6 factory calibration procedure – Teledyne 9110AH - Nitrogen oxides analyzer User Manual
Page 136
TELEDYNE Model 9110AH NO
X
Analyzer Operator Manual, 01620, Rev. F
9-20
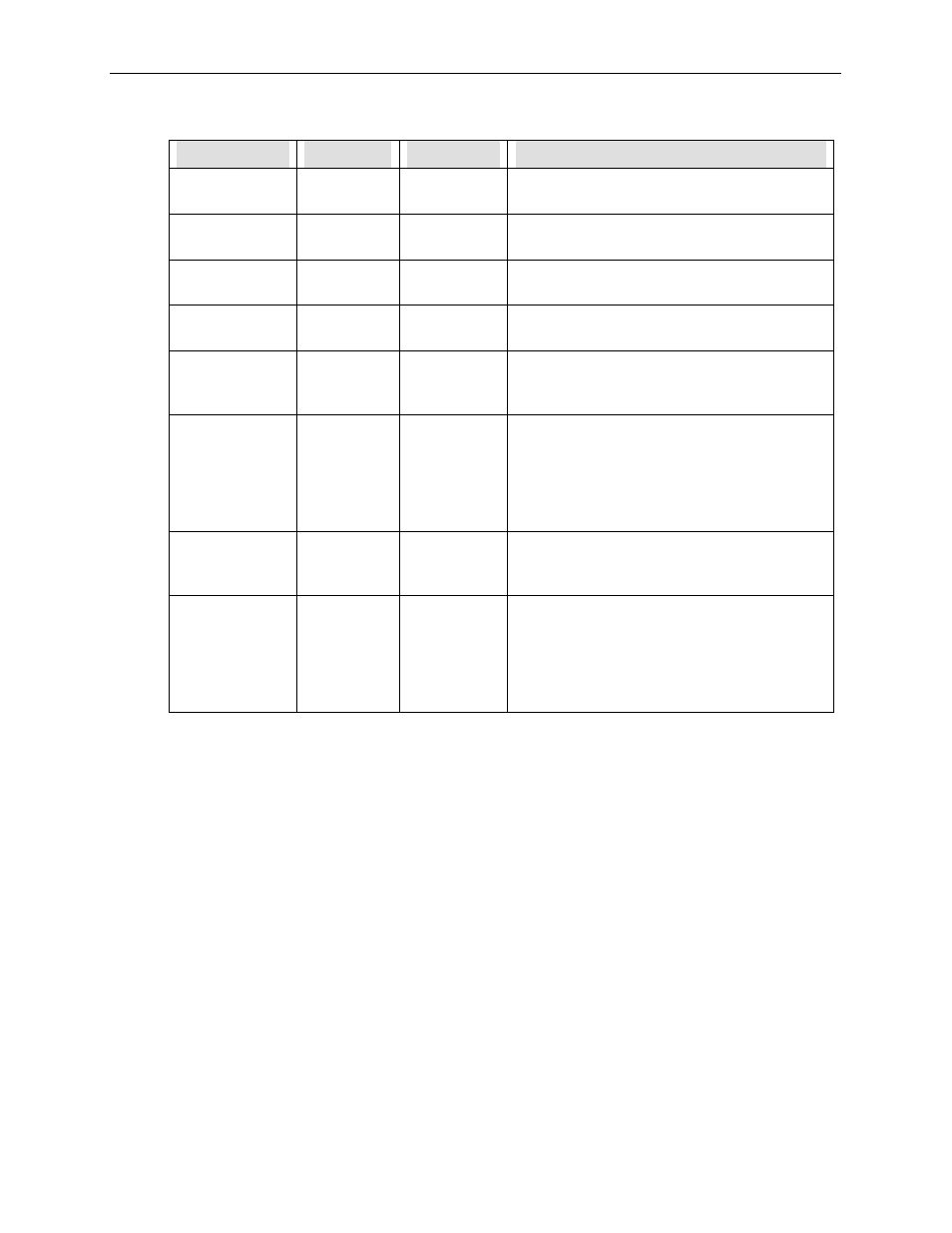
Table 9-6: Test Channel Readings (Continued)
TEST Channel
Minimum*
Maximum*
Description
RCELL TEMP
0
o
C
70
o
C
Reaction Cell temperature is set to 50
o
C. At the
setpoint, a typical reading is 3600 mV.
BLOCK TEMP
0
o
C
70
o
C
The Block temperature is set to 50
o
C. At the
setpoint, a typical reading is 3600 mV.
IZS TEMP
0
o
C
70
o
C
The IZS temperature is set to 50
o
C. At the
setpoint, a typical reading is 3600 mV.
CONV TEMP
0
o
C
1000
o
C
The Converter temperature is 315
o
C. At the
setpoint, a typical voltage is 3150 mV.
PMT TEMP
0
o
C
70
o
C
The PMT temperature is unique in that the
voltage is inverse to the temperature. A typical
reading for 8
o
C would be 4200 mV.
CHASSIS
TEMP
0
o
C
70
o
C
The Chassis (Box) temperature is variable due
to variable ambient air temperature. The Box
temp generally runs about 5
o
C above the
surrounding air temp. Thus in a 25
o
C room, the
Box temp would be about 30
o
C and have a
TEST channel voltage of about 2000 mV.
DCPS
VOLTAGE
0 mV
5000 mV
The DCPS is a composite of several DC power
supply voltages in the instrument. It has been
arbitrarily set at 2500 mV, which is typical.
HVPS
VOLTAGE
0 V
5000 V
The HVPS voltage is a scaled up reading of the
programming voltage going to the HVPS. Zero
to 1000 mV corresponds 0-1000 VDC for the
HVPS, which is the maximum voltage possible.
A typical reading would be 700 mV
corresponding to 700 VDC for the HVPS.
*Minimum and Maximum readings depend on the DAC 3 switch settings of the V/F board. For
the standard 5 VDC range, minimum corresponds to 0 VDC and maximum corresponds to
5 VDC.
9.1.6 Factory Calibration Procedure
The Factory Cal procedure balances the PMT, preamp, and software gain factors so the
instrument has optimum noise, linearity, and dynamic range. It should be used in the cases
where you were unable to zero or span the instrument or slope and offset values were outside
of the acceptable range and other more obvious reasons for problems have been eliminated.
