Hp sum user interface, Deployment scenarios, Graphical deployment on a local host – HP ProLiant Support Pack User Manual
Page 23: Scripted deployment on a local host
HP SUM User Interface 23
HP SUM User Interface
Deployment scenarios
HP SUM deploys firmware and software on a local host or one or more remote hosts. The remote hosts
must be online and running the same operating system as the system running HP SUM. For example,
when the remote hosts are running Linux, HP SUM must also be running on a Linux operating system.
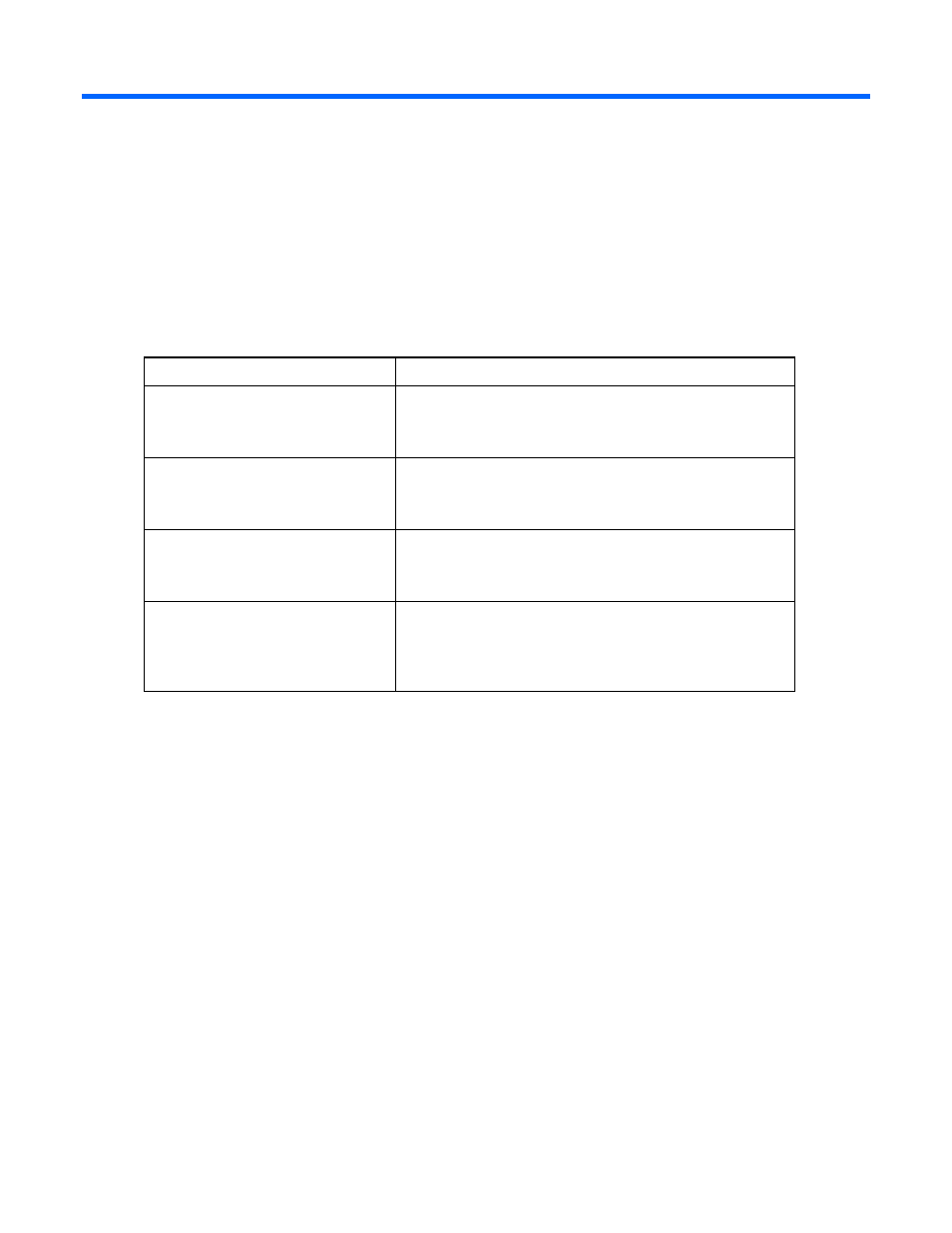
The following table describes when typical HP SUM deployment scenarios are used.
Scenario
Used when
Graphical deployment on a local host
•
Are not familiar with command line tools.
•
Are deploying components on a local, single host.
•
Do not require scripting.
Scripted deployment on a local host
•
Are familiar with command line tools.
•
Are deploying components on a local, single host.
•
Must perform a customized, scripted deployment.
Graphical deployment to a remote
host
•
Are not familiar with command line tools.
•
Are deploying components on one or more remote hosts.
•
Do not require scripting.
Scripted deployment to a remote host
•
Are familiar with command line tools.
•
Are deploying components on one or more hosts.
•
Must perform a customized, scripted deployment to one or
more host systems.
Graphical deployment on a local host
To deploy components to a single local host, use the HP SUM GUI.
1.
Ensure all minimum requirements are met as described in "Minimum requirements (on page
)."
2.
Ensure that the components to be deployed are accessible to the local host.
For information about performing the deployment using the GUI, see "Local host installations (on page
)."
Scripted deployment on a local host
To deploy components to a local host using the command line interface:
1.
Ensure all minimum requirements are fulfilled as described in "Minimum requirements (on page
)."
2.
Ensure that the components to be deployed are accessible to the local host.
3.
Create a script to customize the deployment. See "Scripted deployment (on page
)" for more
information.
4.
Execute the script.
