Festo Контроллер двигателя SFC-ST User Manual
Page 110
A. Technical appendix
A−26
Festo P.BE−SFC−DC−PB−S7−E N en 0604NH
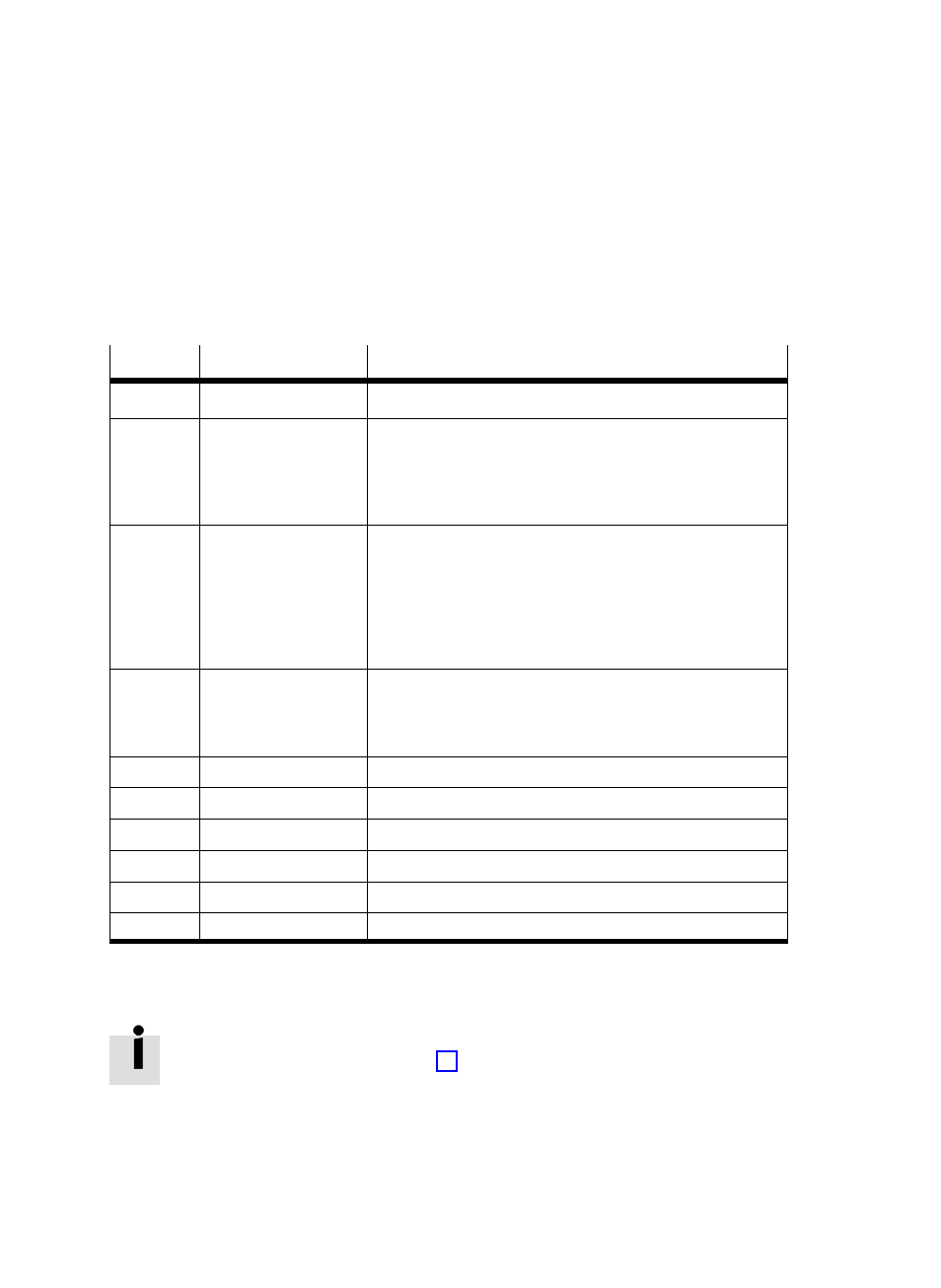
The faults are divided into logical groups according to the
fault numbers. There are both simple and serious faults
within a group.
Range
Name
Comment
0
ć
No fault active
1 ... 19
Processing fault
Examples: No reference travel, nominal position outside softĆ
ware end positions, nominal value calculation not possible.
Although the system is OK, a user comand cannot be procesĆ
sed. In most cases there is a fault in operation.
Source: Sequence control, regulator
20 ... 29
Parameter fault
Example: Software end positions outside the working stroke.
A parameter lies within the limit values so that it can be
written by the user. During the new calculation of the regulaĆ
tor, it was ascertained that it is not permitted in the context
of the other parameters.
Note: Non−permitted parameters are rejected by the paraĆ
meter protocol and do not generate a fault in the controller.
30 ... 49
Regulator
Examples: Positioning timeout, reference travel not succesĆ
ful, contouring error too large, ...
The task could not be processed correctly. No hardware fault
is recognized here. Source: Regulator
50 ... 69
Initialization
Fault in initializing the controller
70 ... 79
Run time of controller
Fault in controller run time: Undervoltage, checksum
80 ... 89
ć
Reserved
90 ... 99
ć
Reserved
100 ... 109
Run time of motor
Run time of motor: Undervoltage, overtemperature, ...
110 ... 119
ć
Reserved
Tab. A/15:
Overview of fault numbers
A detailed description of the warnings and faults can be
found in section A.3.
