I5216 series, Preliminary – Rainbow Electronics ISD5216 User Manual
Page 19
I5216 SERIES
Advanced Information
PRELIMINARY
Publication Release Date: November 30, 2001
-19
Revision A1
I
2
C OPERATION DEFINTIONS
There are many control functions used to operate the I5216. Among them are the following.
READ STATUS COMMAND
: The read status command is a read
request from the Host processor to the I5216 without delivering a
Command Byte. The Host supplies all of the clocks (SCL). In each
case, the entity sending the data drives the data line (SDA). The Read
Status Command is executed by the following I
2
C sequence.
1. Host executes I
2
C START
2. Send Slave Address with R/W bit = “1” (Read) 81h.
3. Slave responds back to Host an Acknowledge (ACK), followed
by 8 bit Status word.
4. Host sends an Acknowledge (ACK) to Slave.
5. Wait for SCL to go HIGH.
6. Slave responds with Upper Address byte of internal address
register.
7. Host sends an ACK to Slave.
8.
Wait for SCL to go high.
9.
Slave responds with Lower Address byte of internal address
register.
10.
Host sends a NO ACK to Slave, then executes I
2
C STOP
Note: The processor could have sent an I
2
C STOP after the Status
Word data transfer, and thus aborted the transfer of the Address bytes
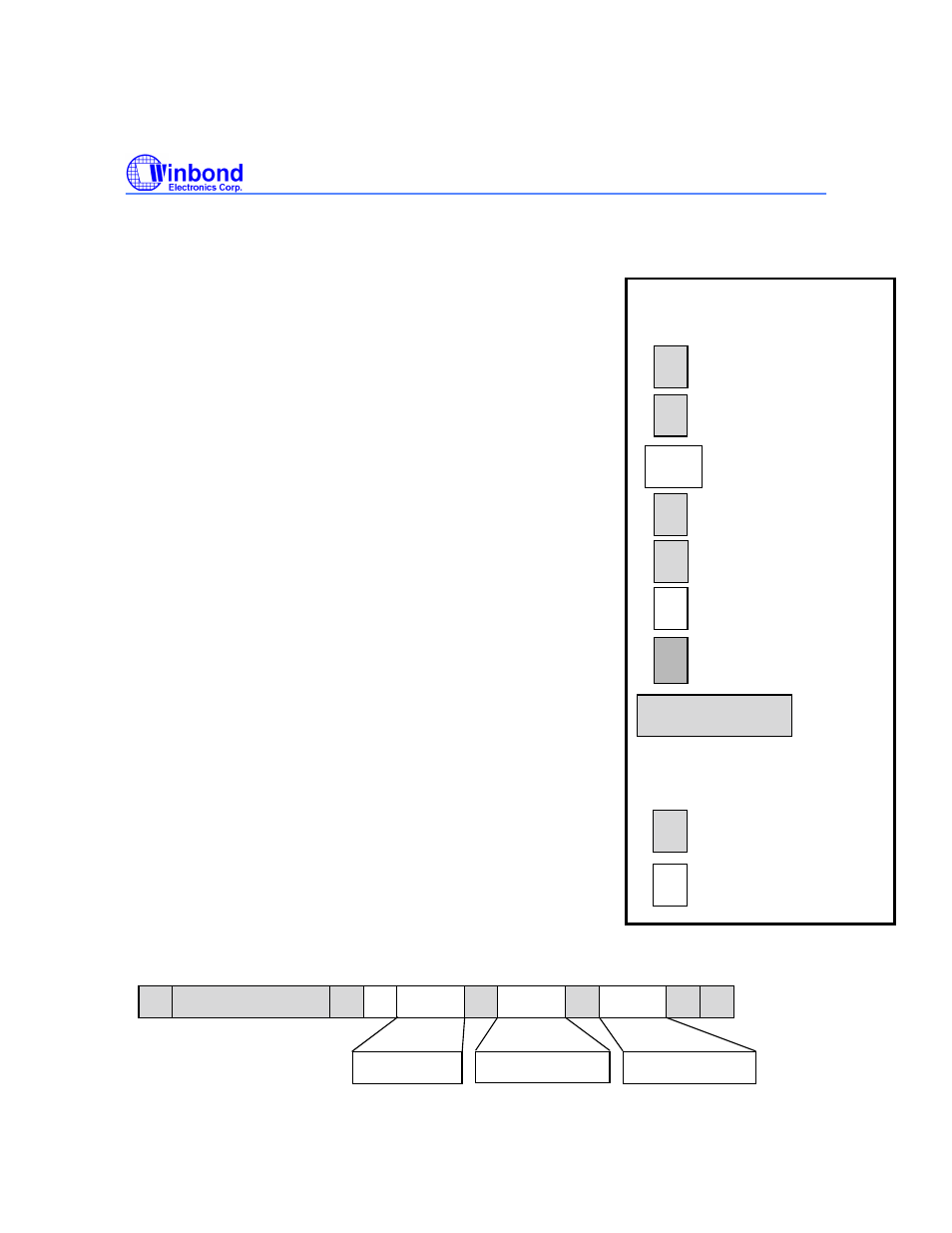
A graphical representation of this operation is found below. See the caption box above for more
explanation.
Conventions used in I
2
C Data
Transfer Diagrams
= START Condition
= STOP Condition
= 8 bit data transfer
= “1” in the R/W bit
= “0” in the R/W bit
= ACK (Acknowledge)
= No ACK
W
S
SLAVE ADDRESS
R
A
DATA
P
= Host to Slave (Gray)
= Slave to Host (White)
The Box color indicates the
direction of data flow
= 7 bit Slave
Address
N
S
SLAVE ADDRESS
A
A
DATA
P
R
DATA
DATA
A
N
Status
High Addr. Low Addr.
