User's guide d-12 code sets – AMT Datasouth AMTACCEL-5350 User Manual
Page 190
User's Guide
D-12 Code Sets
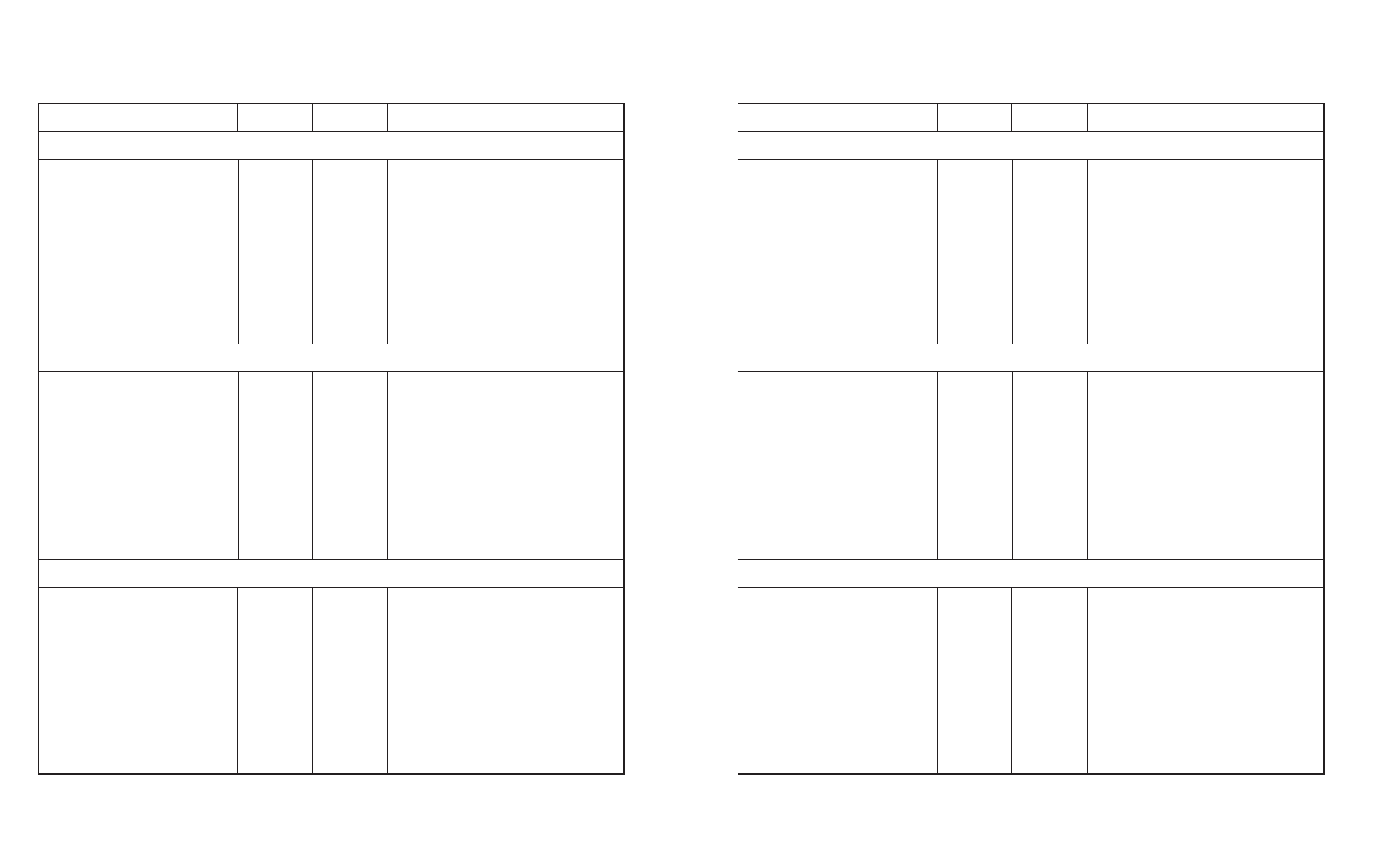
Table D-3. AMT and Diablo 630 Escape Sequences––continued
Function
ASCII
Hexadecimal
Decimal
Description
Margins, Tabs and Page Formatting––continued
Set vertical tab stop ...........
ESC -
1B 2D
27 45
This sequence sets a vertical tab stop at the current line
position. Vertical tab stops are a function of the current
line spacing. Therefore, when line spacing changes, ver-
tical tabs remain at the same line positions, but not at the
same places on the page.
Set lines per page ...............
ESC FF n
1B 0C n
27 12 n
This sequence sets the number of lines per page and sets
the top-of-form at the current print position. The value of
variable n (0 to 182) determines the number of lines per
page. Variable n should equal the actual form length in
inches divided by the current line spacing. For example, if
the form length is 11 inches and the line spacing is 1/6
inch, 11 divided by 1/6 is 66––so n should equal 66
decimal (ASCII B, 42 hex). The number of lines per page
is unaffected by subsequent changes to line spacing.
