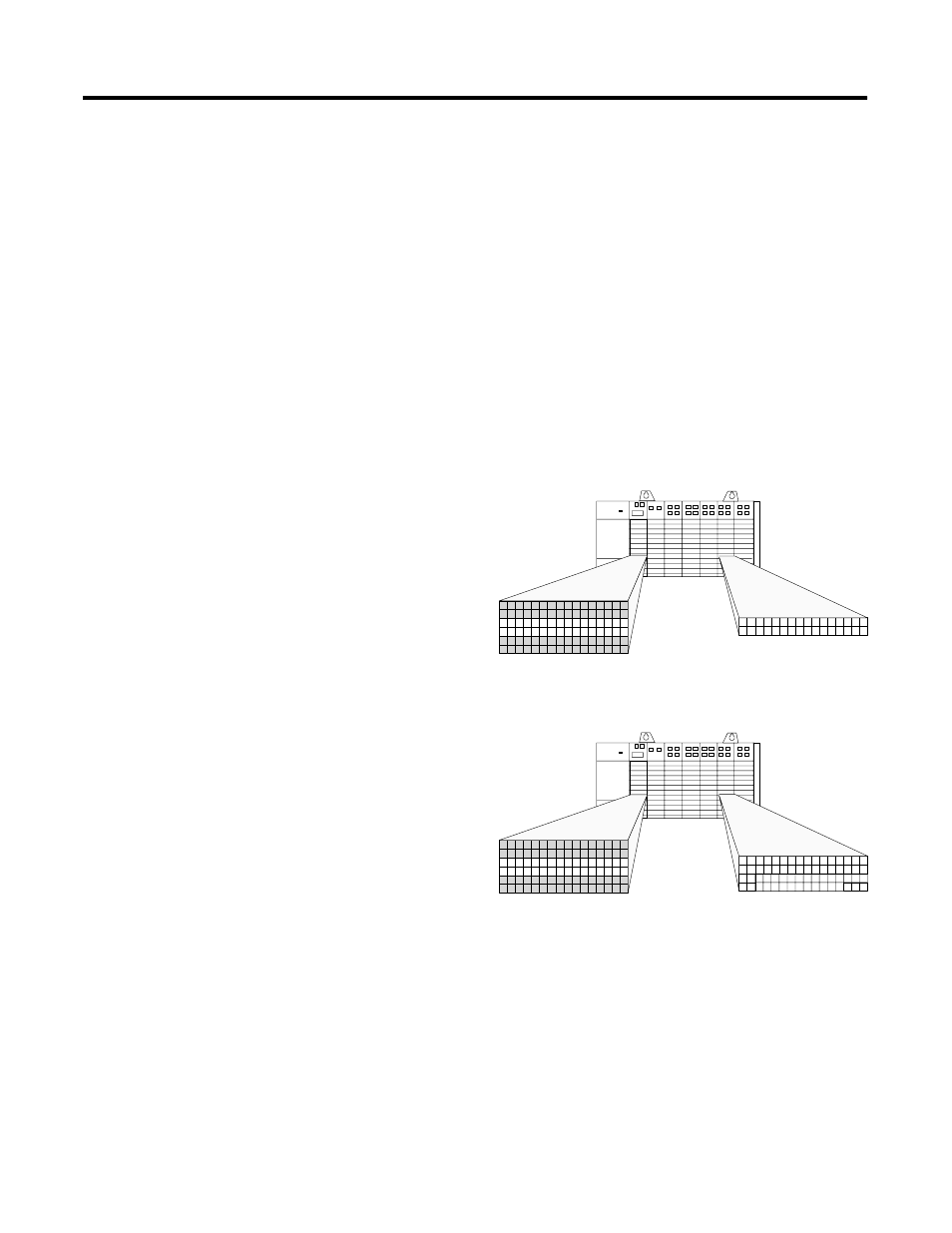
Two words required
by specialty I/O module.
Two words provided by
1747-ASB module.
Two words of input and output image
are required by the specialty I/O
module. The 1747-ASB module is
configured for 1-slot addressing, which
provides two words of input and output
image per slot pair. Because the
specialty I/O module’s image can be
mapped into the provided image, the
specialty I/O module is discretely
mapped. The other slot of the pair is
empty since all of the input and output
image is used.
RIO Discrete Mapping
Two words provided by
1747-ASB module.
Four words required
by specialty I/O module.
Four words of input and output image
are required by the specialty I/O module.
The 1747-ASB module is configured for
1-slot addressing, which provides two
words of input and output image per slot
pair. Because the specialty I/O module’s
image cannot be mapped into the
provided image, the specialty I/O module
is block transfer mapped.
RIO Block Transfer Mapping
