Virtual array – HP Surestore NAS User Manual
Page 75
75
Virtual Array
Virtual Array
Your HP Virtual Array is preconfigured for you at installation by the HP Customer Engineer.
Administrators with a strong working knowledge in HP -UX administration and the Logical Volume
Manager can make changes through the Command View SDM. The term “Virtual Array” refers
to the way the disks within the array are treated as a pool of data storage blocks instead of real
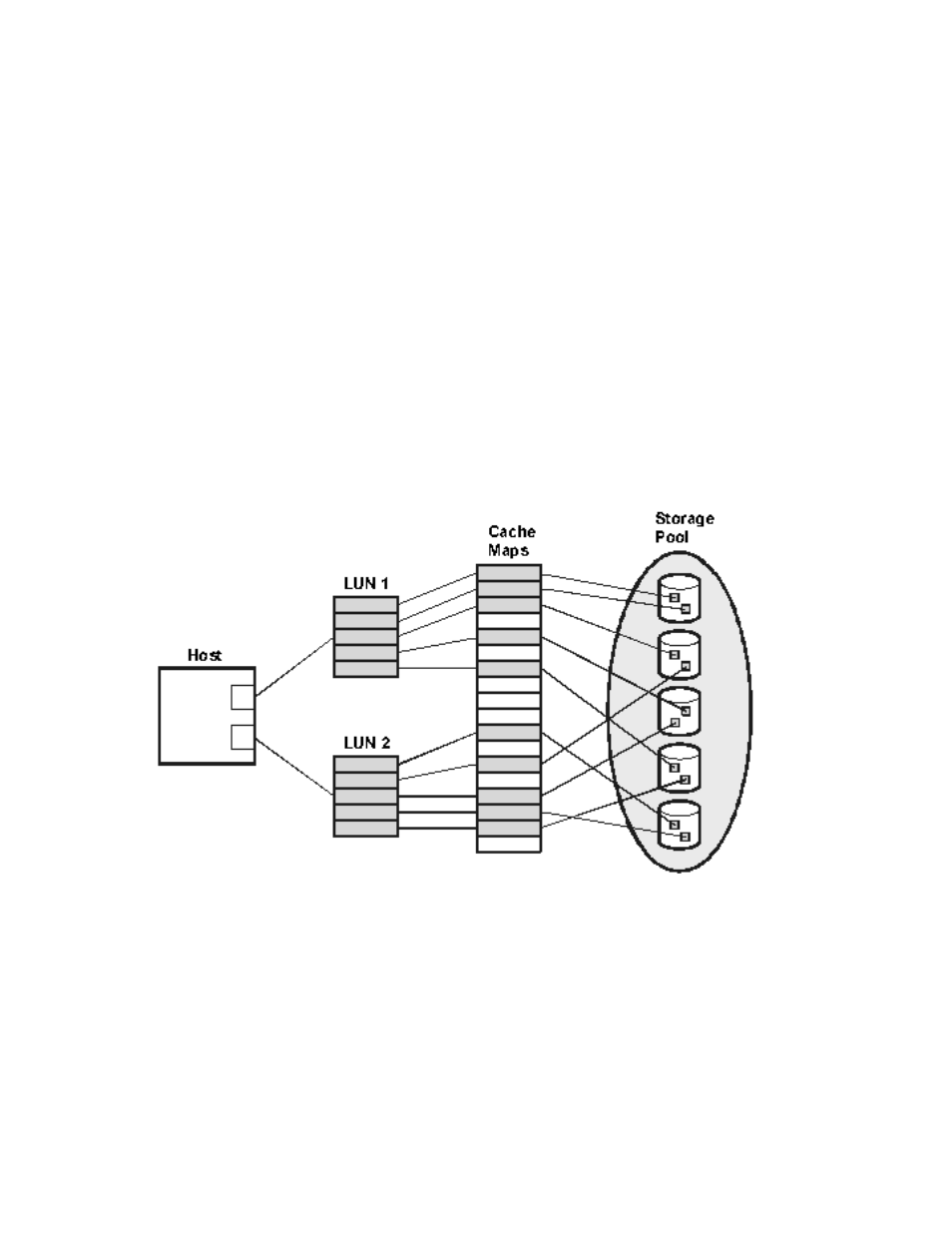
physical disks. HP AutoRAID technology uses powerful mapping techniques to present the host
with a logical view of the available storage in the array (see the figure below).
HP AutoRAID uses a combination of RAID 1+0 and RAID 5DP to manage data storage for you
while optimizing your data access time. This is explained further, below.
Because data is spread across all of the disks in the array, logical-to-physical data maps, stored
in array controller cache memory, keep track of where the data is physically located on the disks
in the array. The host has no visibility of the cache data maps; it is simply presented with logical
units (LUNs) for data storage operations.
Figure 1: Host visibility of storage pool
RAID Levels
Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks (RAID) technology uses different industry-standard
techniques for storing data and maintaining data redundancy. These techniques, called “RAID
levels”, define the method used for distributing data on the disks in a logical unit (LUN). LUNs that
use different RAID levels can be created in the same array. The array covered in this guide
supports the following RAID levels: RAID 1+0 and RAID 5 Double Parity (RAID 5DP).
RAID 1+0