Absolute Moving
Absolute move to ...............
ESC HT n
1B 09 n
27 9 n
This sequence moves the current print position left or right
print position
to a specific print position (0 to 255) on the current line.
The value of variable n minus one defines the print
position to move to. For example, to move to print
position 5, the sequence is ESC HT ACK. Print position
0 is the far left print column. If the sequence defines a
print position beyond the rightmost print position, the
printer ignores this sequence.
Absolute move to ...............
ESC VT n
1B 0B n
27 11 n
This sequence moves paper up or down to a specific print
print line
line (0 to 182) on the page. The value of variable n minus
one defines the line to move to. For example, to move to
line 5, the sequence is ESC VT ACK. Print line 0 is the
top-of-form. If the sequence specifies a line below the
last line of the page, the printer ignores this sequence.
Text Functions
Set print quality (speed)
ESC @ P n
1B 40 50 n
27 64 80 n
This sequence selects the text quality. Letter-quality
Letter ............................
ESC @ P L
1B 40 50 4C
27 64 80 76
characters are formed from a 32-dot-high by 36-dot-wide
matrix. Memo-quality characters are formed from a
Memo .............................
ESC @ P M
1B 40 50 4D
27 64 80 77
16-dot-high by 36-dot-wide matrix. Draft-quality
characters are formed from an 8-dot-high by 15-dot-wide
matrix.
Draft ...............................
ESC @ P D
1B 40 50 44
27 64 80 68
Some fonts do not contain character sets for all print
qualities. If letter-quality is selected, but the font does
not contain this character set, memo-quality is selected;
and vice-versa. If the font contains neither a letter- or
memo-quality character set, the letter- or memo-quality
Courier character set is selected, If draft-quality is
selected, but the font does not contain this character set,
the draft-quality Courier character set is selected.
User's Guide
D-12 Code Sets
Table D-3. AMT and Diablo 630 Escape Sequences––continued
Function
ASCII
Hexadecimal
Decimal
Description
Margins, Tabs and Page Formatting––continued
Set vertical tab stop ...........
ESC -
1B 2D
27 45
This sequence sets a vertical tab stop at the current line
position. Vertical tab stops are a function of the current
line spacing. Therefore, when line spacing changes, ver-
tical tabs remain at the same line positions, but not at the
same places on the page.
Set lines per page ...............
ESC FF n
1B 0C n
27 12 n
This sequence sets the number of lines per page and sets
the top-of-form at the current print position. The value of
variable n (0 to 182) determines the number of lines per
page. Variable n should equal the actual form length in
inches divided by the current line spacing. For example, if
the form length is 11 inches and the line spacing is 1/6
inch, 11 divided by 1/6 is 66––so n should equal 66
decimal (ASCII B, 42 hex). The number of lines per page
is unaffected by subsequent changes to line spacing.
Absolute Moving
Absolute move to ...............
ESC HT n
1B 09 n
27 9 n
This sequence moves the current print position left or right
print position
to a specific print position (0 to 255) on the current line.
The value of variable n minus one defines the print
position to move to. For example, to move to print
position 5, the sequence is ESC HT ACK. Print position
0 is the far left print column. If the sequence defines a
print position beyond the rightmost print position, the
printer ignores this sequence.
Absolute move to ...............
ESC VT n
1B 0B n
27 11 n
This sequence moves paper up or down to a specific print
print line
line (0 to 182) on the page. The value of variable n minus
one defines the line to move to. For example, to move to
line 5, the sequence is ESC VT ACK. Print line 0 is the
top-of-form. If the sequence specifies a line below the
last line of the page, the printer ignores this sequence.
Text Functions
Set print quality (speed)
ESC @ P n
1B 40 50 n
27 64 80 n
This sequence selects the text quality. Letter-quality
Letter ............................
ESC @ P L
1B 40 50 4C
27 64 80 76
characters are formed from a 32-dot-high by 36-dot-wide
matrix. Memo-quality characters are formed from a
Memo .............................
ESC @ P M
1B 40 50 4D
27 64 80 77
16-dot-high by 36-dot-wide matrix. Draft-quality
characters are formed from an 8-dot-high by 15-dot-wide
matrix.
Draft ...............................
ESC @ P D
1B 40 50 44
27 64 80 68
Some fonts do not contain character sets for all print
qualities. If letter-quality is selected, but the font does
not contain this character set, memo-quality is selected;
and vice-versa. If the font contains neither a letter- or
memo-quality character set, the letter- or memo-quality
Courier character set is selected, If draft-quality is
selected, but the font does not contain this character set,
the draft-quality Courier character set is selected.
