I5216 series, Preliminary, C protocol – Rainbow Electronics ISD5216 User Manual
Page 71: Master transmits to slave receiver (write) mode
I5216 SERIES
Advanced Information
PRELIMINARY
Publication Release Date: November 30, 2001
- 71
Revision A1
I
2
C PROTOCOL
Since the I
2
C protocol allows multiple devices on the bus, each device must have an address. This
address is known as a “Slave Address”. A Slave Address consists of 7 bits, followed by a single bit that
indicates the direction of data flow. This single bit is 1 for a Write cycle, which indicates the data is
being sent from the current bus master to the device being addressed. This single bit is a 0 for a Read
cycle, which indicates that the data is being sent from the device being addressed to the current bus
master.
Before any data is transmitted on the I
2
C interface, the current bus master must address the slave it
wishes to transfer data to or from. The Slave Address is always sent out as the 1
st
byte following the
Start Condition sequence. An example of a Master transmitting an address to a ISD5216 slave is
shown below. In this case, the Master is writing data to the slave and the R/W bit is “0”, i.e. a Write
cycle. All the bits transferred are from the Master to the Slave, except for the indicated Acknowledge
bits.
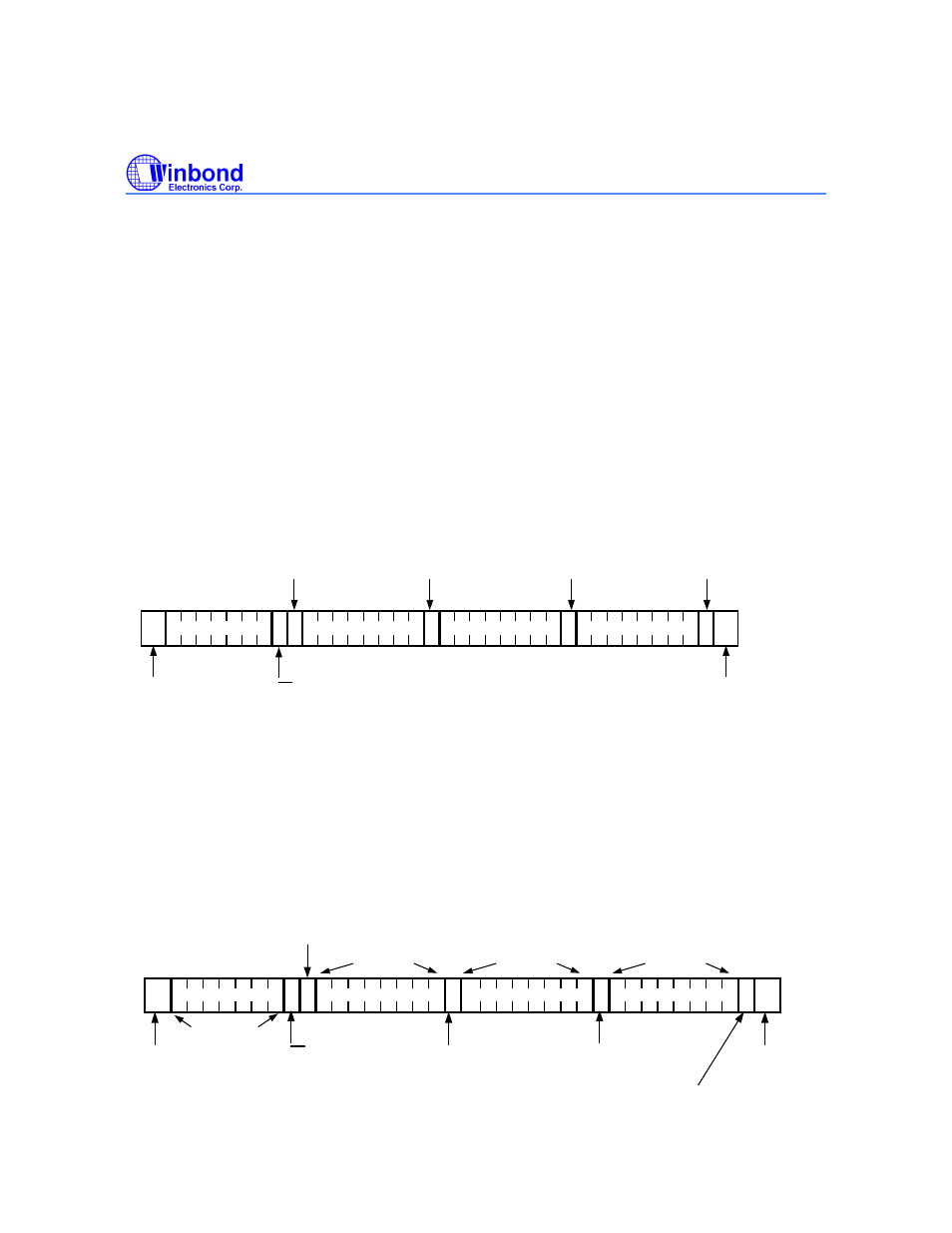
Master Transmits to Slave Receiver (Write) Mode
S
W A
A
A
A
P
SLAVE ADDRESS
COMMAND BYTE
High ADDR. BYTE
Low ADDR. BYTE
acknowledgement
from slave
acknowledgement
from slave
acknowledgement
from slave
acknowledgement
from slave
R/W
Start Bit
Stop Bit
A common procedure in the ISD5116 is the reading of the Status Bytes. The Read Status condition in
the ISD5216 is triggered when the Master addresses the chip with its proper Slave Address,
immediately followed by the R/W bit set to a “0” and without the Command Byte being sent. This is an
example of the Master sending to the Slave, immediately followed by the Slave sending data back to
the Master. The “N” not-acknowledge cycle from the Master ends the transfer of data from the Slave.
Master Reads from Slave immediately after first byte (Read Mode)
R/W
From
Master
Start Bit
From
Master
Stop Bit
From
Master
acknowledgement
from slave
acknowledgement
from Master
not-acknowledged
from Master
acknowledgement
from Master
From Master
From Slave
From Slave
From Slave
S
R
A
A
A
N
P
Low ADDR BYTE
SL AVE ADDRESS
STATUS W O RD
High ADDR. BYTE
